The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend
Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of the world around us, rely on a powerful yet often overlooked element: the legend. While the map itself provides a visual representation of geographic features, the legend acts as the crucial key to unlocking its meaning. It is the Rosetta Stone of cartography, translating the visual language of the map into a comprehensible narrative.
The Essence of a Map Legend
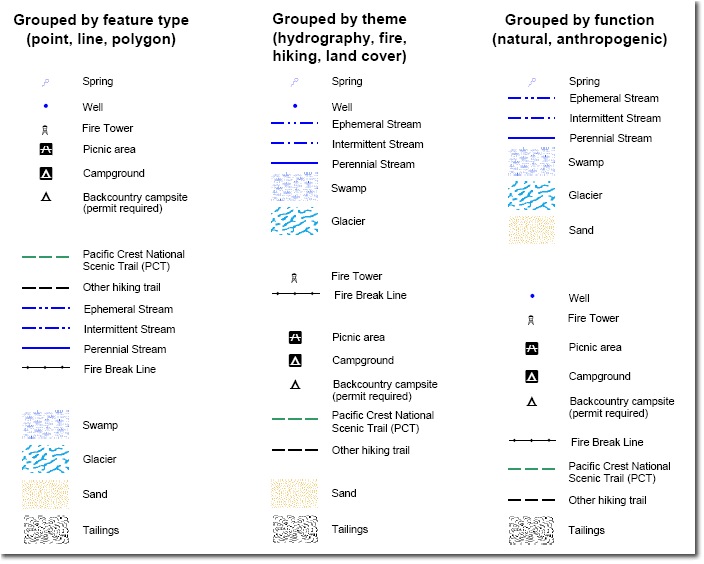
The map legend, also known as the map key, is a table or box typically located on the edge or corner of a map, containing a collection of symbols, patterns, colors, and accompanying text. These elements serve as visual and textual guides, explaining the meaning of each symbol used on the map. For instance, a blue line on a map might represent a river, but without a legend, the viewer would be left to guess. The legend clarifies that the blue line signifies a river, and possibly even provides additional information, such as the river’s name or width.
Benefits of a Clear and Comprehensive Map Legend
A well-crafted map legend is not merely a decorative afterthought; it is a vital component that significantly enhances the map’s usability and effectiveness. Its benefits are multifaceted:
- Clarity and Understanding: A clear legend removes ambiguity, ensuring that the map’s information is readily understood by the viewer. It eliminates guesswork and allows for accurate interpretation of the map’s data.
- Accessibility: The legend makes maps accessible to a wider audience, including those unfamiliar with cartographic conventions. It acts as a bridge between the visual representation and the viewer’s comprehension.
- Enhanced Communication: A comprehensive legend allows the map to communicate a wealth of information concisely and effectively. It conveys not just the location of features but also their attributes, such as elevation, population density, or land use.
- Data Visualization: The legend facilitates the visualization of complex data, transforming abstract information into a visually compelling narrative. It allows for the identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within the mapped data.
- Efficiency: A well-designed legend saves time and effort, enabling viewers to quickly and efficiently extract the information they need from the map. It avoids the need for extensive research or interpretation, streamlining the mapping experience.
Components of a Map Legend
A map legend typically comprises the following elements:
- Symbols: These are visual representations of features on the map, such as dots for cities, lines for roads, or shaded areas for forests. The legend clearly shows the symbol and its corresponding meaning.
- Colors: Colors are often used to distinguish different features on the map. The legend specifies the color used for each feature, enhancing visual clarity and organization.
- Patterns: Patterns, such as hatching or stippling, are used to differentiate between features that share the same color. The legend provides a clear representation of each pattern and its corresponding meaning.
- Text: Accompanying text provides additional information about each symbol, color, or pattern. This may include the name of the feature, its classification, or specific data values.
- Scale: The legend often includes the map’s scale, indicating the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. This is crucial for accurate interpretation of distances and areas.
- North Arrow: While not always present, a north arrow indicates the direction of north on the map, aiding in orientation and understanding the map’s layout.
Types of Map Legends
Map legends can be classified into various types, depending on the complexity of the map and the information it conveys:
- Simple Legends: These are commonly found on basic maps, containing a limited number of symbols and concise explanations. They are suitable for maps with few features and straightforward information.
- Comprehensive Legends: These are used for more complex maps, containing a wider range of symbols, colors, patterns, and detailed text. They are essential for maps with multiple layers of information and intricate data representations.
- Hierarchical Legends: These legends organize information into a hierarchy, often using a tree-like structure to group related symbols or data categories. This approach enhances clarity and facilitates easy navigation within the legend.
- Interactive Legends: These legends are typically found in digital maps and allow users to interact with the legend, selecting specific symbols or categories to filter or highlight information on the map. This provides a dynamic and interactive mapping experience.
Crafting an Effective Map Legend
Creating a compelling and informative map legend requires careful consideration of the following factors:
- Target Audience: The legend should be tailored to the intended audience, considering their level of understanding and familiarity with cartographic conventions.
- Map Content: The legend should accurately reflect the information presented on the map, ensuring that all symbols, colors, and patterns are clearly defined and explained.
- Visual Clarity: The legend should be visually appealing and easy to navigate. Use clear fonts, contrasting colors, and well-organized layouts to enhance readability.
- Conciseness: The legend should be concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary jargon or excessive text. Use clear and straightforward language that is easily understood by the target audience.
- Accessibility: The legend should be accessible to individuals with disabilities, considering factors like color contrast, font size, and alternative formats.
FAQs about Map Legends
1. Why is a map legend important?
A map legend is crucial for understanding the information presented on a map. It translates the visual language of the map into a comprehensible narrative, removing ambiguity and ensuring accurate interpretation of the data.
2. What should a map legend include?
A map legend should include symbols, colors, patterns, accompanying text, scale, and a north arrow (if applicable). These elements provide a clear and comprehensive guide to the map’s content.
3. How do I choose the right symbols for my map legend?
Choose symbols that are visually distinct, easily recognizable, and relevant to the features they represent. Consider using standardized symbols whenever possible to ensure consistency and ease of understanding.
4. How can I make my map legend more visually appealing?
Use clear fonts, contrasting colors, and well-organized layouts to enhance readability. Consider using graphics or icons to make the legend more engaging.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a map legend?
Avoid using too many symbols, colors, or patterns. Ensure that the legend is concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary jargon or excessive text.
Tips for Creating Effective Map Legends
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overwhelming the viewer with too much information. Start with the essential elements and add complexity as needed.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid technical jargon or overly complex wording. Use straightforward language that is easily understood by the target audience.
- Prioritize Visual Clarity: Use clear fonts, contrasting colors, and well-organized layouts to enhance readability.
- Emphasize Key Features: Highlight important features by using larger symbols, bolder fonts, or brighter colors.
- Consider Accessibility: Ensure that the legend is accessible to individuals with disabilities, considering factors like color contrast, font size, and alternative formats.
Conclusion
The map legend, though often overlooked, plays a pivotal role in unlocking the meaning and utility of maps. It acts as a bridge between the visual representation and the viewer’s comprehension, ensuring that the map’s information is readily understood and effectively communicated. By understanding the importance of the legend and crafting it with care, mapmakers can create powerful and accessible tools for exploration, analysis, and communication.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!