The Power of Layering Information: Exploring Map Maker Overlays
Related Articles: The Power of Layering Information: Exploring Map Maker Overlays
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Layering Information: Exploring Map Maker Overlays. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Layering Information: Exploring Map Maker Overlays
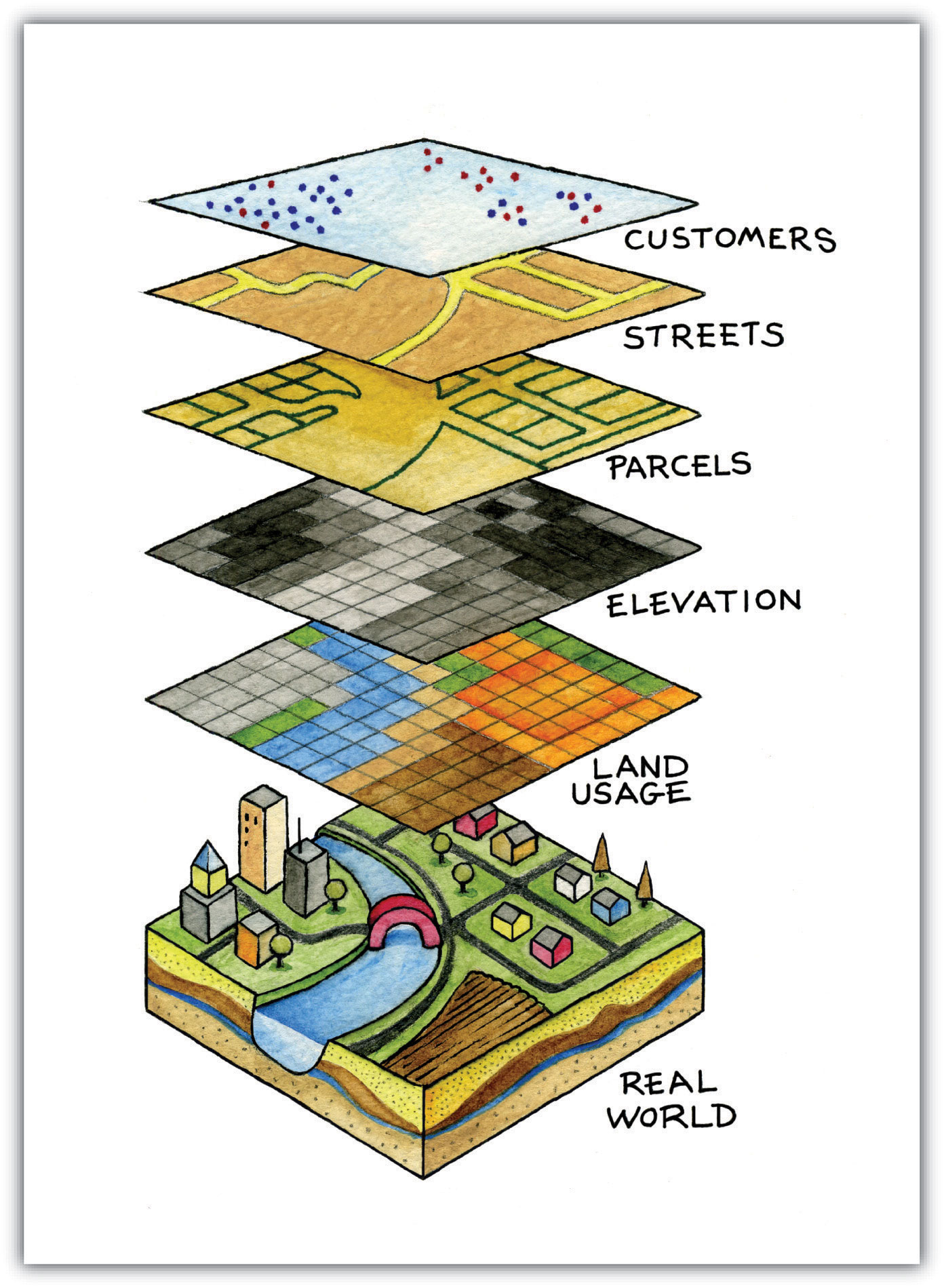
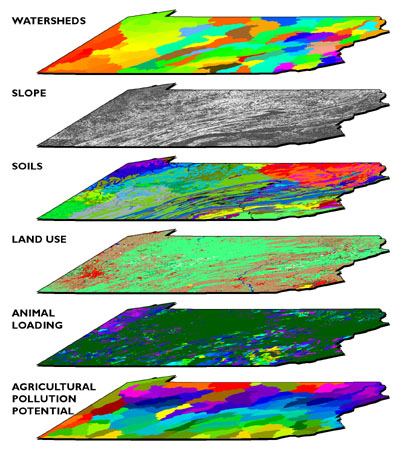
In the realm of cartography, the ability to overlay different layers of information onto a base map has revolutionized our understanding of the world. This practice, known as map maker overlay, empowers users to visualize complex data sets, analyze spatial relationships, and gain valuable insights from geographically referenced information.
Understanding the Concept of Map Maker Overlays
A map maker overlay, in its simplest form, is the process of adding one or more layers of data onto an existing map. These layers can represent various types of information, such as:
- Geographic Features: Road networks, rivers, lakes, buildings, land use patterns, and elevation contours.
- Demographic Data: Population density, income levels, age distribution, and ethnic composition.
- Environmental Data: Air quality, water pollution, soil fertility, and climate patterns.
- Infrastructure Data: Power lines, gas pipelines, communication networks, and transportation systems.
- Social Data: Crime rates, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and cultural landmarks.
The overlay process allows these layers to be superimposed on the base map, creating a composite view that reveals the spatial relationships between different data sets. This visual representation facilitates a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of various phenomena and provides a powerful tool for decision-making, planning, and research.
The Benefits of Utilizing Map Maker Overlays
The applications of map maker overlays are vast and extend across various disciplines. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced Visualization: Overlays provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize complex data sets, making it easier to understand spatial patterns and relationships.
- Improved Decision-Making: By overlaying relevant data layers, users can gain insights into potential risks, opportunities, and constraints, informing better decision-making in fields like urban planning, disaster management, and resource allocation.
- Data Analysis and Exploration: Overlays enable users to explore the spatial distribution of data, identify clusters and outliers, and uncover hidden trends and correlations.
- Communication and Collaboration: Overlays provide a common visual language for communicating spatial information, facilitating collaboration between stakeholders with diverse backgrounds and perspectives.
- Interactive Exploration: Modern mapping software allows for dynamic overlays, enabling users to interact with the data, zoom in and out, and select specific layers for analysis.
Types of Map Maker Overlays
Map maker overlays can be categorized based on the type of data they represent and the methods used for their creation. Some common types include:
- Geographic Feature Overlays: These overlays display geographic features like roads, buildings, and water bodies, providing context and spatial reference for other data layers.
- Thematic Overlays: These overlays represent specific themes or variables, such as population density, crime rates, or air pollution levels. They often use color gradients, symbols, or patterns to visually represent the data.
- Statistical Overlays: These overlays display statistical data, such as population estimates, economic indicators, or environmental measurements, using choropleth maps, dot density maps, or other cartographic techniques.
- Dynamic Overlays: These overlays are interactive and allow users to adjust the data layers, zoom in and out, and select specific areas for analysis. They are often used in web mapping applications and dashboards.
The Importance of Data Accuracy and Quality
The effectiveness of map maker overlays hinges on the accuracy and quality of the underlying data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading conclusions and flawed decision-making. Therefore, it is crucial to:
- Source data from reliable and reputable sources.
- Verify data accuracy and completeness.
- Apply appropriate data transformations and projections.
- Consider potential biases and limitations in the data.
Applications of Map Maker Overlays
Map maker overlays are widely used in various fields, including:
- Urban Planning: Overlaying population density, land use patterns, and infrastructure data helps planners understand urban growth patterns, identify potential development areas, and design efficient transportation systems.
- Disaster Management: Overlaying flood risk zones, evacuation routes, and population density data helps emergency responders plan evacuation strategies and allocate resources effectively.
- Environmental Monitoring: Overlaying air quality data, water pollution levels, and land use patterns helps environmental scientists monitor environmental changes, identify pollution sources, and develop mitigation strategies.
- Business and Marketing: Overlaying demographic data, consumer spending patterns, and business locations helps businesses identify target markets, optimize marketing campaigns, and choose optimal locations for new stores or offices.
- Education and Research: Overlaying historical data, climate data, and socioeconomic data helps researchers understand historical trends, analyze environmental changes, and explore social and economic factors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What software can I use to create map maker overlays?
A: There are numerous software options available for creating map maker overlays, ranging from free and open-source tools to professional-grade applications. Some popular choices include:
- QGIS: A free and open-source geographic information system (GIS) software.
- ArcGIS: A professional-grade GIS software suite offered by Esri.
- Google Earth Pro: A desktop application that allows users to view and analyze satellite imagery and create overlays.
- Mapbox Studio: A web-based platform for creating and publishing custom maps with overlays.
Q: What are the limitations of map maker overlays?
A: While map maker overlays offer powerful capabilities, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations:
- Data availability: The effectiveness of overlays depends on the availability of accurate and relevant data.
- Data accuracy: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading conclusions.
- Data visualization: Overlays can sometimes be visually cluttered, making it difficult to interpret complex data sets.
- Technical expertise: Creating and analyzing overlays may require some technical expertise in GIS software and data management.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Maker Overlays
- Clearly define the purpose of the overlay.
- Choose the appropriate data layers based on the objective.
- Use clear and consistent symbology and legends.
- Consider the audience and their level of understanding.
- Provide context and explanations for the data presented.
- Use interactive elements and tools to enhance user engagement.
Conclusion
Map maker overlays have emerged as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, offering valuable insights across various disciplines. By layering information on a base map, users can gain a deeper understanding of the world around them, make informed decisions, and facilitate collaboration and communication. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and versatile map maker overlay tools to emerge, further expanding the possibilities for spatial data exploration and analysis.


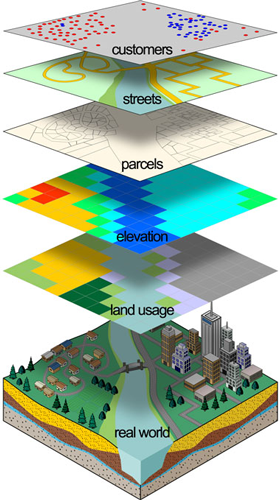


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Layering Information: Exploring Map Maker Overlays. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!