Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Legends and Symbols
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Legends and Symbols
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Legends and Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Legends and Symbols
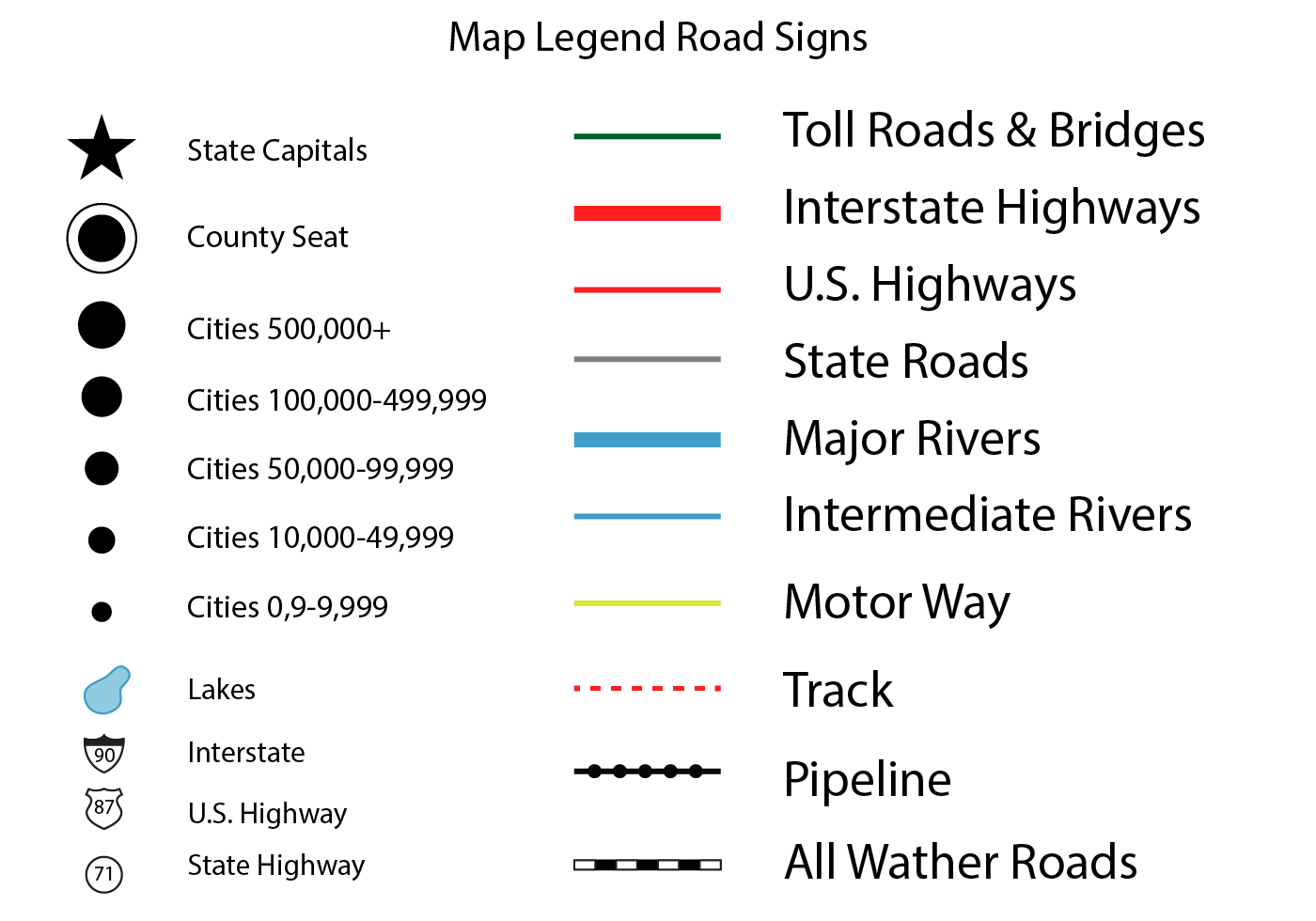
Maps are visual representations of the world, but they are not simply pictures. They are complex systems of information, using symbols and conventions to convey spatial relationships and data. To understand the meaning behind these visual representations, one must first understand the language of maps – the legends and symbols that provide the key to unlocking the map’s message.
The Foundation of Understanding: Map Legends
A map legend, also known as a key or map key, is a crucial component of any map. It serves as a glossary, providing a clear explanation of the symbols used on the map. Without a legend, a map would be a confusing jumble of lines, colors, and shapes, devoid of meaning.
Legends typically contain:
- Visual Representations: The legend displays the symbols used on the map, such as lines, shapes, colors, or icons. Each symbol represents a specific feature or data point.
- Textual Descriptions: Alongside each symbol, the legend provides a clear and concise textual description of what the symbol represents. This could be a physical feature like a river, a road, or a mountain, or it could represent a specific data point like population density, elevation, or rainfall.
- Scale and Units: The legend often includes information about the scale of the map and the units used to measure distances or data.
Types of Map Legends
Legends can be organized in various ways, depending on the complexity of the map and the type of information being conveyed. Common types include:
- Linear Legends: These legends display symbols along a line, often used for features like roads, rivers, or elevation contours.
- Boxed Legends: These legends present symbols in a rectangular or square format, with each symbol and its description placed within a separate box.
- Tabular Legends: These legends organize symbols and descriptions in a table format, particularly useful for displaying multiple categories of data.
- Combined Legends: Some maps use a combination of these formats to effectively present different types of information.
The Language of Maps: Symbols and Their Meaning
Map symbols are the visual language used to represent real-world features and data. Their design is often standardized, ensuring consistency and clarity across different maps. Common types of symbols include:
- Point Symbols: These represent features that can be considered a single point, such as cities, towns, landmarks, or specific locations. They can be simple dots, circles, squares, or more complex icons.
- Line Symbols: These represent features that extend over a distance, such as roads, rivers, boundaries, or power lines. They can be solid lines, dashed lines, dotted lines, or lines with different colors and thicknesses.
- Area Symbols: These represent features that occupy a specific area, such as forests, lakes, countries, or zones. They are often represented by different colors, patterns, or hatchings.
Beyond the Basics: Data Visualization and Symbolism
Map symbols are not limited to simply representing physical features. They can also be used to visualize data, conveying information about population density, rainfall, temperature, or other quantifiable variables.
- Proportional Symbols: These symbols vary in size based on the magnitude of the data they represent. Larger symbols indicate larger values, while smaller symbols represent smaller values.
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use different shades or colors to represent data values across geographical areas. Darker colors typically indicate higher values, while lighter colors represent lower values.
- Isoline Maps: These maps use lines to connect points of equal value, creating contours that represent changes in data across a region. For example, contour lines on a topographic map connect points of equal elevation, illustrating the terrain’s shape.
The Importance of Map Legends and Symbols
Map legends and symbols are essential for several reasons:
- Clarity and Understanding: Legends provide the key to interpreting the map’s message, ensuring that readers can understand the symbols and their meanings.
- Consistency and Standardization: Standardized symbols promote consistency across different maps, making it easier to compare and analyze information from various sources.
- Efficiency and Communication: Symbols convey information efficiently, allowing maps to present complex data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
- Accessibility: Legends and symbols can make maps accessible to a wider audience, including those who may not be familiar with cartographic conventions.
FAQs about Map Legends and Symbols
Q: Why are map legends important?
A: Map legends are crucial for understanding the symbols used on a map, allowing readers to interpret the information accurately. Without a legend, a map would be a meaningless jumble of symbols.
Q: What are some common types of map symbols?
A: Common map symbols include point symbols for locations, line symbols for features with length, and area symbols for features covering a specific area.
Q: How can I learn more about map symbols?
A: Many online resources, textbooks, and cartography courses offer detailed information about map symbols and their meanings.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective map legends?
A: When creating map legends, ensure the symbols are clearly visible, the descriptions are concise and accurate, and the legend is placed in a prominent location on the map.
Tips for Understanding Map Legends and Symbols
- Read the Legend Carefully: Pay close attention to the descriptions provided for each symbol, ensuring you understand the meaning of each visual representation.
- Look for Patterns: Observe how symbols are used on the map, noting any patterns or relationships between different types of symbols.
- Consider the Context: The context of the map, including its purpose and the type of data being represented, can help you understand the symbols and their meanings.
- Use Online Resources: Several online resources, such as Wikipedia and cartography websites, provide detailed information about map symbols and conventions.
Conclusion
Map legends and symbols are the backbone of cartographic communication. They provide the key to unlocking the information contained within maps, making them accessible and understandable to a wide audience. By understanding the language of maps, we can navigate the world around us, analyze spatial data, and gain valuable insights into the complexities of our planet.
![]()


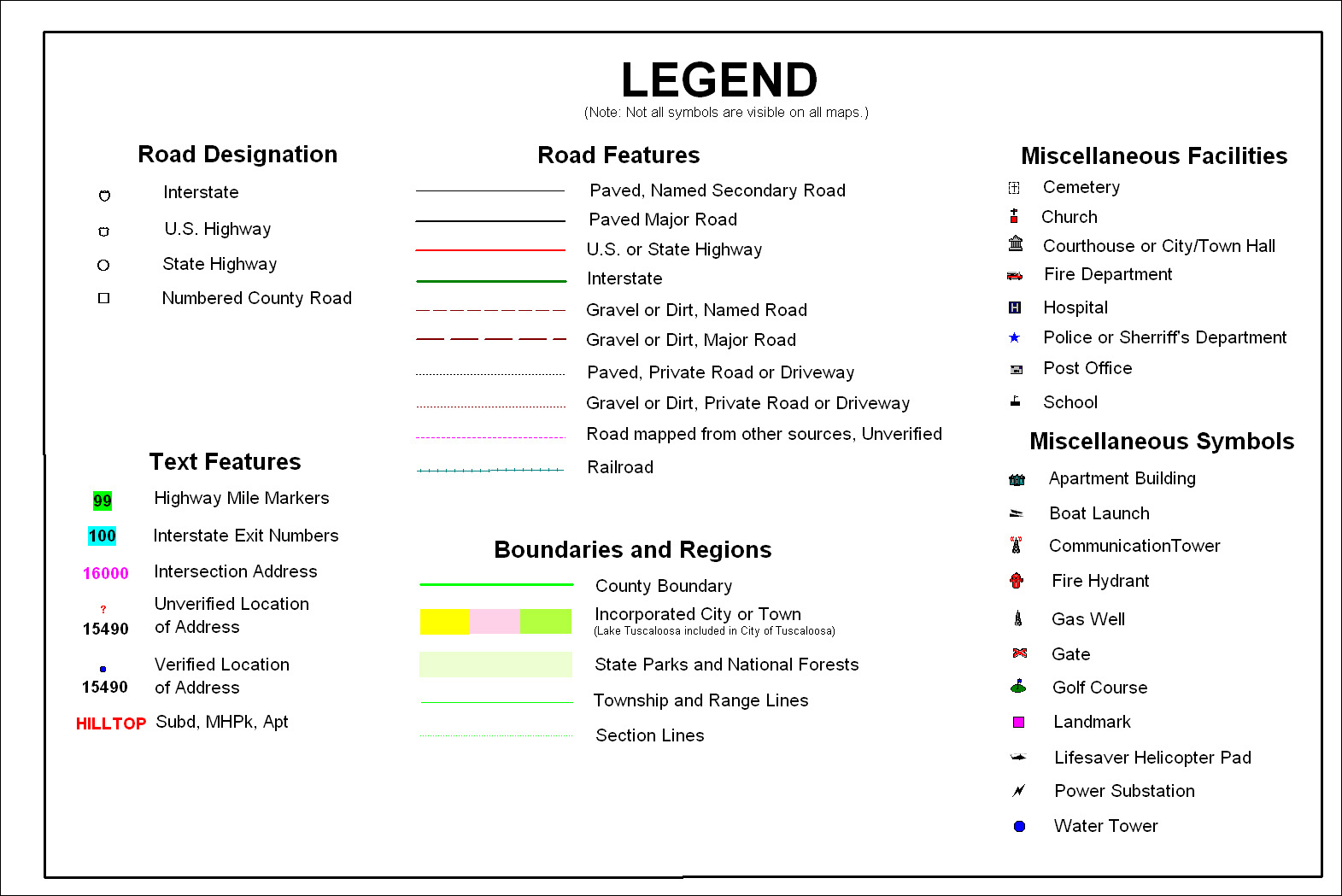

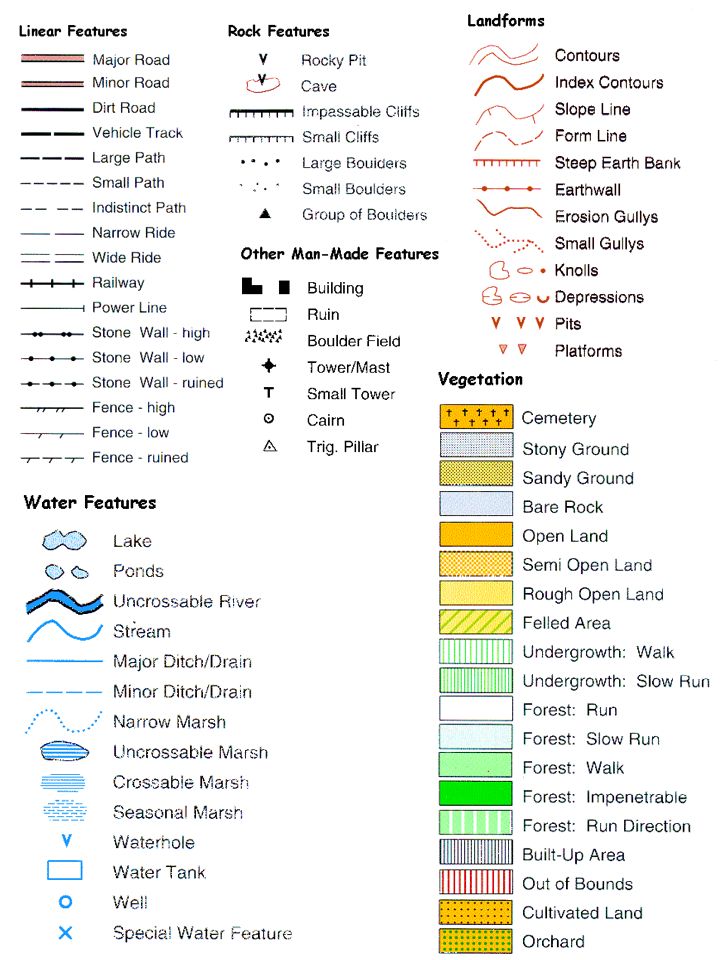


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Legends and Symbols. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!