Understanding the Power of Horizontal Legends in Thematic Mapping
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Horizontal Legends in Thematic Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Horizontal Legends in Thematic Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Horizontal Legends in Thematic Mapping

Thematic maps, often used to depict spatial patterns and distributions of data, rely heavily on legends to effectively communicate information to viewers. These legends act as keys, translating the visual symbols used on the map into meaningful data representations. While traditional legends are typically positioned vertically, a horizontal legend offers a distinct approach with unique advantages, particularly in the realm of data visualization and map readability.
The Significance of Horizontal Legends
Horizontal legends, as opposed to their vertical counterparts, present map symbols and their corresponding data values in a linear, left-to-right arrangement. This horizontal orientation offers a number of benefits:
-
Enhanced Readability: A horizontal legend naturally aligns with the typical reading direction in most languages, making it easier for viewers to quickly grasp the legend’s content. This is especially crucial when dealing with complex maps featuring numerous categories or data ranges.
-
Efficient Space Utilization: Horizontal legends can effectively utilize the available map space, particularly in situations where vertical space is limited, such as in narrow map layouts or when incorporating other map elements. This optimizes map design, ensuring that the legend does not overshadow other important features.
-
Improved Visual Flow: By extending horizontally, a legend can seamlessly integrate with the map’s visual flow, creating a more cohesive and aesthetically pleasing composition. This smooth transition between map and legend enhances the overall visual experience, guiding the viewer’s attention through the map’s information.
-
Flexibility in Placement: Horizontal legends offer greater flexibility in placement. They can be positioned at the top, bottom, or even within the map itself, allowing for optimal integration with the map’s design and the surrounding context. This adaptability enables mapmakers to tailor the legend’s placement based on specific map requirements and visual preferences.
-
Clarity in Data Interpretation: The horizontal arrangement of symbols and values fosters a more linear and intuitive understanding of the data. This clarity is particularly beneficial when dealing with continuous data, such as temperature or precipitation, where the gradual progression of values is readily apparent in the horizontal layout.
Applications of Horizontal Legends
Horizontal legends find widespread applications in diverse fields, including:
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): In GIS applications, where data visualization plays a crucial role, horizontal legends enhance the clarity and readability of thematic maps, facilitating data analysis and interpretation.
-
Cartography: Cartographers utilize horizontal legends to create visually appealing and informative maps, ensuring that the legend seamlessly complements the map’s design and effectively communicates the intended message.
-
Data Visualization: Beyond maps, horizontal legends can be employed in various data visualization tools, such as charts and graphs, to enhance the presentation and understanding of data trends and patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: When is it most appropriate to use a horizontal legend?
A: Horizontal legends are particularly suitable for maps featuring a large number of categories or data ranges, maps with limited vertical space, and maps where a linear, left-to-right flow of information is desired.
Q: Are there any disadvantages to using a horizontal legend?
A: While horizontal legends offer numerous advantages, they can become less effective when dealing with a limited number of categories or data ranges, where a vertical legend might be more concise and efficient.
Q: How can I effectively design a horizontal legend?
A: When designing a horizontal legend, ensure that the symbols are visually distinct, the text labels are clear and concise, and the overall arrangement is logical and easy to follow. Consider using color coding, spacing, and font size to enhance readability and visual appeal.
Tips for Creating Effective Horizontal Legends
-
Choose Appropriate Symbols: Select symbols that are visually distinct and easily recognizable, ensuring that they accurately represent the data categories or ranges.
-
Use Clear and Concise Labels: Provide concise and descriptive labels for each symbol, clearly indicating the corresponding data values or categories.
-
Maintain Consistent Spacing: Ensure consistent spacing between symbols and labels to maintain visual balance and clarity.
-
Utilize Color Coding: Employ color coding effectively to enhance visual distinction and guide the viewer’s attention to specific categories or data ranges.
-
Consider Font Size and Style: Choose a font size and style that is legible and complements the overall map design.
Conclusion
Horizontal legends offer a valuable alternative to traditional vertical legends, providing a distinct approach to data visualization with numerous advantages. By leveraging the benefits of horizontal orientation, mapmakers can create more readable, visually appealing, and informative maps, enhancing the communication and interpretation of spatial data. Understanding the power of horizontal legends empowers map creators to effectively convey information and engage viewers in the exploration of geographic patterns and trends.


![[Solved] Side by side horizontal legends in in ggplot2 9to5Answer](https://i.stack.imgur.com/fm1hx.png)
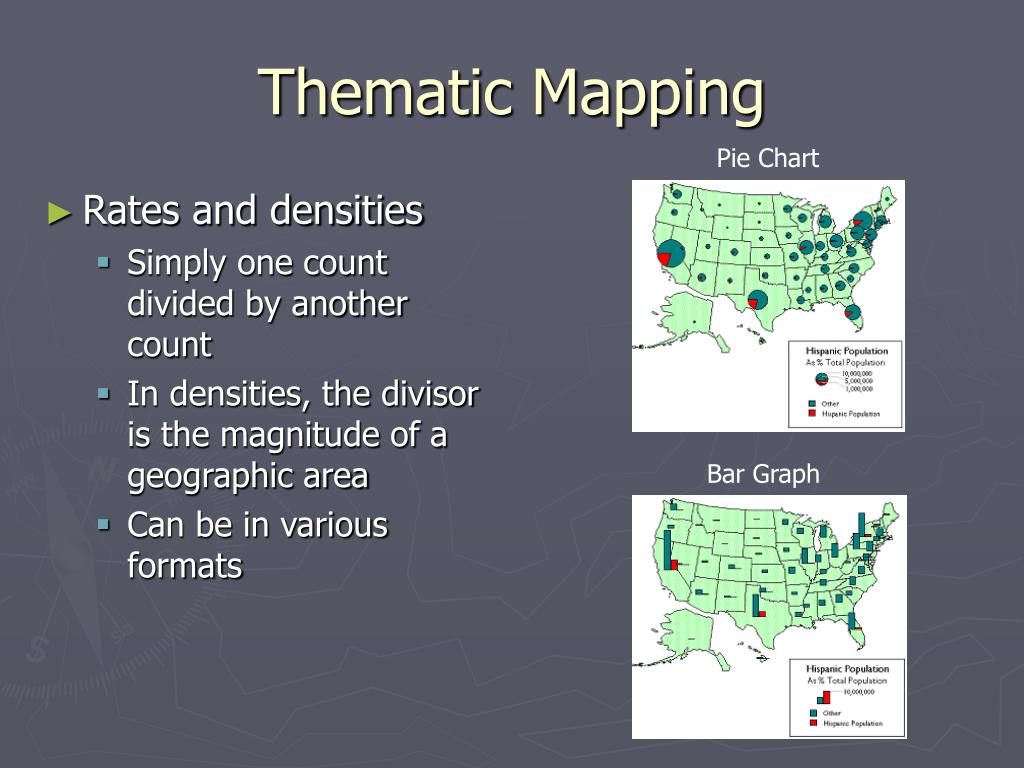
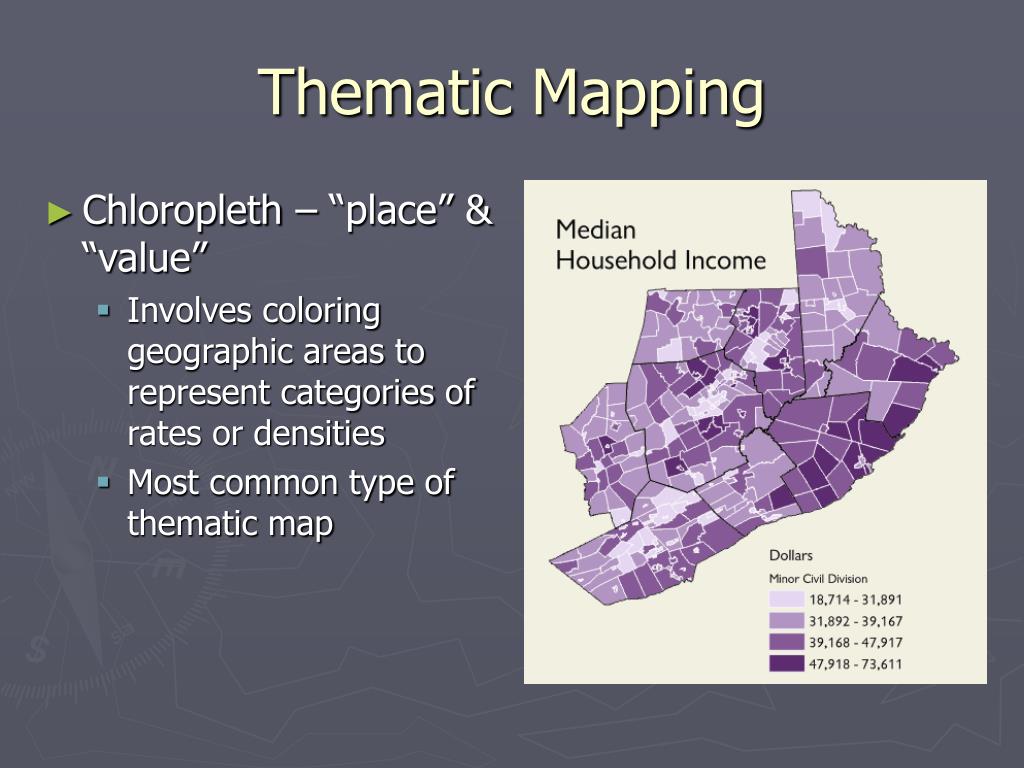

![[example] multi-line horizontal legend](https://shots.codepen.io/etpinard/pen/pbQrQK-800.jpg?version=1470675539)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Horizontal Legends in Thematic Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!