Navigating the Globe: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Globe: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Globe: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Globe: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

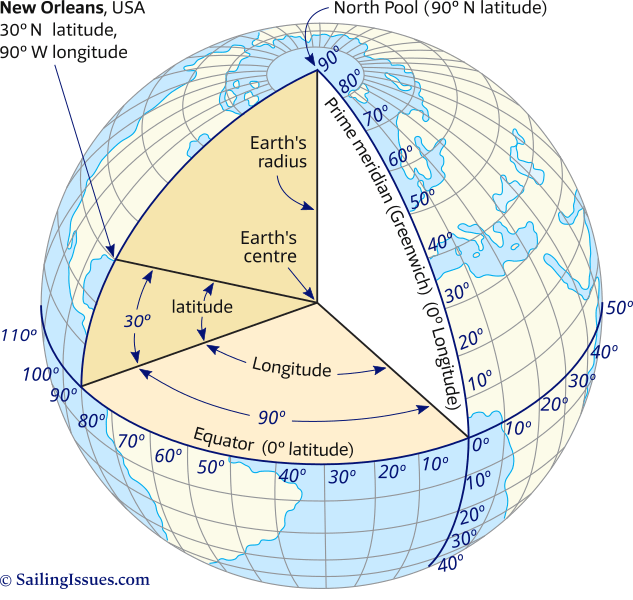
The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, is a complex system of interconnected landmasses and oceans. To navigate this intricate web, to pinpoint locations and measure distances, we rely on a system of coordinates: latitude and longitude. This system, akin to a global grid, allows us to define any point on Earth’s surface with remarkable precision.
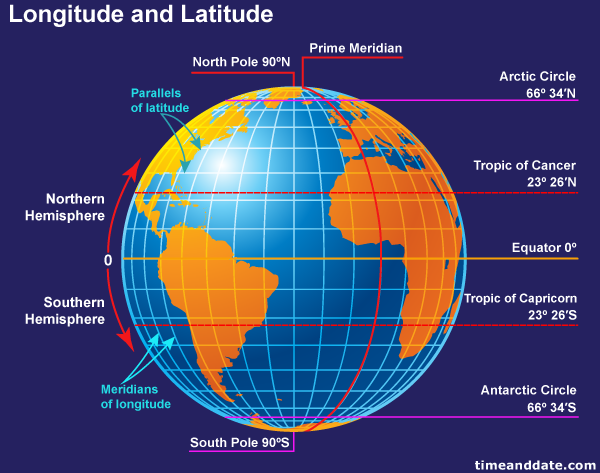
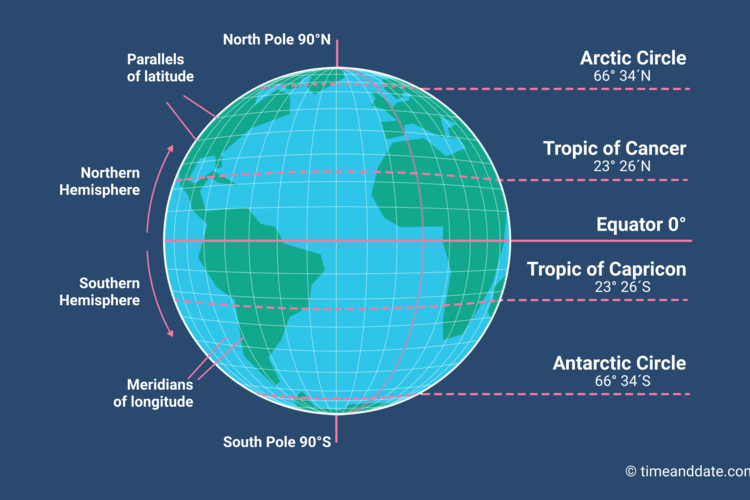
Latitude: Lines of Parallel
Imagine slicing the Earth horizontally, like a giant orange. Each slice would represent a line of latitude, running parallel to the equator. The equator, the imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees, serves as the starting point for measuring latitude.
- North of the equator: Latitude values increase from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North Pole.
- South of the equator: Latitude values decrease from 0 degrees at the equator to -90 degrees at the South Pole.
Latitude lines are crucial for determining a location’s distance from the equator. They also influence climate, as regions closer to the equator experience more direct sunlight and warmer temperatures.
Longitude: Lines of Meridian
Now, imagine slicing the Earth vertically, from the North Pole to the South Pole. Each slice represents a line of longitude, also known as a meridian. The Prime Meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, is the starting point for measuring longitude.
- East of the Prime Meridian: Longitude values increase from 0 degrees to 180 degrees.
- West of the Prime Meridian: Longitude values decrease from 0 degrees to -180 degrees.
Longitude lines help determine a location’s distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. They are vital for understanding time zones, as the Earth rotates on its axis, and each 15-degree increment in longitude corresponds to a different time zone.
The Power of Coordinates
Together, latitude and longitude form a powerful tool for:
- Precise Location Identification: Each point on Earth can be uniquely defined by its latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling accurate navigation and mapping.
- Distance Calculation: By knowing the latitude and longitude of two points, one can calculate the distance between them using various formulas and tools.
- Time Zone Determination: Longitude is directly linked to time zones, allowing for accurate timekeeping across the globe.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists utilize latitude and longitude to track weather patterns and predict future conditions.
- Resource Management: Resource exploration, conservation, and management rely heavily on precise location identification through latitude and longitude.
Applications Across Disciplines
The importance of latitude and longitude extends far beyond navigation and mapping. These coordinates play a vital role in numerous fields:
- Geography: Understanding geographical features, analyzing spatial patterns, and mapping various phenomena.
- Cartography: Creating maps, charts, and atlases for various purposes, including navigation, planning, and research.
- Navigation: Guiding ships, aircraft, and other vehicles across the globe, ensuring safe and efficient travel.
- Geology: Studying geological formations, analyzing plate tectonics, and mapping mineral deposits.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring environmental changes, tracking wildlife movements, and analyzing ecological patterns.
- Astronomy: Observing celestial objects, mapping the night sky, and studying astronomical phenomena.
- Military Operations: Planning and executing military missions, navigating troops and equipment, and coordinating operations.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
While the concept of latitude and longitude may seem straightforward, there are nuances and complexities worth exploring:
- Spheroid Earth: The Earth is not a perfect sphere, but rather an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This shape influences the accuracy of latitude and longitude calculations, leading to the development of different geodetic datums.
- Geodetic Datums: Geodetic datums are reference systems used to define the shape and size of the Earth. Different datums are used for different purposes and regions, leading to potential discrepancies in coordinate values.
- Coordinate Systems: Latitude and longitude are expressed in different coordinate systems, including geographic coordinates (degrees, minutes, seconds), decimal degrees, and UTM coordinates. Understanding these systems is crucial for accurate data analysis and interpretation.
- Map Projections: When representing the spherical Earth on a flat map, distortions are inevitable. Different map projections utilize various techniques to minimize these distortions, leading to variations in the representation of latitude and longitude.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines run parallel to the equator, while longitude lines converge at the poles.
Q: Why is the Prime Meridian located in Greenwich, England?
A: The Prime Meridian was initially chosen as a point of reference for longitude measurement by the British Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. This location was chosen due to its historical significance and its position as a major maritime hub.
Q: How are latitude and longitude used in GPS?
A: GPS (Global Positioning System) utilizes satellites orbiting Earth to determine a receiver’s precise location. These satellites transmit signals that contain information about their position and time. By comparing the time it takes for signals to reach different receivers, the GPS system can calculate the receiver’s latitude, longitude, and altitude.
Q: Can latitude and longitude change over time?
A: While latitude and longitude are generally considered fixed, slight changes can occur due to tectonic plate movement, continental drift, and other geological processes. However, these changes are typically very small and occur over long periods.
Tips: Mastering Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Grid: Imagine the Earth as a giant grid with latitude lines running horizontally and longitude lines running vertically. This visualization helps understand the relationship between coordinates and locations.
- Use Online Tools: Numerous online tools and websites provide interactive maps that allow you to explore latitude and longitude, calculate distances, and convert coordinates between different systems.
- Practice with Real-World Examples: Try identifying the latitude and longitude of familiar locations, such as your city or a landmark you have visited. This hands-on experience helps solidify your understanding.
- Explore Different Coordinate Systems: Familiarize yourself with different coordinate systems used in various applications. Understanding these systems is crucial for accurate data interpretation and analysis.
Conclusion: A Global Framework for Connection
Latitude and longitude, seemingly simple concepts, form the foundation of our understanding of the Earth’s surface. They enable us to navigate, map, and analyze the world around us with unprecedented precision. From charting new territories to tracking environmental changes, these coordinates continue to play a vital role in shaping our understanding of the planet we call home. As technology advances, the importance of latitude and longitude will only grow, ensuring our ability to connect, explore, and navigate the vast and intricate world we inhabit.


/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Globe: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!