Navigating the World of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartography
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartography
Cartography, the art and science of mapmaking, has been an integral part of human civilization for millennia. From ancient cave paintings depicting hunting grounds to modern satellite imagery mapping the entire globe, maps have served as essential tools for understanding and interacting with the world around us. In today’s data-driven society, the role of cartography has evolved, becoming increasingly sophisticated and vital in various fields.
The Evolution of Cartography: From Papyrus to Pixels
The earliest known maps, dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE, were rudimentary representations of landscapes and waterways etched onto clay tablets or papyrus scrolls. These early cartographers relied on observation, exploration, and rudimentary surveying techniques to create their maps. Over time, advancements in technology and scientific understanding revolutionized mapmaking.
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century enabled the mass production of maps, disseminating knowledge and facilitating exploration. The Age of Discovery, fueled by cartographic advancements, saw the creation of detailed nautical charts and world maps, revolutionizing global trade and navigation.
The 19th century witnessed the rise of precise surveying methods, enabling the creation of accurate maps with detailed topographic features. The development of photography further transformed cartography, allowing for the incorporation of aerial imagery into mapmaking.
The Digital Revolution and the Rise of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
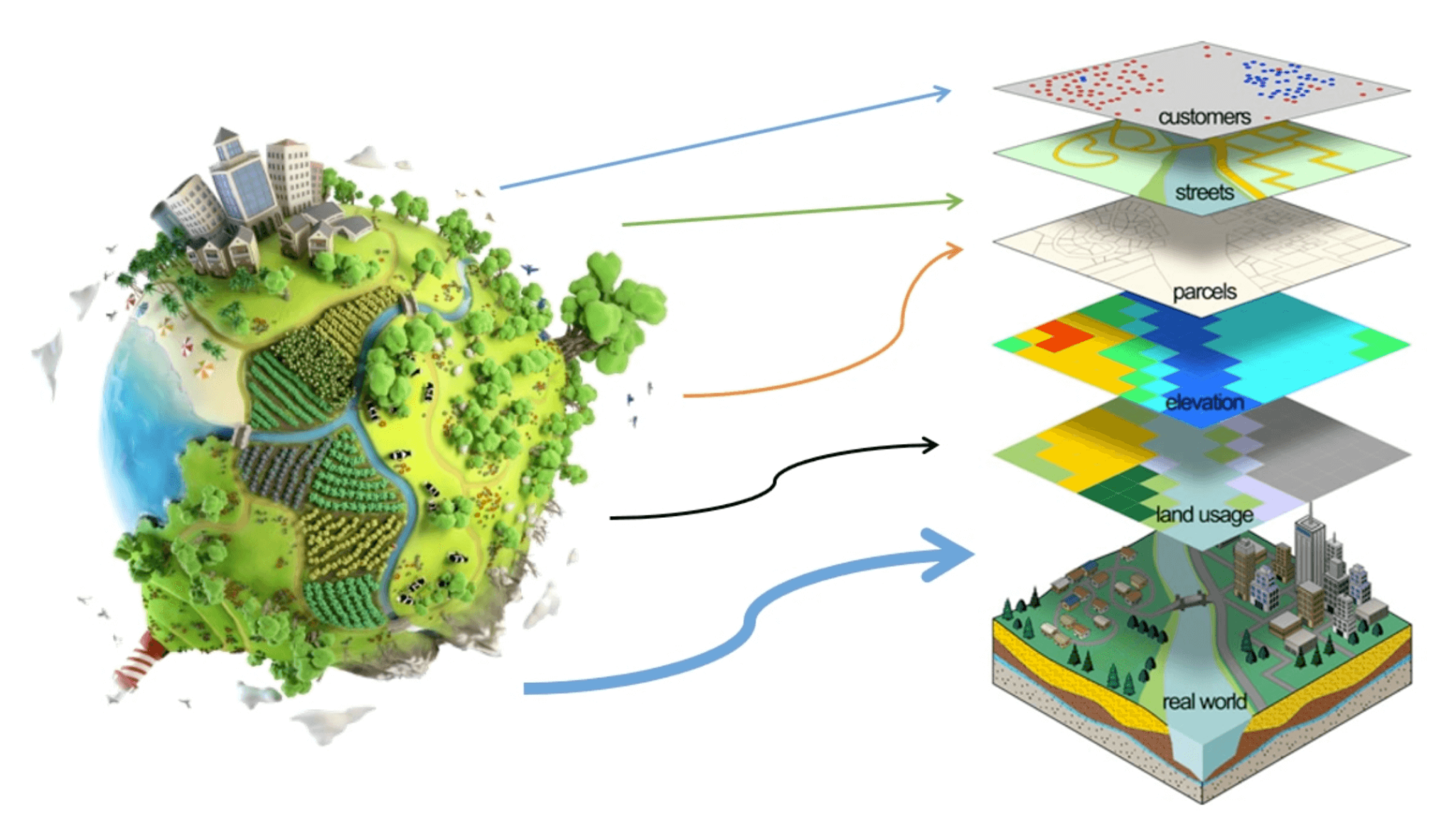
The 20th century saw the advent of computers and the development of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS software revolutionized mapmaking by allowing cartographers to store, analyze, and visualize vast amounts of spatial data. This digital transformation enabled the creation of interactive, dynamic maps, offering unprecedented insights into various aspects of the world.
The Importance of Cartography in Modern Society
Cartography plays a crucial role in a wide range of fields, influencing decision-making and shaping our understanding of the world. Here are some key areas where cartography remains indispensable:
- Navigation and Transportation: Maps are essential for navigating roads, waterways, and air routes, guiding travelers and facilitating the efficient movement of goods and people.
- Urban Planning and Development: Cartographers help urban planners design sustainable cities, analyze population density, and optimize infrastructure development.
- Environmental Monitoring and Conservation: Maps are used to track deforestation, monitor climate change, and manage natural resources, aiding in conservation efforts.
- Public Health and Disease Control: Geographic data plays a crucial role in understanding disease outbreaks, identifying risk factors, and implementing effective public health interventions.
- Disaster Management and Response: Maps are essential for assessing damage after natural disasters, coordinating relief efforts, and evacuating affected populations.
- Business and Marketing: Cartographic data helps businesses understand customer demographics, identify market opportunities, and optimize logistics and distribution networks.
- Education and Research: Maps are valuable educational tools, providing visual representations of complex concepts and facilitating research in various fields.
The Future of Cartography: Emerging Trends and Innovations
Cartography continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for spatial data. Here are some emerging trends shaping the future of mapmaking:
- Big Data and Data Visualization: The increasing availability of large datasets, including satellite imagery, sensor data, and social media feeds, presents new opportunities for cartographers to create more comprehensive and insightful maps.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI algorithms are being used to automate mapmaking processes, improve data analysis, and generate predictive models for spatial phenomena.
- 3D Mapping and Virtual Reality (VR): 3D maps and VR technologies offer immersive experiences, allowing users to explore and interact with spatial data in new ways.
- Crowdsourcing and Citizen Science: The involvement of the public in data collection and mapmaking is becoming increasingly common, leading to the creation of more detailed and localized maps.
FAQs about Cartography
Q: What are the different types of maps?
A: Maps can be categorized based on their purpose, scale, and content. Common types include:
- Topographic maps: Depict physical features such as elevation, landforms, and water bodies.
- Thematic maps: Focus on a specific theme, such as population density, climate patterns, or disease distribution.
- Road maps: Show transportation routes and landmarks.
- Nautical charts: Designed for navigation at sea, including depths, currents, and hazards.
- Aerial maps: Created from aerial photographs, providing a bird’s-eye view of the landscape.
Q: What are the key elements of a map?
A: A typical map includes:







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!