Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding USGS Topographic Map Legends
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding USGS Topographic Map Legends
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding USGS Topographic Map Legends. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding USGS Topographic Map Legends

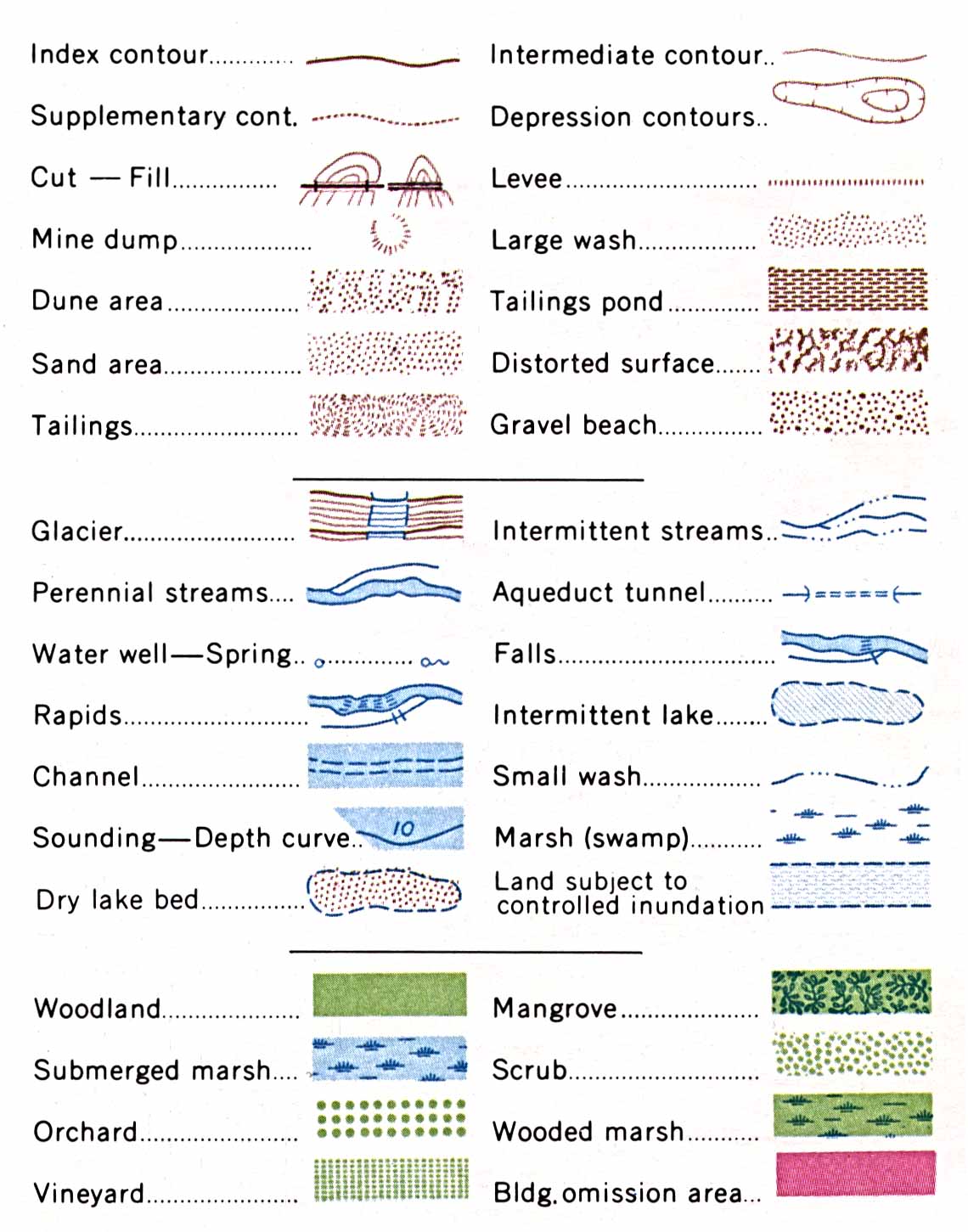
Topographic maps, created by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), are essential tools for navigating, understanding, and analyzing the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of the landscape, incorporating elevation, natural features, and human-made structures. A crucial element of these maps is the legend, a key to unlocking the information encoded within the map’s symbols and colors. This article delves into the intricacies of the USGS topographic map legend, explaining its components and highlighting its vital role in map interpretation.
Understanding the Language of the Landscape
The USGS topographic map legend acts as a visual dictionary, translating the map’s symbols and colors into their real-world counterparts. It is a structured guide, typically located at the bottom or margin of the map, containing several distinct sections.
1. Symbol Legend:
This section is the heart of the legend, displaying a wide range of symbols representing various features found on the map. Each symbol is accompanied by a brief description, clarifying its meaning. These symbols can represent:
- Natural Features: Rivers, lakes, streams, forests, wetlands, mountains, valleys, and rock formations are depicted using specific symbols. For example, a blue line with a series of small blue triangles indicates a river, while a green pattern denotes a forest area.
- Cultural Features: Roads, bridges, buildings, railroads, power lines, and other human-made structures are represented by unique symbols. A thick black line with a dashed pattern signifies a major road, while a small square with a cross represents a church.
- Elevation: The topography of the land is represented using contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. Contour lines, typically brown, are spaced at regular intervals, with closer spacing indicating steeper slopes.
- Other Features: The symbol legend may also include symbols for specific features like airports, cemeteries, and even historical landmarks.
2. Color Legend:
The color legend provides a comprehensive guide to the color scheme used on the map. Different colors are used to differentiate various features, enhancing the map’s clarity and readability. Common color conventions include:
- Blue: Water bodies like rivers, lakes, and oceans are typically depicted in shades of blue, with darker shades indicating deeper water.
- Green: Vegetation, including forests, grasslands, and cultivated fields, is often represented in shades of green.
- Brown: Contour lines, representing elevation changes, are usually drawn in brown, with darker shades indicating higher elevations.
- Black: Roads, railroads, and other human-made structures are typically shown in black, with thicker lines representing major roads or railroads.
3. Scale Bar:
The scale bar provides a visual representation of the map’s scale, indicating the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the ground. This allows users to accurately measure distances and determine the size of features depicted on the map.
4. Datum and Projection:
The legend often includes information about the map’s datum and projection, which define the reference system used for creating the map. The datum is a reference point used to locate features on the Earth’s surface, while the projection transforms the spherical Earth onto a flat map.
Benefits of Understanding the Legend
The USGS topographic map legend serves as a vital tool for map users, offering numerous benefits:
- Accurate Interpretation: By understanding the legend, users can accurately interpret the symbols and colors on the map, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Effective Navigation: The legend provides the necessary information for navigating the terrain, identifying landmarks, and planning routes.
- Detailed Analysis: The legend allows for detailed analysis of the landscape, enabling users to identify patterns, understand land use, and assess environmental conditions.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: A thorough understanding of the legend empowers users to make informed decisions related to land management, resource extraction, and infrastructure development.
FAQs about USGS Topographic Map Legends
Q: Where can I find USGS topographic map legends?
A: USGS topographic map legends are typically located at the bottom or margin of the map. They can also be accessed online through the USGS website or various mapping applications.
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a road map?
A: Topographic maps focus on representing the terrain and elevation, while road maps prioritize depicting roads, highways, and other transportation routes.
Q: Are all USGS topographic map legends the same?
A: While the basic structure of the legend remains consistent, the specific symbols and colors used can vary depending on the map’s scale, purpose, and geographic region.
Q: How can I learn more about USGS topographic map legends?
A: The USGS website provides comprehensive resources, including tutorials, guides, and online tools, to help users understand and utilize topographic maps.
Tips for Effective Legend Usage
- Start with the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the common symbols and colors used on USGS topographic maps.
- Pay Attention to the Scale: Understand the relationship between the map scale and the size of features depicted.
- Use Online Resources: Utilize the USGS website and mapping applications to access additional information and legend explanations.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Regularly use topographic maps and legends to enhance your understanding and interpretation skills.
Conclusion
The USGS topographic map legend is an indispensable tool for unlocking the wealth of information contained within these maps. By understanding the language of the legend, users can accurately interpret the landscape, navigate effectively, and make informed decisions based on the data presented. Whether for recreational activities, professional work, or simply understanding the world around us, mastering the USGS topographic map legend opens doors to a deeper appreciation of the Earth’s surface and its intricate features.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding USGS Topographic Map Legends. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!