The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend
Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend

Maps are visual representations of the world, a powerful tool for navigation, exploration, and understanding spatial relationships. Yet, without a key to unlock their meaning, these intricate representations remain silent. This key, often overlooked but undeniably crucial, is the map legend, a fundamental element that translates the map’s symbols and visual language into comprehensible information.
The map legend, also known as the map key, serves as a glossary, providing a comprehensive guide to the map’s visual elements. It acts as a bridge between the abstract symbols and the real-world features they represent, ensuring accurate interpretation and understanding of the map’s content.
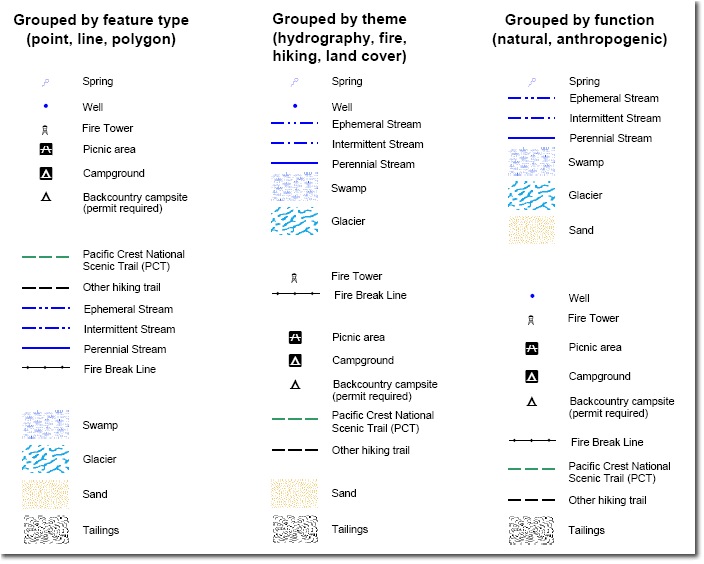
Understanding the Structure of a Map Legend
A map legend typically consists of two main components:
- Symbols: These are the visual representations used on the map to depict different features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, or geographical boundaries. They can take various forms, including lines, shapes, colors, patterns, or icons.
- Explanations: Each symbol is accompanied by a corresponding explanation, defining its meaning and the real-world feature it represents. This explanation may include text descriptions, numerical values, or specific classifications.
The arrangement of the legend can vary depending on the map’s purpose and design. However, it is generally placed in a clear and prominent location, often within the map’s margin or in a dedicated panel.
The Importance of Map Legends: A Crucial Bridge Between Visuals and Meaning
The map legend plays a vital role in ensuring the map’s effectiveness and its ability to communicate information accurately. Its importance can be summarized as follows:
- Clarity and Understanding: The legend provides a clear and concise explanation of the map’s visual language, eliminating ambiguity and facilitating accurate interpretation of the depicted features.
- Accessibility: The legend makes the map accessible to a wider audience, including those unfamiliar with the map’s specific symbols or conventions.
- Data Interpretation: The legend allows for the accurate interpretation of the data presented on the map, enabling users to draw meaningful conclusions and insights.
- Efficiency: The legend streamlines the map reading process, saving time and effort by eliminating the need to constantly refer to external sources for symbol definitions.
- Standardization: The use of consistent and standardized symbols within a legend promotes clarity and consistency across different maps, facilitating cross-referencing and comparisons.
Types of Map Legends: Tailoring Information to the Purpose
Map legends can be categorized based on their structure, content, and purpose. Some common types include:
- Textual Legends: These legends primarily rely on text descriptions to define the symbols. They are commonly used in maps with a limited number of symbols and simple features.
- Symbolic Legends: These legends utilize a combination of symbols and concise text explanations. They are suitable for maps with a wider range of symbols and more complex features.
- Hierarchical Legends: These legends organize symbols based on their hierarchy or classification, often using nested categories or sub-legends. They are effective for maps with a large number of symbols or complex data sets.
- Color Legends: These legends utilize color variations to represent different data values or categories. They are commonly used in thematic maps that focus on specific variables or distributions.
- Scale Legends: These legends depict the relationship between the map’s scale and the real-world distances. They are essential for maps that require accurate measurements or spatial analysis.
Beyond the Basic: Enhancing the Effectiveness of Map Legends
While a basic map legend fulfills its primary function of symbol definition, incorporating additional elements can enhance its effectiveness and user experience:
- Descriptive Text: Providing additional descriptive text for each symbol can offer further context and clarify the specific characteristics of the feature represented.
- Examples: Including visual examples of the symbols in context can further clarify their meaning and application.
- Visual Hierarchy: Employing visual hierarchy techniques, such as font size, color contrast, or symbol size, can emphasize key elements and guide the user’s attention.
- Interactive Legends: In digital maps, interactive legends can allow users to explore the map’s data in a dynamic and interactive way, providing deeper insights and analysis.
- Accessibility Features: Designing legends with accessibility features, such as high-contrast colors, alternative text descriptions, or auditory cues, ensures inclusivity and accessibility for all users.
FAQs about Map Legends
Q: What is the difference between a map legend and a map key?
A: While the terms "map legend" and "map key" are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle distinction. A map legend is a more comprehensive guide that includes all the symbols and their explanations, while a map key might focus on a specific subset of symbols or features.
Q: Are map legends necessary for all maps?
A: Yes, map legends are essential for all maps, regardless of their complexity or purpose. They ensure clarity, accuracy, and accessibility, making the map’s information readily understandable.
Q: Can a map legend be too detailed?
A: While a comprehensive legend is beneficial, an overly detailed one can become overwhelming and hinder readability. The level of detail should be tailored to the map’s purpose and target audience.
Q: How can I create an effective map legend?
A: Creating an effective map legend involves considering the following factors:
- Clarity: Use clear and concise language to explain symbols.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in the use of symbols and their explanations throughout the map.
- Visual Hierarchy: Employ visual techniques to emphasize key elements and guide the user’s attention.
- Accessibility: Consider accessibility features to ensure inclusivity.
Tips for Effective Map Legend Design
- Keep it Concise: Avoid lengthy or overly complex explanations.
- Use Consistent Font and Colors: Maintain consistency in the font style and color scheme for a cohesive look.
- Prioritize Key Elements: Highlight important symbols or features using visual hierarchy techniques.
- Test Readability: Ensure the legend is easy to read and understand, even for those unfamiliar with the map’s specific conventions.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Cartographic Communication
The map legend, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in unlocking the meaning of maps and ensuring their effective communication. By providing a clear and concise translation of the map’s visual language, the legend enables accurate interpretation, accessibility, and efficient understanding of the information presented. As cartography continues to evolve and integrate new technologies, the map legend remains a fundamental element, ensuring that maps continue to be powerful tools for exploration, navigation, and understanding the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unsung Hero of Cartography: Deciphering the Map Legend. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!