The Art of Cartography in Dungeons & Dragons: Shaping Worlds and Adventures
Related Articles: The Art of Cartography in Dungeons & Dragons: Shaping Worlds and Adventures
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Art of Cartography in Dungeons & Dragons: Shaping Worlds and Adventures. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art of Cartography in Dungeons & Dragons: Shaping Worlds and Adventures

Dungeons & Dragons, a tabletop role-playing game steeped in fantasy, relies heavily on the power of imagination. However, the abstract landscapes of the mind often benefit from a tangible representation: the map. While pre-made maps offer a starting point, the true magic of D&D unfolds when players and Dungeon Masters (DMs) create their own worlds, and mapmaking becomes an integral part of this creative process.
The Importance of Maps in Dungeons & Dragons
Maps serve as more than just visual aids in D&D. They provide a foundation for:
- Worldbuilding: Maps allow for the creation of detailed and coherent worlds. From sprawling forests to treacherous mountains, each geographical feature can be carefully considered and integrated into the narrative.
- Campaign Setting: A well-crafted map establishes the context for the campaign, providing a sense of place and history. Players can understand the relationships between locations, the influence of terrain on societies, and the potential challenges they might face.
- Adventure Design: Maps act as blueprints for adventures. They help DMs visualize potential encounters, plot routes, and strategically place points of interest, ensuring a dynamic and engaging gameplay experience.
- Player Engagement: Maps provide a tangible representation of the world they are exploring, enhancing the sense of immersion and allowing players to visualize their surroundings. They can actively track their progress, plan their routes, and make informed decisions based on the map’s information.
- Narrative Development: Maps can contribute to the narrative by revealing clues, suggesting hidden secrets, and even shaping the characters’ choices. They become a tool for storytelling, adding depth and complexity to the campaign.
Types of Maps in Dungeons & Dragons
The world of D&D mapping encompasses various styles and scales:
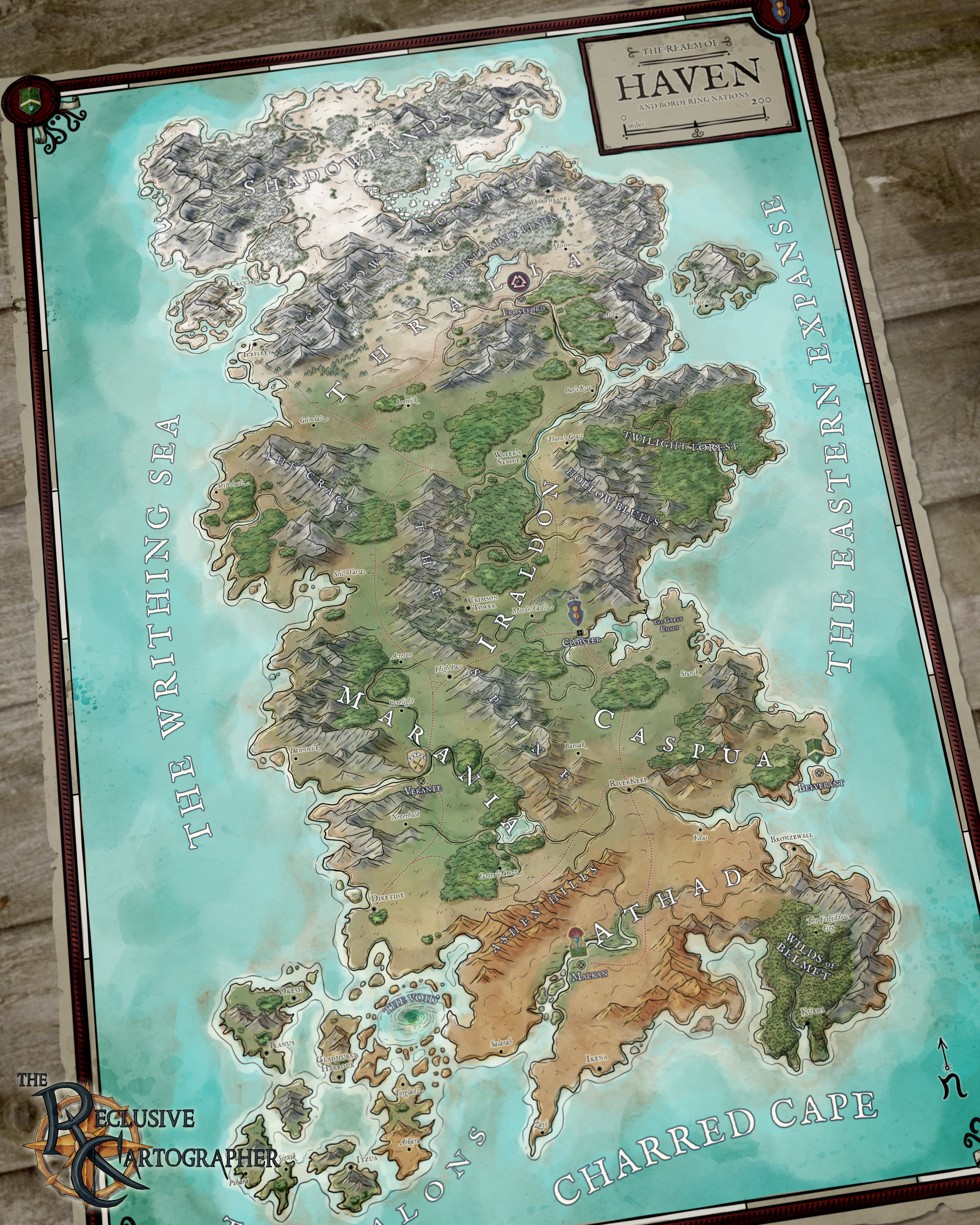
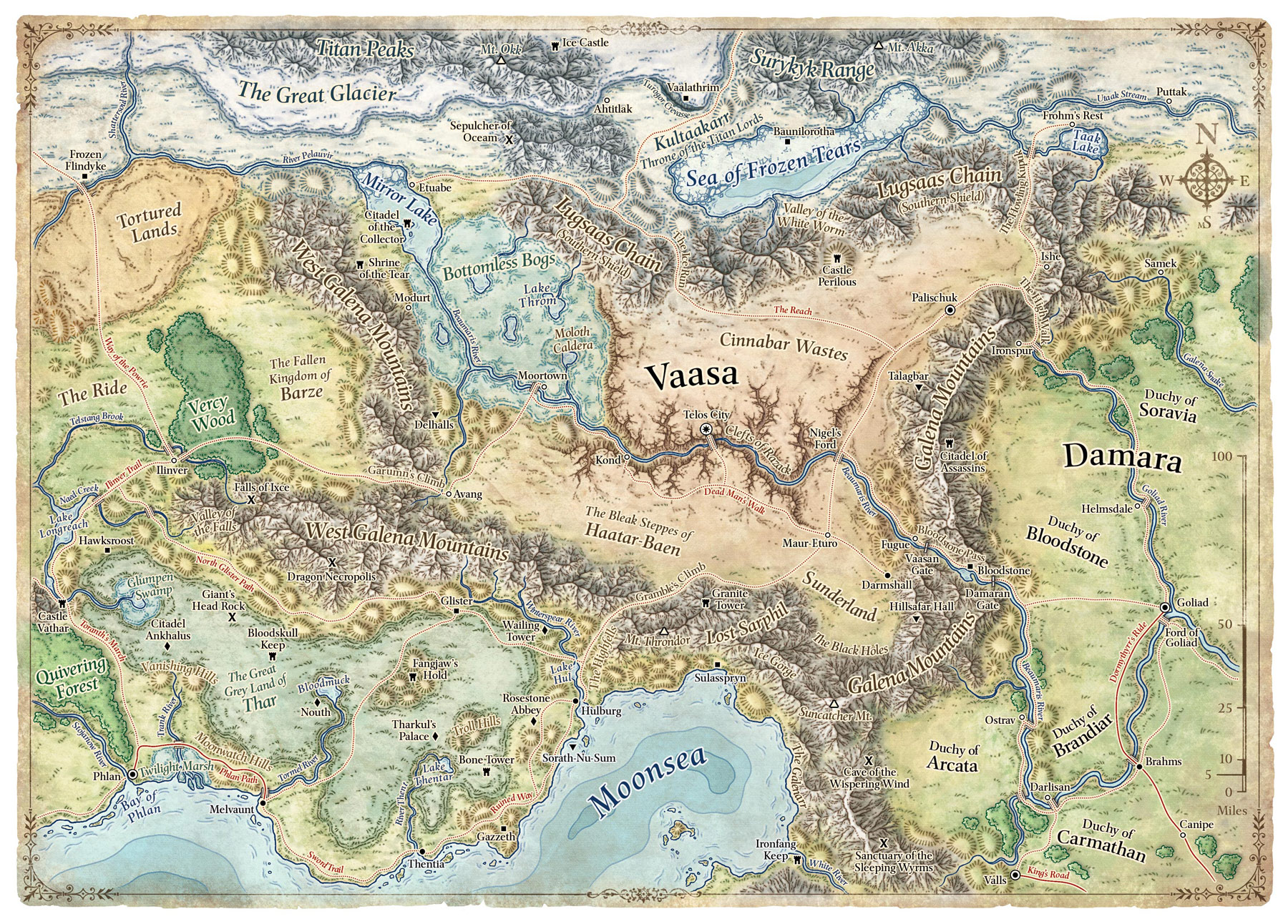
- Campaign Maps: These large-scale maps depict entire continents or even the globe, showcasing the overarching geography and political landscape of the campaign setting.
- Regional Maps: These maps focus on specific regions within a larger world, providing more detail about the landscape, towns, and points of interest within a particular area.
- Dungeon Maps: These maps represent the interiors of dungeons, caves, or other underground structures, detailing the layout of rooms, corridors, and potential hazards.
- Battle Maps: These maps are designed for combat encounters, providing a grid system for tracking character movements, positioning enemies, and visualizing the flow of battle.
Tools and Techniques for D&D Mapmaking
The tools and techniques used for D&D mapmaking are as diverse as the game itself:
- Hand-Drawn Maps: Traditional methods using pencils, pens, and markers remain popular, allowing for artistic expression and a personalized touch.
- Digital Tools: Software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and specialized mapping programs offer a wide range of features for creating detailed and intricate maps.
- Online Mapping Tools: Websites and applications like Inkarnate, Wonderdraft, and Dungeon Fog provide user-friendly interfaces for creating maps with various styles, symbols, and features.
- Terrain Modeling: For physical maps, techniques like sandboxing, using foamboard, or even building models can create realistic and immersive representations of the game world.
Tips for Creating Effective D&D Maps
- Define the Scope: Clearly determine the purpose and scale of the map to ensure it effectively serves its intended function.
- Consider the Terrain: Use varied terrain features like mountains, forests, rivers, and deserts to create a visually interesting and geographically diverse map.
- Mark Points of Interest: Highlight key locations, towns, settlements, and landmarks to provide context and guide players through the world.
- Use Symbols and Legends: Employ clear symbols and a legend to represent different features, ensuring easy understanding and navigation.
- Add Narrative Elements: Incorporate details that enhance the story, such as ruins, ancient temples, or areas of historical significance.
- Experiment with Styles: Explore different map styles, from traditional to modern, to find a style that suits the campaign and your creative vision.
- Collaborate with Players: Involve players in the mapmaking process, allowing them to contribute ideas and shape the world they will explore.
FAQs about D&D Mapmaking
1. What are some popular mapmaking software options for D&D?
Popular software options include Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Inkarnate, Wonderdraft, and Dungeon Fog. These programs offer various features, from basic drawing tools to advanced terrain generation and symbol libraries.
2. What are some essential symbols to include on a D&D map?
Essential symbols include:
- Roads: Representing pathways and routes of travel.
- Settlements: Marking towns, villages, and cities.
- Points of Interest: Highlighting landmarks, dungeons, and other significant locations.
- Terrain Features: Representing mountains, forests, rivers, and other geographical features.
- Political Boundaries: Defining the borders of kingdoms, empires, or other political entities.
3. How can I add a sense of history and lore to my D&D map?
Incorporate elements that suggest a rich history, such as:
- Ruins: Remnants of ancient civilizations, indicating past conflicts or events.
- Monuments: Memorials to significant figures or events, providing historical context.
- Place Names: Choose names that reflect the region’s history or culture.
- Legends and Stories: Introduce local legends or tales that contribute to the world’s lore.
4. What are some tips for creating engaging dungeon maps?
When creating dungeon maps:
- Use a Grid System: Employ a grid system for accurate movement and combat.
- Create Variety: Include different room shapes, sizes, and layouts to avoid monotony.
- Include Obstacles: Add obstacles like walls, doors, traps, and environmental hazards to create challenges.
- Highlight Key Features: Emphasize important areas like treasure rooms, boss chambers, and secret passages.
5. How can I use mapmaking to improve my D&D game?
Mapmaking can enhance your D&D game by:
- Creating a More Immersive World: Maps provide a tangible representation of the game world, increasing player immersion.
- Facilitating Better Storytelling: Maps can be used to guide the narrative, reveal clues, and create suspense.
- Enhancing Player Agency: Maps allow players to visualize their surroundings, make informed decisions, and plan their actions.
Conclusion
Mapmaking in Dungeons & Dragons is an art form that goes beyond mere visual representation. It is a powerful tool for worldbuilding, adventure design, and storytelling. By combining creativity, knowledge of the game, and a keen eye for detail, DMs and players can craft maps that bring their fantasy worlds to life and enhance the overall D&D experience. As the game continues to evolve, the role of mapmaking will undoubtedly remain central to the imaginative and collaborative spirit of D&D, ensuring that every adventure unfolds within a richly detailed and captivating world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art of Cartography in Dungeons & Dragons: Shaping Worlds and Adventures. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!