Navigating the Smog: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Los Angeles
Related Articles: Navigating the Smog: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Los Angeles
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Smog: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Los Angeles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Smog: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Los Angeles
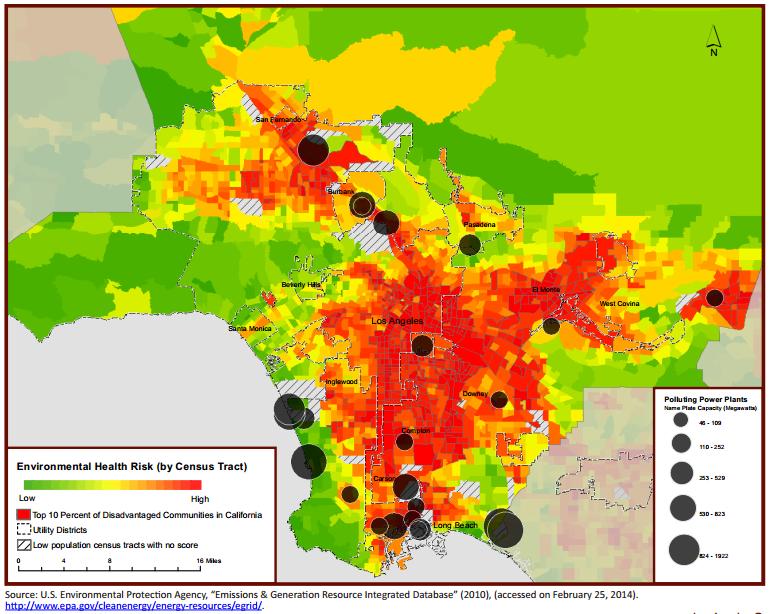
The Los Angeles Basin, a sprawling urban expanse nestled between the Pacific Ocean and the San Gabriel Mountains, is renowned for its vibrant culture, diverse population, and unfortunately, a history of severe air pollution. This chronic challenge, a product of dense population, heavy industry, and unique geographical features, has spurred the development of a critical tool: the air quality map. This digital representation of real-time and historical air quality data provides a comprehensive understanding of the region’s breathing space, empowering residents, policymakers, and researchers alike to make informed decisions about health, safety, and environmental stewardship.
Unveiling the Layers of Pollution:
The air quality map of Los Angeles, typically presented as a color-coded visual, showcases the concentration of various pollutants across the region. These pollutants, often invisible to the naked eye, pose significant threats to human health and the environment. The map typically features data on:
- Ozone (O3): This colorless gas, formed by chemical reactions involving nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds in the presence of sunlight, is a primary component of smog. High ozone levels can cause respiratory problems, particularly in children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These tiny particles, emitted from sources such as vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, and wildfires, can penetrate deep into the lungs and cause cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. PM2.5, with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, is particularly concerning due to its ability to reach the smallest airways.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): This colorless and odorless gas, primarily released by vehicle exhaust, can reduce the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood, leading to cardiovascular problems and headaches.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): This reddish-brown gas, primarily emitted from vehicle exhaust and industrial processes, contributes to the formation of ozone and can irritate the respiratory system.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): This colorless gas, emitted from power plants and industrial processes, can cause respiratory problems and contribute to acid rain.
Navigating the Map: A Guide to Interpretation:
The color-coded scale on the air quality map typically utilizes a range of colors, with green representing clean air and red signifying hazardous conditions. The map often includes data for different time periods, allowing users to track trends and identify potential hotspots of pollution.
The Importance of the Air Quality Map:
The air quality map serves as a crucial tool for numerous stakeholders:
- Public Health Officials: The map enables health authorities to identify areas with elevated pollution levels and issue health advisories, particularly for vulnerable populations. This allows for proactive measures to minimize the health impacts of air pollution.
- Environmental Agencies: The map provides real-time data that informs regulatory decisions and helps monitor the effectiveness of pollution control measures. This data is essential for developing targeted strategies to improve air quality.
- Researchers: The map offers valuable data for scientific studies on the sources, transport, and health impacts of air pollution. This data helps researchers understand the complex dynamics of air quality and develop innovative solutions.
- Individuals: The map empowers residents to make informed decisions about their daily activities. Individuals can use the map to plan outdoor activities, choose routes with lower pollution levels, and take precautions during periods of high pollution.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Factors at Play:
While the air quality map provides a snapshot of the current situation, it’s crucial to understand the factors that contribute to air pollution in Los Angeles:
- Geography: The Los Angeles Basin’s unique geography, characterized by mountains surrounding a relatively flat basin, traps pollutants and creates a persistent smog layer.
- Population Density: The region’s dense population, coupled with a high concentration of vehicles, contributes significantly to air pollution.
- Industry: Industrial activities, including manufacturing, transportation, and energy production, release significant amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Meteorological Conditions: Weather patterns, particularly temperature inversions, can trap pollutants near the ground, leading to elevated air pollution levels.
FAQs about the Air Quality Map:
1. How often is the air quality map updated?
The air quality map is typically updated in real-time, reflecting the latest air quality data collected from monitoring stations throughout the region.
2. What are the sources of air quality data used in the map?
The air quality data used in the map is collected from a network of monitoring stations operated by government agencies and research institutions. These stations continuously measure the concentration of various pollutants in the air.
3. What are the health effects of air pollution?
Air pollution can have a wide range of health effects, including respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and developmental problems in children.
4. How can I contribute to improving air quality?
Individuals can contribute to improving air quality by reducing their reliance on private vehicles, opting for public transportation, cycling, or walking. Additionally, supporting policies that promote clean energy sources and reduce industrial emissions can significantly impact air quality.
Tips for Utilizing the Air Quality Map:
- Check the map regularly: Stay informed about the current air quality conditions in your area.
- Plan outdoor activities: Consider the air quality forecast when planning outdoor activities, particularly during periods of high pollution.
- Limit outdoor activities: Reduce outdoor activities during periods of high pollution, especially for sensitive groups like children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory problems.
- Use air purifiers: Consider using air purifiers indoors, particularly in areas with high air pollution levels.
- Support clean air initiatives: Advocate for policies and regulations that promote clean air and reduce pollution.
Conclusion:
The air quality map of Los Angeles serves as a vital tool for understanding and addressing the region’s air pollution challenges. By providing real-time data and insights into the distribution and concentration of pollutants, the map empowers individuals, policymakers, and researchers to make informed decisions that promote public health and environmental sustainability. While the map offers a snapshot of the current situation, it’s essential to recognize the complex factors contributing to air pollution and work collaboratively towards a cleaner and healthier Los Angeles. Through ongoing monitoring, data analysis, and proactive measures, we can strive to breathe easy in the City of Angels.





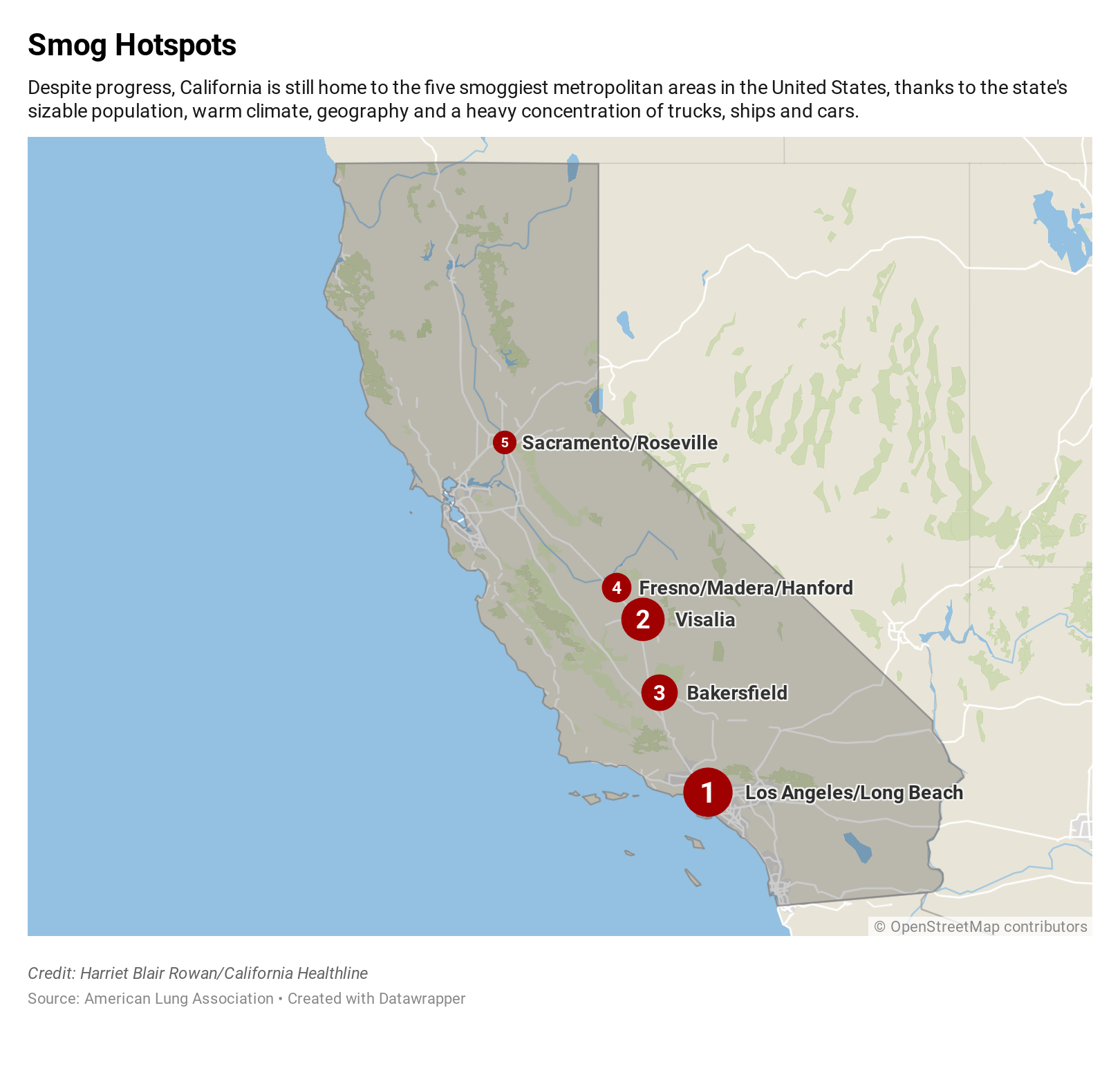
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/61214029/Screen_20Shot_202015-06-12_20at_203.13.17_20PM.0.1449911431.0.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Smog: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Los Angeles. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!