Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends and Keys
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends and Keys
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends and Keys. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends and Keys
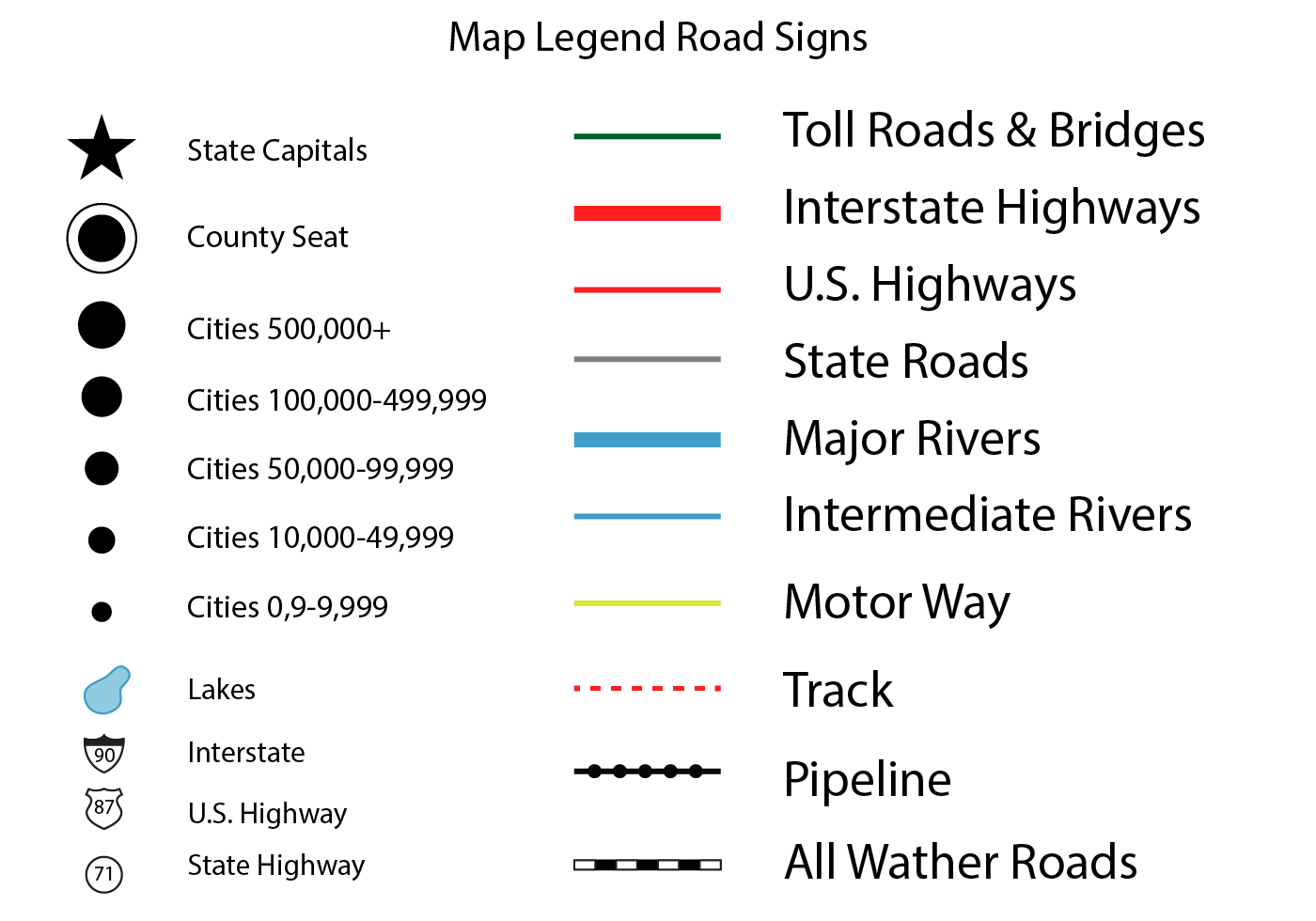
Maps, as visual representations of geographic information, are powerful tools for understanding the world around us. However, their effectiveness hinges on our ability to interpret the symbols and markings they employ. This is where the map legend, often referred to as a map key, plays a crucial role.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Map Legend vs. Key
The terms "map legend" and "map key" are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference in their connotations. While both refer to the explanatory section of a map that defines symbols and their corresponding meanings, a map legend typically encompasses a broader range of information. It may include:
- Symbols: Geometric shapes, colors, or icons representing specific features like cities, roads, rivers, or landforms.
- Scale: The ratio between the map’s distance and the actual distance on the ground, indicating how much the map has been shrunk.
- North Arrow: An arrow pointing towards true north, providing orientation for the map.
- Date of Creation: Indicating the map’s relevance and potential for updates.
- Source Information: Acknowledging the data sources used to create the map.
In contrast, a map key focuses primarily on the symbols and their meanings, serving as a direct translation guide for interpreting the map’s visual language. It may not necessarily include elements like scale, north arrow, or date information.
The Importance of Map Legends and Keys
The significance of map legends and keys cannot be overstated. They act as the bridge between the abstract symbols on the map and the real-world features they represent. Without them, maps would be little more than confusing collections of lines and colors, rendering them useless for navigation, analysis, or communication.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Map Legend:
- Clarity and Accessibility: A clear and concise map legend ensures that users can easily understand the map’s content, regardless of their prior knowledge or experience.
- Accuracy and Consistency: The legend ensures that symbols are used consistently throughout the map, preventing misinterpretations and facilitating accurate spatial analysis.
- Efficient Communication: By providing a quick reference guide, the legend allows for efficient communication of complex geographic information, saving time and effort.
- Enhanced Comprehension: A well-organized legend helps users understand the relationships between different features on the map, fostering a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships.
- Accessibility for Diverse Audiences: A thoughtfully designed legend can be adapted to accommodate users with different learning styles and disabilities, promoting inclusivity in map interpretation.
Types of Map Legends
Map legends can be categorized based on their presentation and the type of information they convey:
- Textual Legend: This type uses text to describe each symbol and its corresponding meaning, often employing a simple table format.
- Graphic Legend: This legend relies on visual representations, using the same symbols as the map itself alongside their corresponding labels.
- Combined Legend: This type combines textual and graphic elements, providing a more comprehensive explanation of the map’s symbols.
- Interactive Legend: These legends are often found in digital maps and allow users to interact with the symbols, revealing additional information or filtering specific features.
Examples of Map Legends in Action:
- Topographic Maps: Legends on topographic maps typically include symbols for elevation contours, water bodies, roads, and other features, along with a scale and north arrow.
- Road Maps: Road map legends often feature different colored lines representing different types of roads (e.g., highways, interstates, local roads), alongside symbols for points of interest like gas stations, restaurants, and hotels.
- Weather Maps: Weather maps utilize symbols to represent different weather conditions like temperature, precipitation, wind direction, and pressure systems.
- Historical Maps: Legends on historical maps may include symbols representing historical events, battles, or settlements, providing a visual narrative of the past.
FAQs: Map Legends and Keys
Q: What is the difference between a map legend and a map key?
A: While both terms are often used interchangeably, a map legend typically encompasses a broader range of information, including scale, north arrow, and date of creation, while a map key focuses primarily on the symbols and their meanings.
Q: Is it necessary to have a legend for every map?
A: Yes, it is generally considered essential for any map to have a legend, especially if it uses symbols to represent features. A legend ensures clarity, accuracy, and accessibility for the map’s users.
Q: How can I create a clear and effective map legend?
A: A clear and effective map legend should be:
- Concise: Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex explanations.
- Organized: Group symbols logically by category or type.
- Visually Appealing: Use contrasting colors and sizes to ensure readability.
- Accessible: Consider users with different learning styles and disabilities.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a map legend?
A: Avoid:
- Overcrowding: Ensure ample space between symbols and text.
- Using too many symbols: Limit the number of symbols to prevent confusion.
- Using unclear or ambiguous symbols: Choose symbols that are easily recognizable and interpreted.
- Ignoring accessibility: Ensure the legend is accessible to all users.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- Start with the Legend: Always begin by carefully reviewing the map legend before attempting to interpret the map’s content.
- Look for Key Elements: Pay attention to the scale, north arrow, and date of creation, as they provide context for the map’s information.
- Identify the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map and their corresponding meanings.
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: Understanding the map’s intended use can help you interpret its information more effectively.
- Practice and Experiment: The more you interact with maps and legends, the more proficient you will become at interpreting their information.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Communication
Map legends and keys are essential components of effective cartography, bridging the gap between abstract symbols and the real-world features they represent. By providing a clear and concise explanation of the map’s visual language, they enable users to navigate, analyze, and understand geographic information with greater accuracy and efficiency. As we continue to rely on maps to navigate our world, understanding the importance and function of map legends and keys remains crucial for unlocking the full potential of these powerful tools of visual communication.


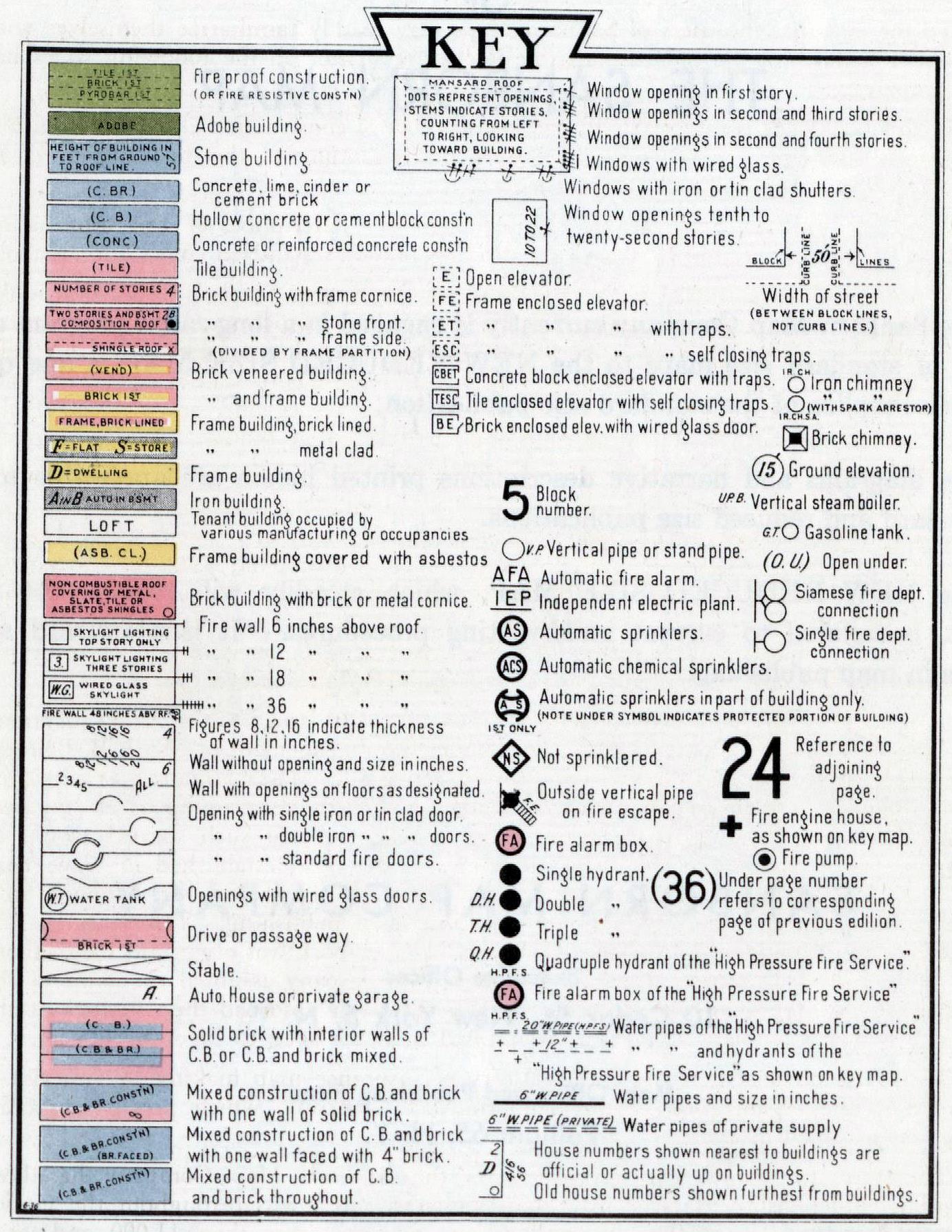




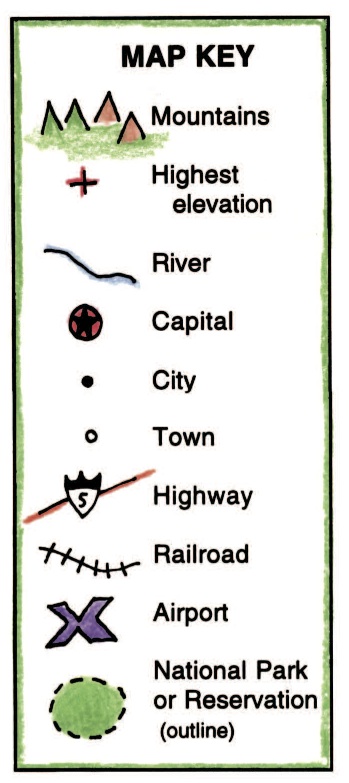
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Legends and Keys. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!