Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
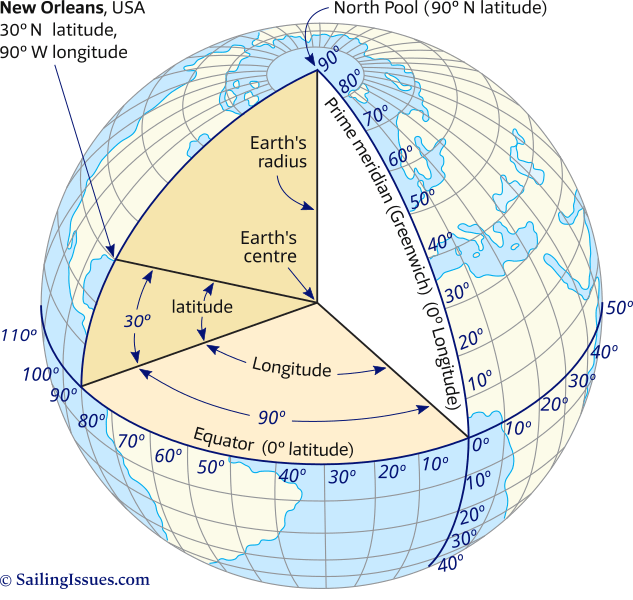
Our planet, a vast and complex sphere, is a canvas upon which countless stories unfold. From towering mountains to sprawling oceans, from bustling cities to remote villages, the Earth’s surface is a tapestry of diverse landscapes and experiences. To navigate this intricate tapestry, to pinpoint precise locations and measure distances, we rely on a powerful tool: the system of longitude and latitude.
Longitude and latitude, two fundamental concepts in geography, serve as a global grid, dividing the Earth into a network of invisible lines that enable us to locate any point on its surface with remarkable accuracy. These lines, often referred to as meridians and parallels, form the bedrock of mapmaking, navigation, and countless other fields that rely on precise location information.
The Meridian of Prime: Defining the Starting Point
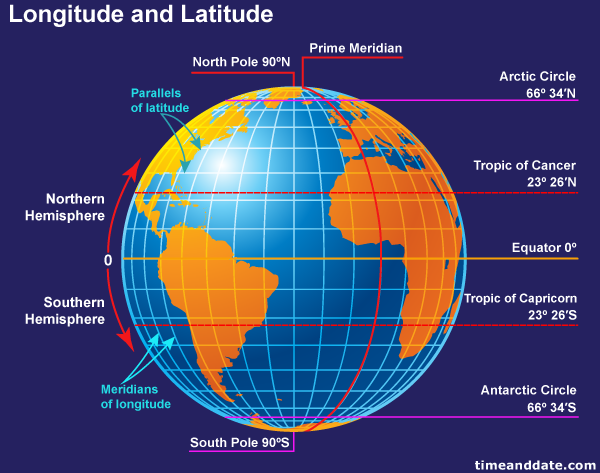
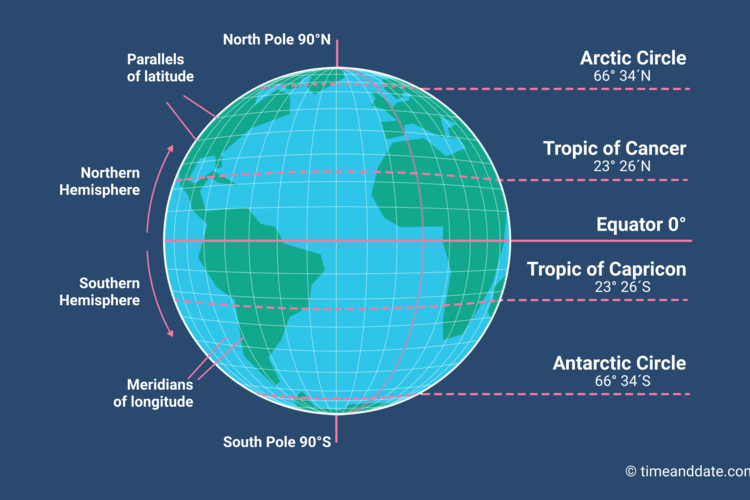
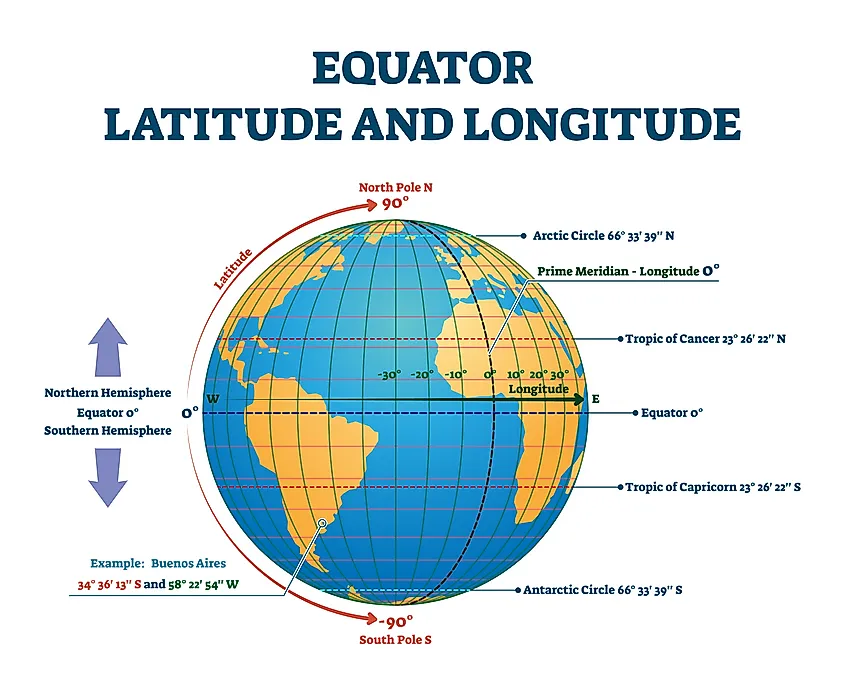
Imagine a line running from the North Pole to the South Pole, slicing through the Earth. This line, known as the Prime Meridian, serves as the zero-degree point for measuring longitude. It is an arbitrary line, chosen by international agreement, and passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England.
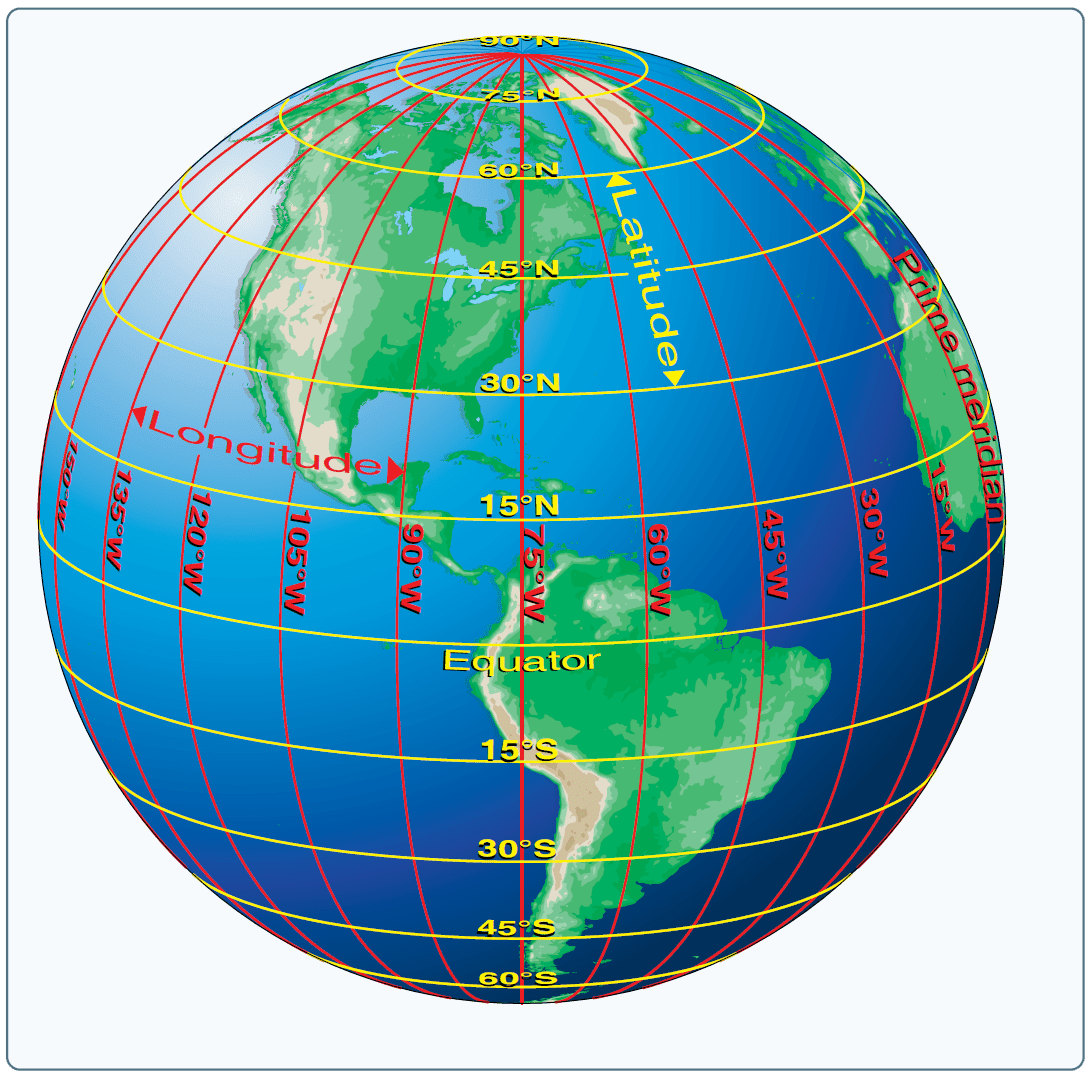
Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, defines a location’s position relative to this starting point. Lines of longitude, also known as meridians, converge at the poles and form semi-circles that encircle the Earth. Each meridian represents a specific longitude value, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° east or west.
Circles of Latitude: Tracing the Equator
While longitude defines the east-west position, latitude measures the north-south position. Imagine another line, this time circling the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles. This line, known as the Equator, serves as the zero-degree point for measuring latitude.
Latitude is measured in degrees north or south of the Equator, with lines of latitude, also called parallels, running parallel to the Equator. Each parallel represents a specific latitude value, ranging from 0° at the Equator to 90° north or south at the poles.
A Global Grid: Intersecting Lines for Precise Location
The combination of longitude and latitude creates a global grid, where every point on Earth can be identified by its unique intersection of a meridian and a parallel. This grid, known as the Geographic Coordinate System, forms the foundation for mapmaking, navigation, and numerous other applications.
Beyond the Grid: The Importance of Longitude and Latitude
The significance of longitude and latitude extends far beyond the realm of maps and navigation. Here are some of the key areas where this system plays a vital role:
- Navigation: Longitude and latitude are crucial for navigating ships, airplanes, and even spacecraft. Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, which relies on satellite signals, utilizes these coordinates to determine precise locations on Earth.
- Mapping: Maps, whether printed or digital, use longitude and latitude as the foundation for their representation of the Earth’s surface. These coordinates enable accurate representation of geographic features, distances, and relationships between different locations.
- Weather Forecasting: Weather patterns are influenced by geographic location, and longitude and latitude play a critical role in weather forecasting models. By understanding the position of weather systems relative to these coordinates, meteorologists can predict weather events with greater accuracy.
- Earth Sciences: Geologists, oceanographers, and other earth scientists use longitude and latitude to study and analyze Earth’s physical processes. These coordinates help them track tectonic plate movements, map ocean currents, and monitor environmental changes.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use longitude and latitude to pinpoint the location of celestial objects in the sky. This information is essential for understanding the movement of stars, planets, and other celestial bodies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Longitude and Latitude
1. How are longitude and latitude measured?
Longitude and latitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. A degree is divided into 60 minutes, and each minute is further divided into 60 seconds. This system allows for precise location determination.
2. Why is the Prime Meridian located in Greenwich, England?
The Prime Meridian’s location in Greenwich, England, was chosen by international agreement in the late 19th century. It was a practical choice, as the Royal Observatory in Greenwich was already a prominent center for astronomical observation and timekeeping.
3. What is the difference between longitude and latitude?
Longitude measures the east-west position relative to the Prime Meridian, while latitude measures the north-south position relative to the Equator. Longitude lines converge at the poles, while latitude lines run parallel to the Equator.
4. How does GPS technology use longitude and latitude?
GPS technology utilizes satellite signals to determine a receiver’s location based on its distance from multiple satellites. By triangulating these distances, GPS receivers can calculate the precise longitude and latitude coordinates of the device’s location.
5. Can longitude and latitude be used to determine time zones?
Yes, longitude plays a significant role in defining time zones. As the Earth rotates, different locations experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Time zones are generally based on 15-degree intervals of longitude, with each interval representing one hour of difference in time.
Tips for Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- Visualize the Grid: Imagine a globe with lines of longitude and latitude drawn on it. This will help you understand how these lines intersect to form a grid that covers the entire Earth.
- Use Online Maps: Explore online mapping tools and zoom in on different locations. Observe how the coordinates change as you move the map cursor.
- Practice Finding Locations: Try to find the longitude and latitude coordinates of your city, country, or other points of interest. This will help you solidify your understanding of how this system works.
- Connect to Real-World Applications: Think about how longitude and latitude are used in everyday life, from navigation apps to weather forecasts. This will make the concept more relevant and engaging.
Conclusion
Longitude and latitude, an intricate system of lines woven across our planet, provide a powerful framework for understanding the Earth’s surface. They serve as the foundation for navigation, mapping, weather forecasting, and countless other fields that rely on precise location information. By understanding this system, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our world and the remarkable tools that enable us to navigate and explore its vastness.



/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!