The Essential Guide to Map Legends: Understanding the Key to Geographic Interpretation
Related Articles: The Essential Guide to Map Legends: Understanding the Key to Geographic Interpretation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Essential Guide to Map Legends: Understanding the Key to Geographic Interpretation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Guide to Map Legends: Understanding the Key to Geographic Interpretation
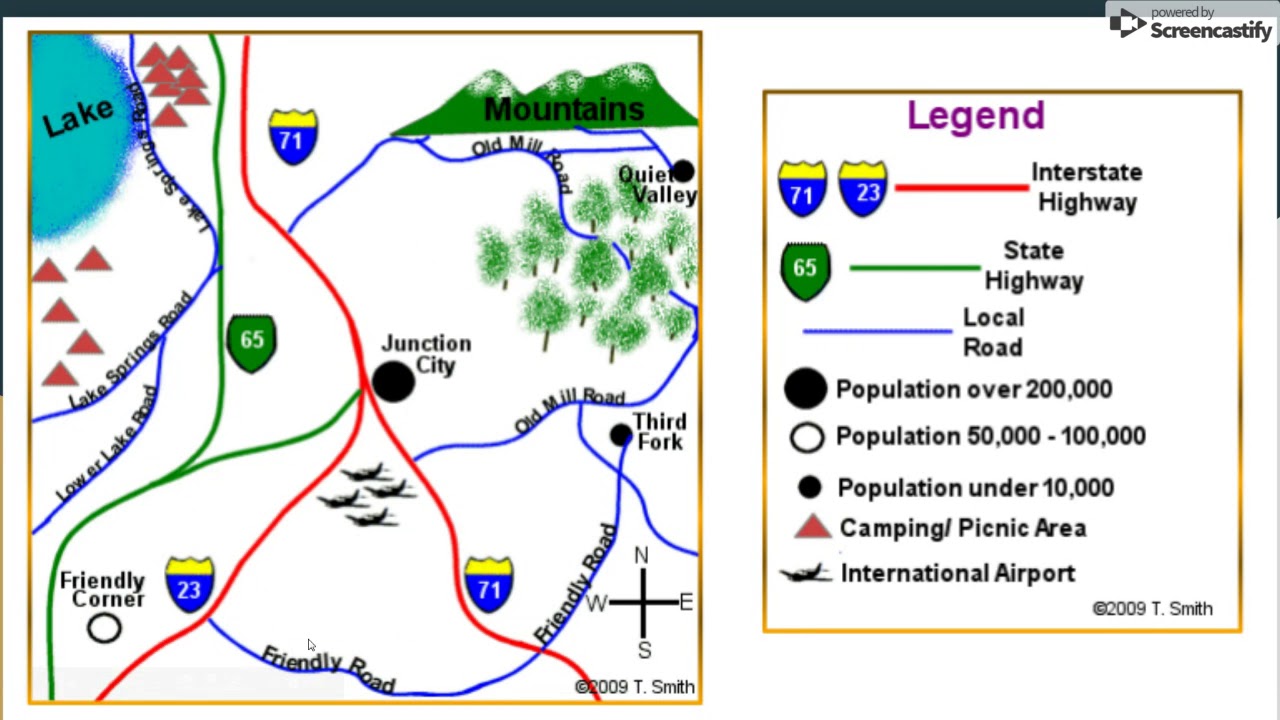
Maps, in their various forms, serve as powerful tools for navigating our physical and conceptual landscapes. From road maps guiding travelers to intricate geological maps illuminating Earth’s history, these visual representations rely on a crucial element: the legend.
A map legend, also known as a map key, serves as a crucial intermediary between the map’s visual language and the reader’s understanding. It acts as a glossary, translating the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map into meaningful information. Without a clear and comprehensive legend, maps become mere abstract patterns, devoid of their intended meaning.
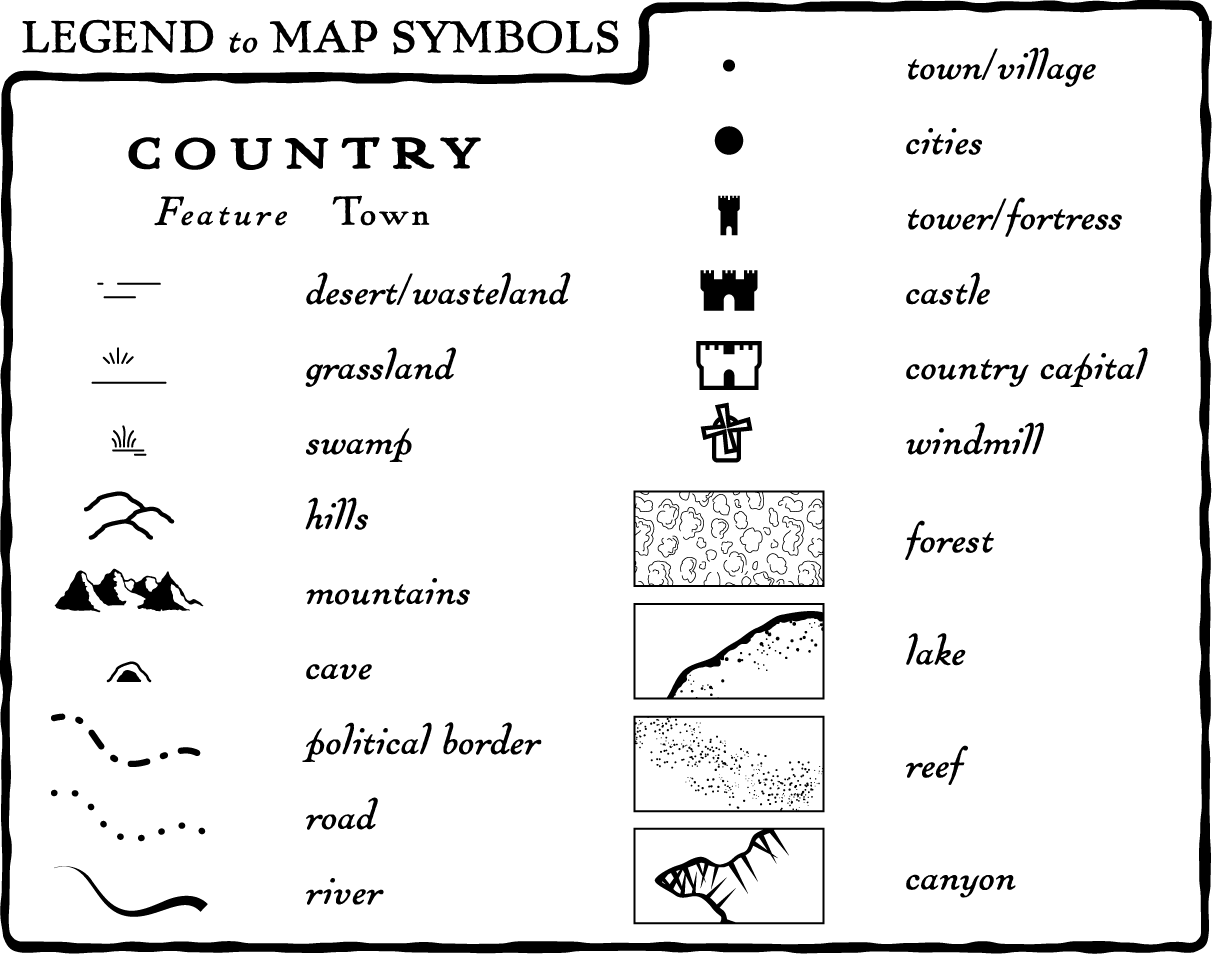
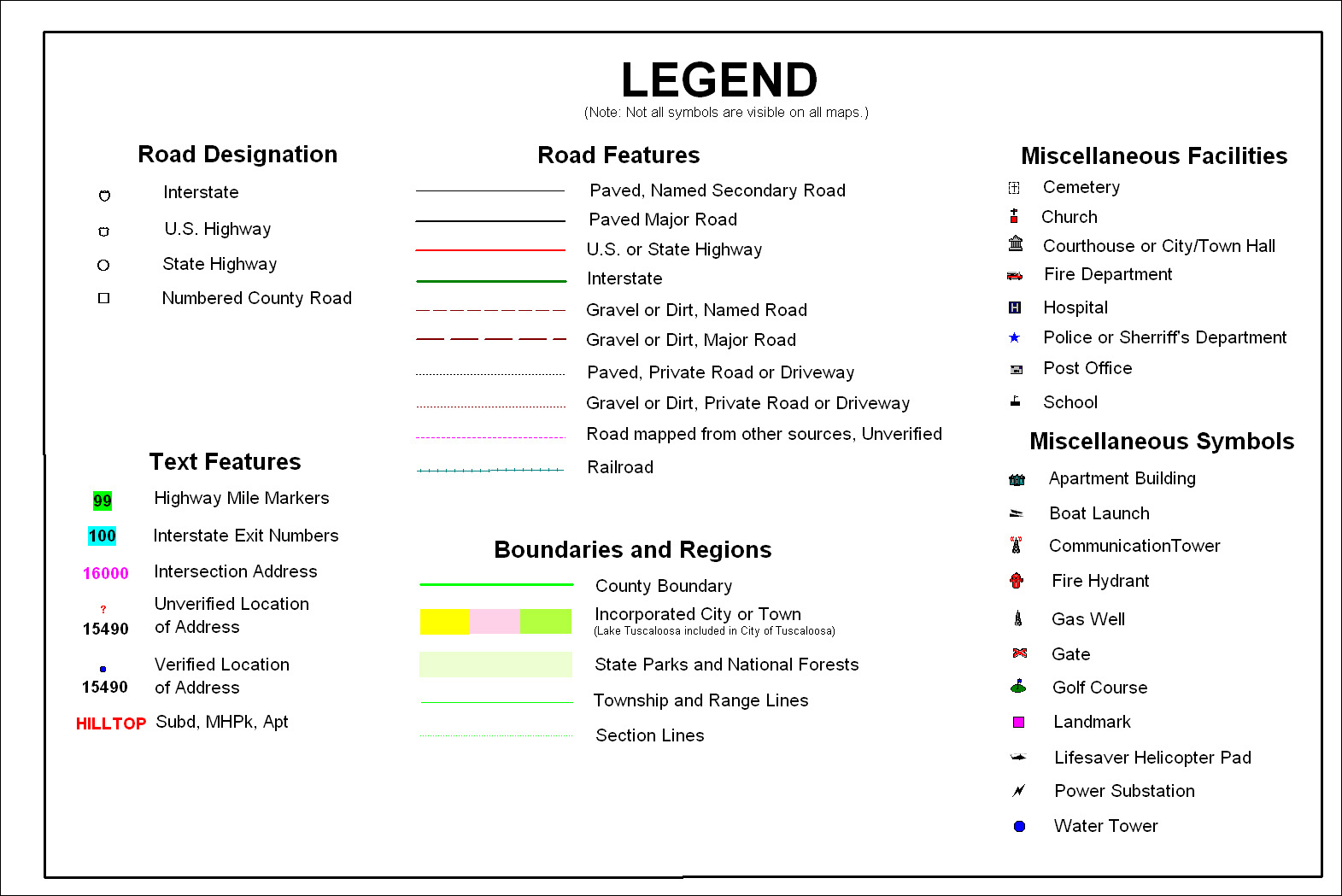
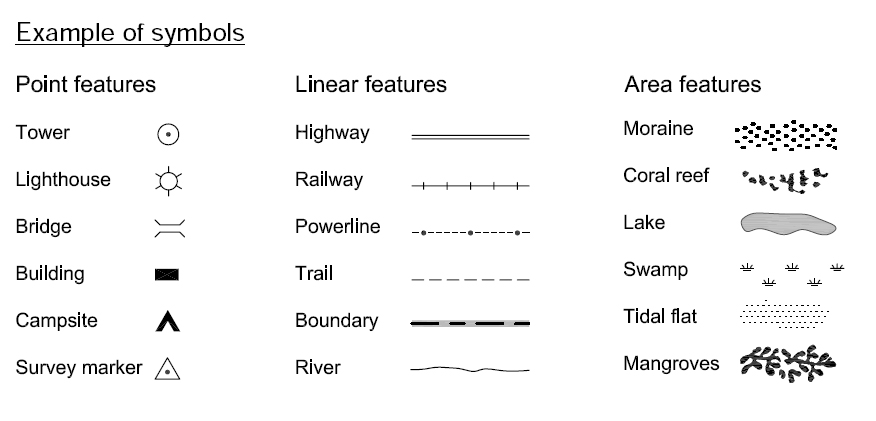
Dissecting the Components of a Map Legend:
A well-designed map legend typically comprises several key components:
- Symbol Key: This section directly links visual elements on the map with their corresponding real-world entities. For example, a road map might use a thin blue line to represent a highway and a thicker black line to indicate a local road.
- Color Palette: Maps often use colors to differentiate various features. The legend clarifies the meaning of each color. For instance, a topographical map might employ shades of green for different elevations, with darker shades signifying higher altitudes.
- Pattern Representation: Patterns, such as hatching or stippling, are frequently used to convey specific information on maps. The legend explains the meaning of each pattern. A geological map might use different hatching patterns to distinguish between various rock formations.
- Scale Bar: A scale bar provides a visual representation of the map’s scale, indicating the relationship between distances on the map and distances in the real world. This helps users accurately estimate distances between locations.
- North Arrow: A north arrow, often depicted as an arrow pointing upwards, indicates the direction of true north. This is essential for orienting the map and understanding directions.
Beyond the Basics: The Importance of a Well-Designed Legend:
The effectiveness of a map hinges on the clarity and comprehensiveness of its legend. A poorly designed legend can lead to confusion, misinterpretations, and ultimately, a flawed understanding of the information presented.
Here’s how a well-constructed legend contributes to effective map interpretation:
- Enhanced Clarity: A legend translates the visual language of the map into easily understandable information, making the map accessible to a wider audience.
- Reduced Ambiguity: By providing a clear explanation of symbols, colors, and patterns, the legend eliminates ambiguity and ensures consistent interpretation of the map’s data.
- Improved Accuracy: A comprehensive legend, including a scale bar and north arrow, enables accurate measurement of distances and determination of directions, fostering precise spatial analysis.
- Enhanced Accessibility: A well-designed legend ensures that maps can be readily understood by individuals with diverse backgrounds and levels of geographic knowledge.
The Evolution of Map Legends in the Digital Age:
The advent of digital maps and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has introduced new possibilities for map legends. Interactive legends, often displayed as pop-up windows, allow users to explore specific features in more detail. This interactivity enhances user engagement and facilitates deeper understanding.
FAQs about Map Legends:
Q: Why are map legends essential for understanding maps?
A: Map legends act as a translator between the map’s visual language and the reader’s understanding, making the map’s information accessible and interpretable.
Q: What are the key components of a map legend?
A: A typical map legend includes a symbol key, color palette, pattern representation, scale bar, and north arrow.
Q: How can a poorly designed legend affect map interpretation?
A: A poorly designed legend can lead to confusion, misinterpretations, and an inaccurate understanding of the map’s information.
Q: How have map legends evolved in the digital age?
A: Digital maps have introduced interactive legends that allow users to explore specific features in more detail, enhancing user engagement and understanding.
Tips for Creating Effective Map Legends:
- Keep it Simple and Concise: Avoid overly complex symbols and descriptions. Use clear and straightforward language.
- Use Consistent Terminology: Maintain consistency in the language used to describe features throughout the legend.
- Organize Information Logically: Arrange symbols, colors, and patterns in a logical order to facilitate easy reference.
- Consider Accessibility: Design the legend with clarity and readability in mind, ensuring it is accessible to individuals with diverse needs.
Conclusion:
Map legends are not mere ancillary elements; they are essential components that unlock the meaning and value of maps. By providing a clear and comprehensive translation of the map’s visual language, legends empower users to interpret data, make informed decisions, and navigate the complexities of our spatial world. As maps continue to evolve in the digital age, well-designed legends remain crucial for ensuring their accessibility, clarity, and impact.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Guide to Map Legends: Understanding the Key to Geographic Interpretation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!