Demystifying the Map Legend: A Guide to Understanding and Designing Effective Visual Keys
Related Articles: Demystifying the Map Legend: A Guide to Understanding and Designing Effective Visual Keys
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Map Legend: A Guide to Understanding and Designing Effective Visual Keys. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Map Legend: A Guide to Understanding and Designing Effective Visual Keys
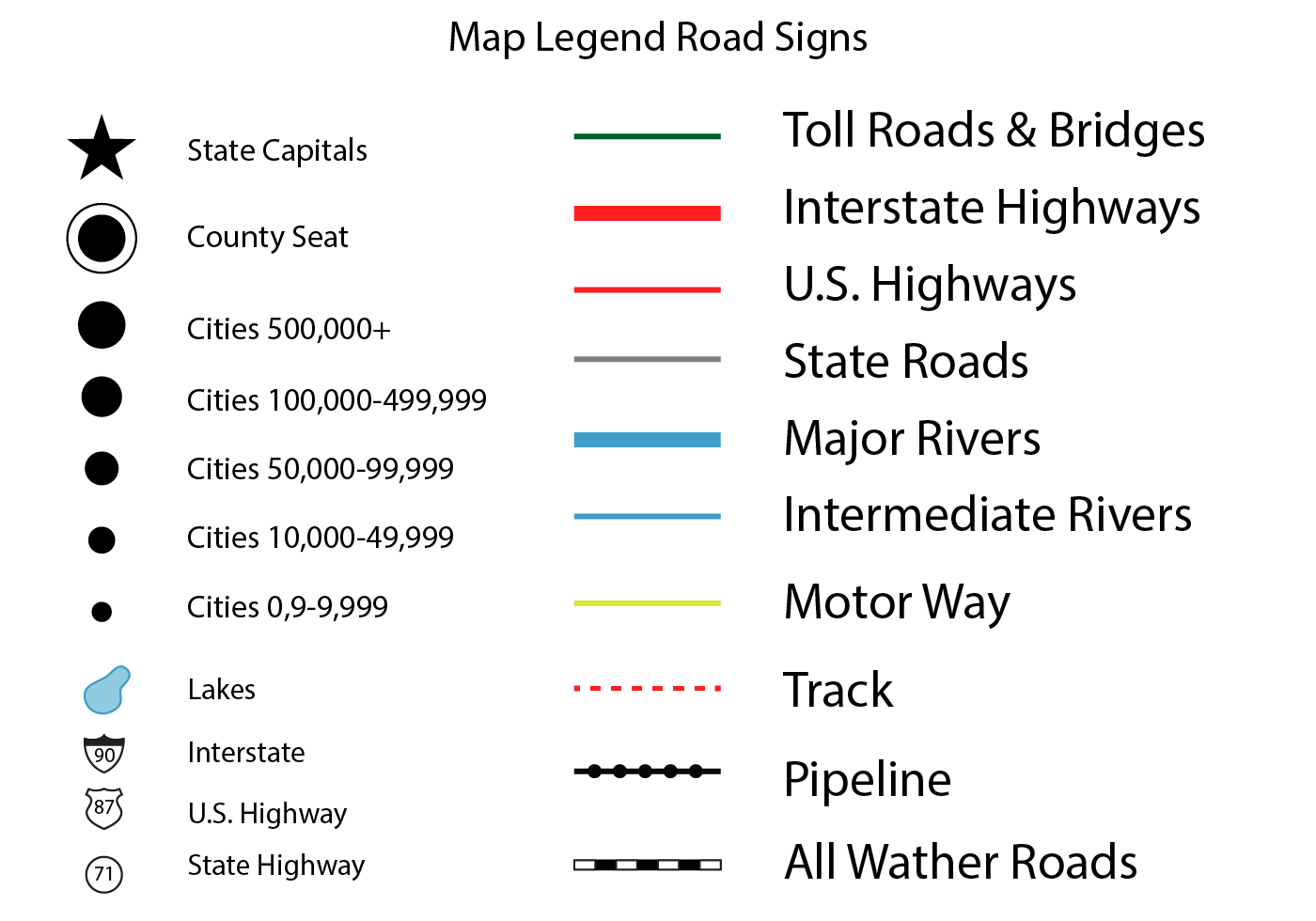
Maps, in their myriad forms, serve as powerful tools for navigating the physical and abstract landscapes we encounter. Whether charting the course across a bustling city, exploring the intricate network of the human body, or visualizing complex data sets, maps rely on a crucial element: the legend. This seemingly simple component, often relegated to a corner or border of the map, plays a pivotal role in ensuring clarity, comprehension, and ultimately, the effectiveness of any map.
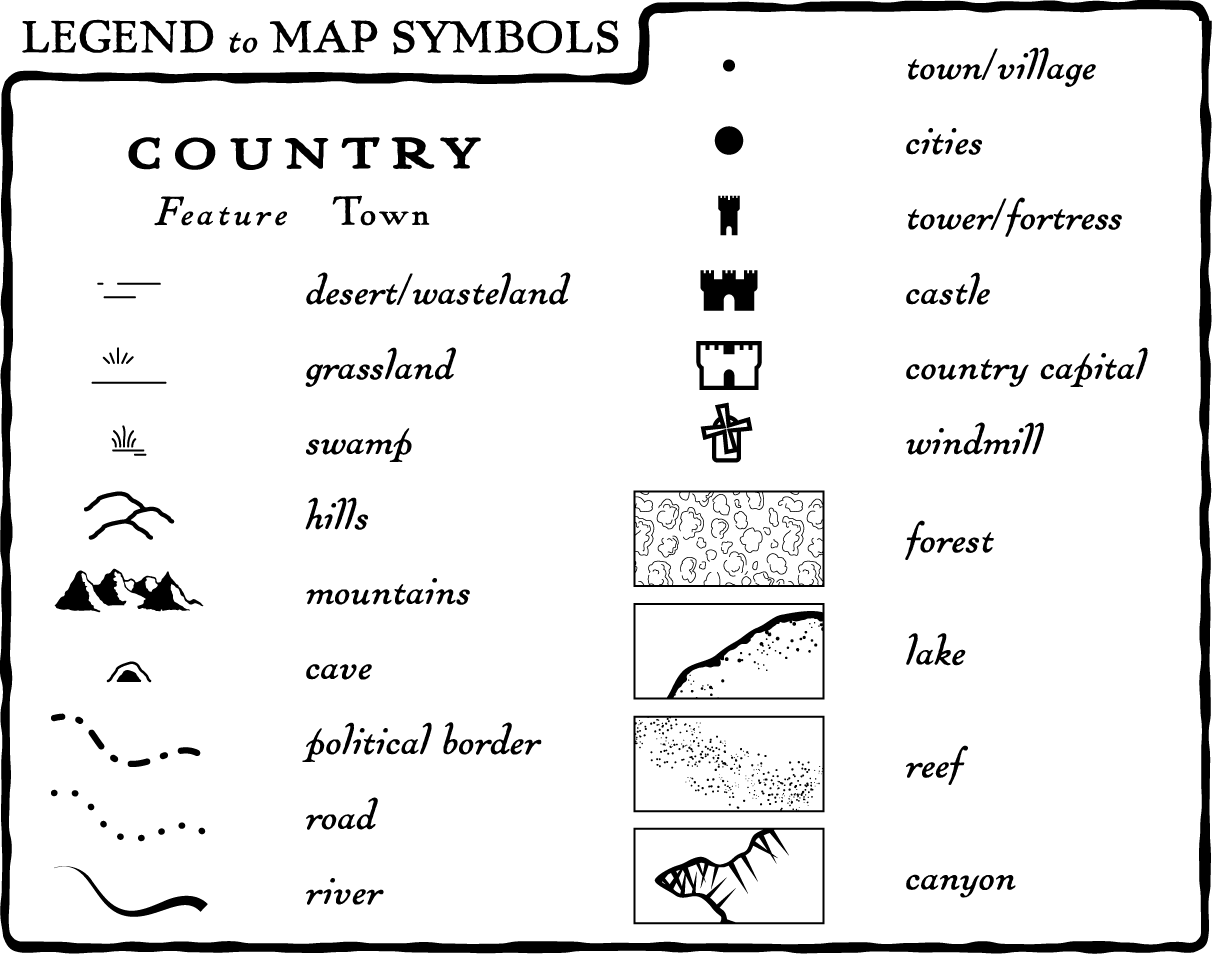
The map legend, also known as the map key, serves as a visual glossary, translating the map’s symbols, colors, patterns, and other visual cues into understandable information. It acts as a bridge between the abstract representation of the map and the real-world phenomena it depicts. Without a well-designed legend, a map can become an indecipherable jumble of lines, shapes, and colors, rendering its intended message unintelligible.
Understanding the Essence of a Map Legend
The map legend is fundamentally a system of visual communication. It leverages the principles of visual design to convey information effectively. The key elements of a map legend include:
- Symbols: These represent specific features or data points on the map. They can be simple icons, shapes, lines, or even patterns. The choice of symbols should be intuitive and visually distinct, avoiding confusion and ambiguity.
- Labels: Clear and concise labels accompany each symbol, providing a textual description of the feature or data point. Labels should be legible, using a font size and style that complements the overall map design.
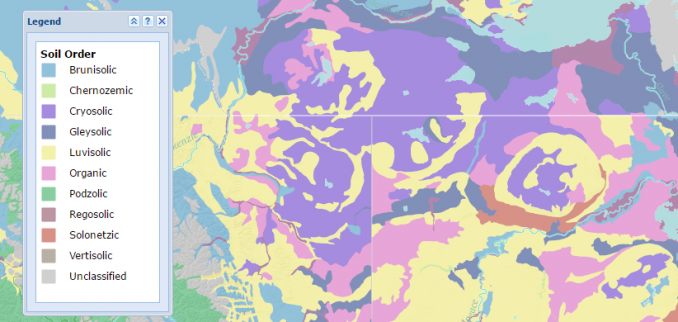
- Colors: Color plays a crucial role in map legends, particularly when representing categorical data or data gradients. Colors should be chosen strategically, considering accessibility, cultural associations, and the intended message. A colorblind-friendly palette is essential for ensuring inclusivity.
- Scales: When representing continuous data, such as elevation or population density, a scale is crucial to understand the relationship between the visual representation and the actual values. Scales should be clearly labeled and visually represented on the legend.
- Organization: The arrangement of legend elements is important for clarity. A logical order, grouping related symbols, and using visual cues like borders or spacing can enhance readability.
The Importance of a Well-Designed Map Legend
A well-designed map legend contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of a map. Its benefits include:
- Enhanced Clarity: A clear and comprehensive legend eliminates ambiguity and facilitates accurate interpretation of the map’s information.
- Improved User Experience: A user-friendly legend promotes a positive experience, allowing users to easily navigate and understand the map’s content.
- Increased Accessibility: A well-designed legend caters to diverse users, including those with visual impairments or colorblindness.
- Data Accuracy: A clear legend ensures that the data represented on the map is accurately understood and interpreted.
- Effective Communication: The legend serves as a vital communication tool, enabling the map to convey its intended message effectively.
Designing Effective Map Legends: Key Considerations
Designing a map legend requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Target Audience: Understanding the intended audience is crucial. Consider their prior knowledge, technical expertise, and potential accessibility needs.
- Map Purpose: The purpose of the map dictates the type and level of detail included in the legend. A map for navigation requires a different legend than one visualizing complex data patterns.
- Data Type: The type of data being represented informs the design choices. Categorical data requires distinct symbols and labels, while continuous data necessitates a scale and potentially a color gradient.
- Visual Design: The legend should complement the overall map design, maintaining visual consistency and using a color palette that enhances readability.
- Accessibility: Consider accessibility features like color contrast, font size, and alternative formats for users with visual impairments.
FAQs about Map Legends
Q: What is the difference between a map legend and a map key?
A: The terms "map legend" and "map key" are often used interchangeably. However, "map legend" is a more comprehensive term, encompassing all elements of the visual glossary, while "map key" might specifically refer to the symbols and their corresponding labels.
Q: How many symbols should a map legend include?
A: The number of symbols depends on the complexity of the map and the data being represented. A simple map might have only a few symbols, while a complex map could have dozens. The key is to balance comprehensiveness with clarity.
Q: Should a map legend be placed in a specific location?
A: While there is no hard and fast rule, it is generally recommended to place the legend in a prominent location, such as a corner or border of the map. It should be easily accessible to the user without obstructing the map’s content.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing a map legend?
A: Common mistakes include:
- Using too many symbols or colors, leading to confusion.
- Choosing colors that are difficult to distinguish or have unintended cultural associations.
- Using a font size or style that is too small or difficult to read.
- Placing the legend in an obscure location.
Tips for Creating Effective Map Legends
- Keep it simple: Prioritize clarity over complexity. Avoid unnecessary symbols or details.
- Use consistent design: Maintain a consistent style and color scheme throughout the legend and the map.
- Employ visual hierarchy: Use size, color, and spacing to emphasize important elements.
- Test your legend: Ask others to review your legend and provide feedback on its clarity and effectiveness.
- Consider accessibility: Ensure the legend is accessible to users with visual impairments or colorblindness.
Conclusion
The map legend is an essential element of any map, serving as a vital bridge between the visual representation and the real-world information it conveys. A well-designed legend enhances clarity, improves user experience, promotes accessibility, and ensures accurate data interpretation. By carefully considering the target audience, map purpose, data type, visual design, and accessibility, designers can create effective map legends that empower users to navigate and understand the world around them.
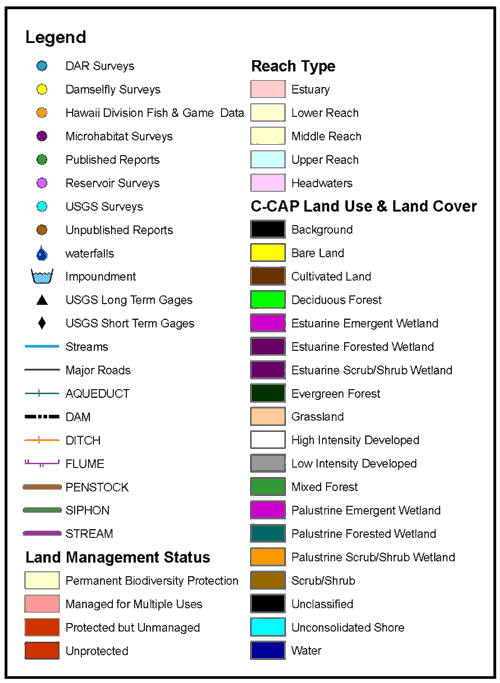
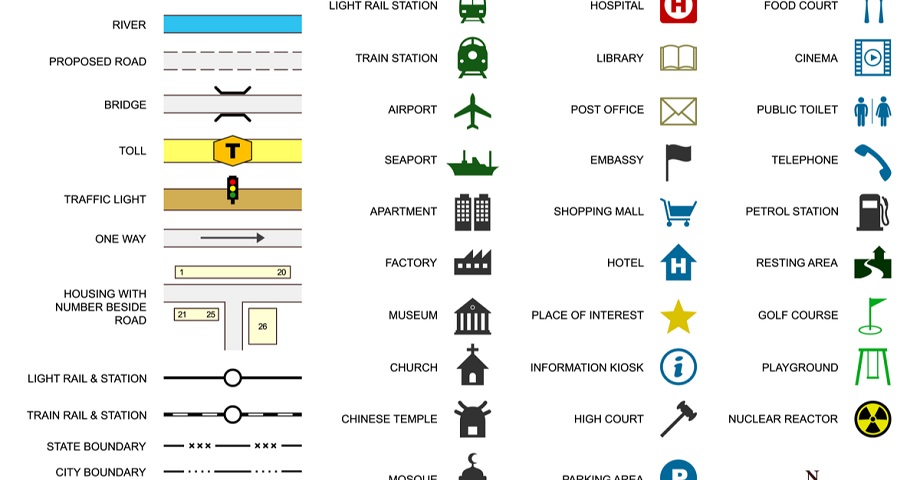
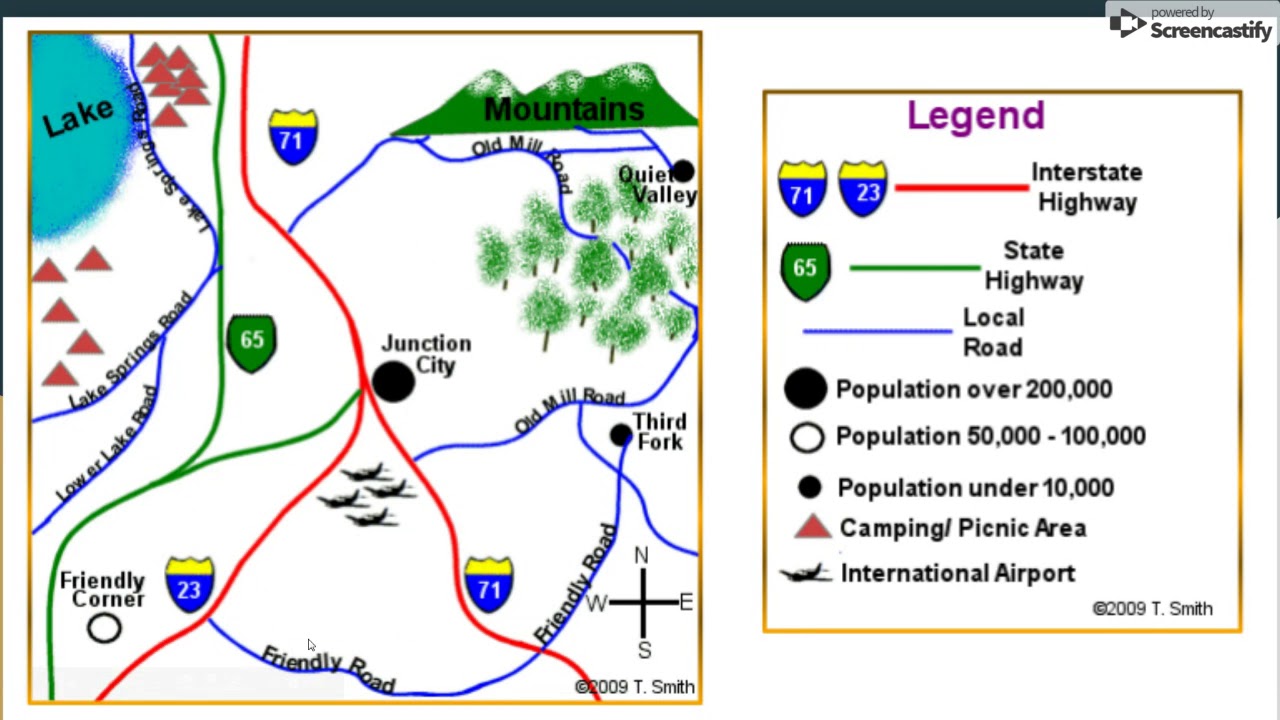



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Map Legend: A Guide to Understanding and Designing Effective Visual Keys. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!