Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to the Physical Map of the Philippines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to the Physical Map of the Philippines
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to the Physical Map of the Philippines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to the Physical Map of the Philippines

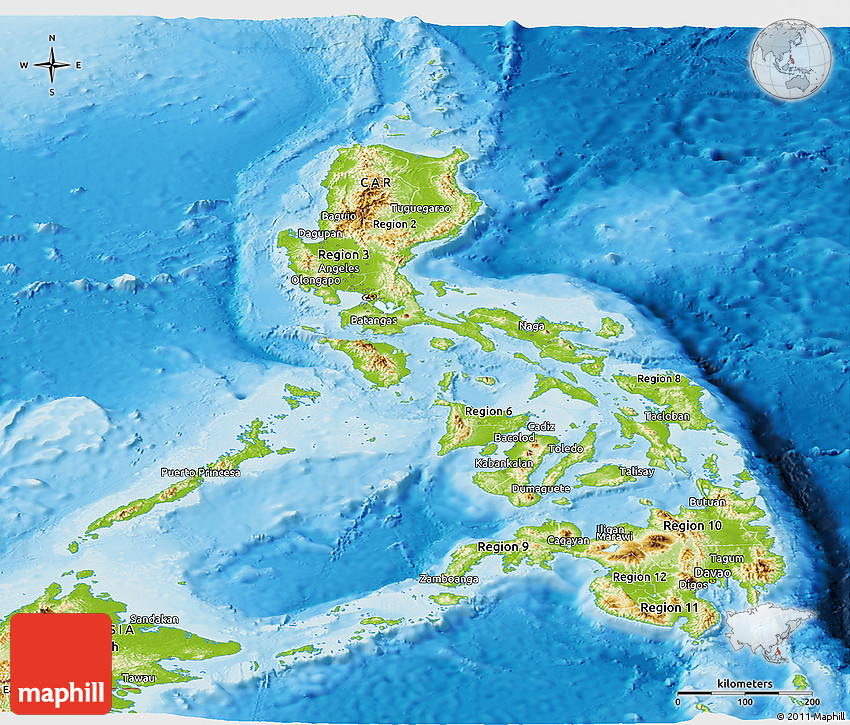
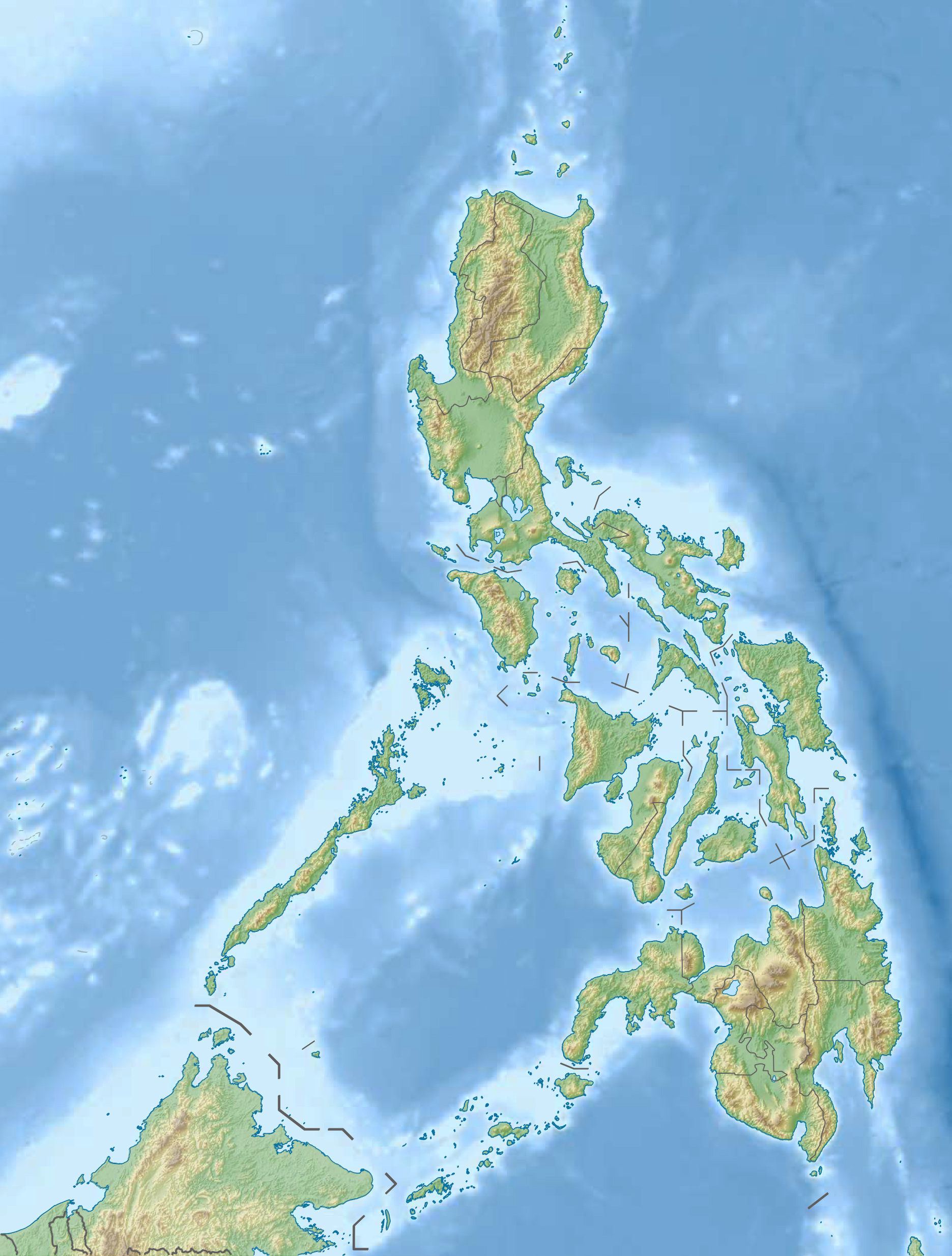
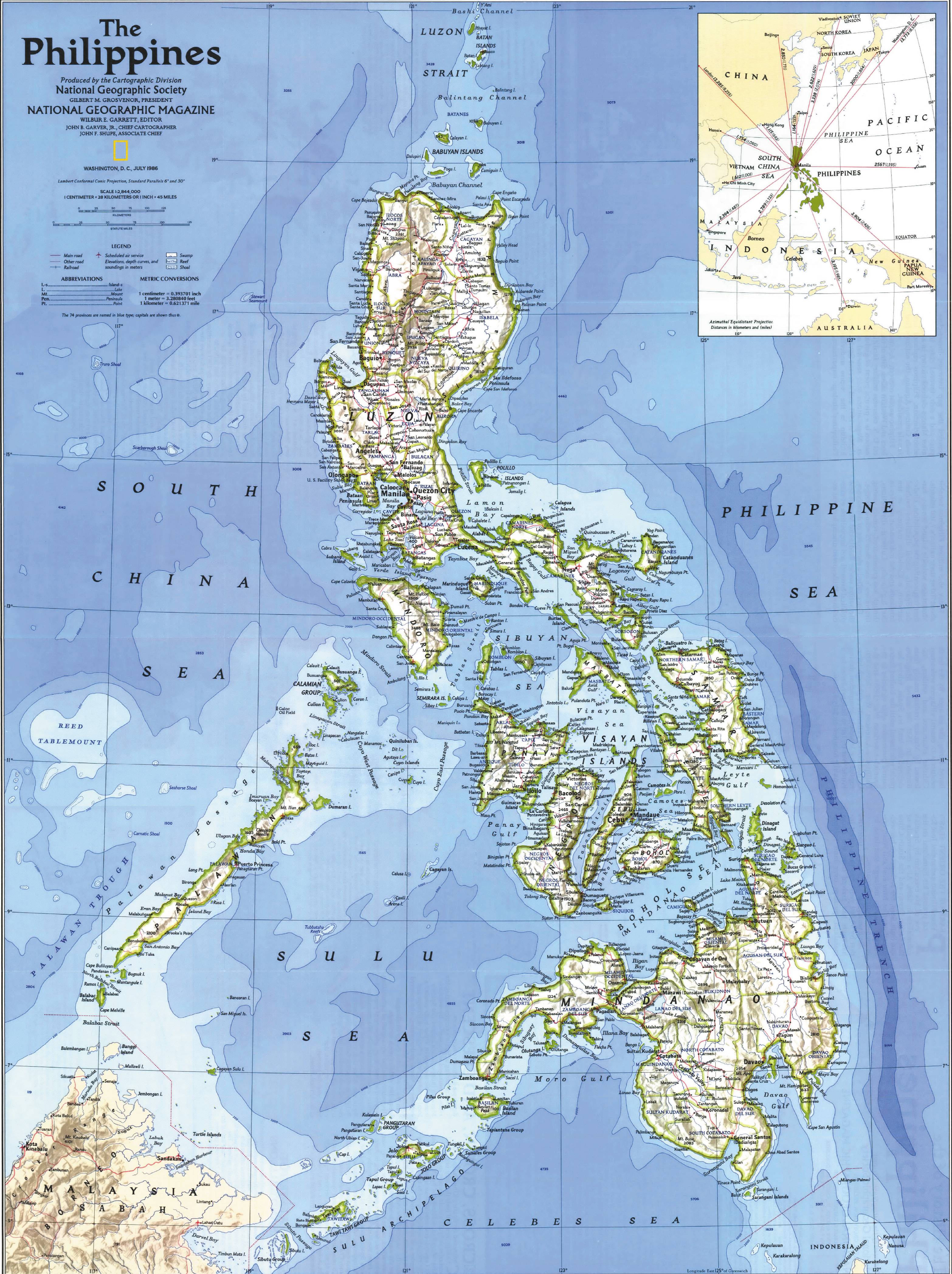
The Philippines, an archipelago of over 7,000 islands scattered across the western Pacific Ocean, boasts a diverse and captivating landscape. Its geography, shaped by volcanic activity, tectonic shifts, and the relentless forces of nature, has profoundly influenced its history, culture, and development. A physical map, with its intricate details and accompanying legend, serves as an invaluable tool for understanding the country’s remarkable terrain.
Understanding the Topography: A Visual Journey
A physical map of the Philippines reveals a complex tapestry of landforms. Its primary features include:
-
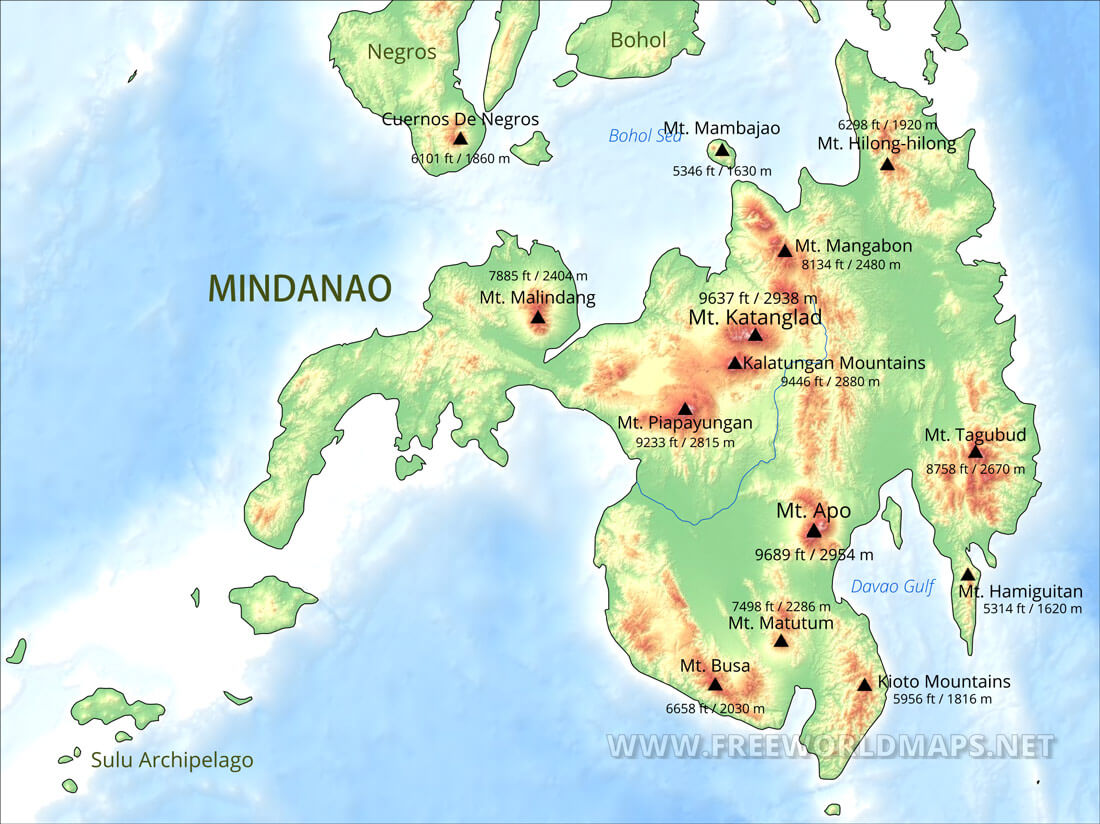
Mountains: The Philippines is home to numerous mountain ranges, a testament to its volcanic past. The Cordillera Central, running through Luzon, is the most prominent, housing the country’s highest peak, Mount Apo. Other significant ranges include the Zambales Mountains, the Sierra Madre, and the Caraballo Mountains. These mountainous areas are often densely forested and serve as important watersheds.
-
Volcanoes: The Philippines sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region known for its intense seismic and volcanic activity. This has resulted in the formation of numerous volcanoes, some dormant, others active. Notable volcanoes include Mount Mayon, known for its near-perfect conical shape, and Taal Volcano, a picturesque caldera lake. Volcanic soils are highly fertile, contributing to the agricultural richness of the country.
-
Plains and Valleys: Interwoven between the mountains and hills are fertile plains and valleys, providing essential agricultural land. The Central Luzon Plain, the largest in the country, is a prime example, supporting a wide range of crops and livestock. These plains are also heavily populated, serving as important centers of commerce and industry.
-
Rivers and Lakes: A network of rivers and lakes crisscrosses the archipelago, playing a vital role in transportation, irrigation, and hydropower generation. The Cagayan River, the longest in the Philippines, flows through the northern part of Luzon. Lake Taal, nestled within a volcanic caldera, is one of the most famous lakes, attracting tourists with its stunning beauty.
-
Coastlines and Islands: The Philippines boasts a vast coastline, with numerous islands and peninsulas. The islands are diverse in size and shape, ranging from small islets to large landmasses. This unique geography has influenced the country’s maritime culture, with fishing and trade playing crucial roles in its history and economy.
Decoding the Legend: Key to Understanding the Map
The legend accompanying a physical map of the Philippines provides a vital key to understanding its features. It typically includes:
-
Elevation: The legend often utilizes color gradients to represent different elevation levels, ranging from sea level to the highest peaks. This allows for a visual interpretation of the country’s topography, highlighting the areas of high and low altitude.
-
Land Cover: Different land cover types are represented through symbols or colors. Forests, grasslands, wetlands, and urban areas are typically depicted, providing insights into the distribution of vegetation and human settlements.
-
Water Bodies: Rivers, lakes, and seas are typically shown in blue, with different shades indicating depth or size. This helps in understanding the hydrological network and its significance.
-
Political Boundaries: Provincial and regional boundaries are often marked on physical maps, providing a framework for understanding the country’s administrative divisions.
-
Symbols and Icons: Specific symbols or icons may be used to represent important features like cities, airports, national parks, and historical sites. These icons provide additional context and information about the location and significance of these places.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Understanding the Physical Landscape
A physical map, with its legend, is more than just a visual representation of the Philippines’ geography. It offers a powerful tool for understanding:
-
Resource Distribution: The map reveals the distribution of natural resources, including fertile land, water bodies, and mineral deposits. This knowledge is crucial for planning sustainable development and resource management.
-
Disaster Risk Assessment: The map highlights areas prone to natural disasters like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and typhoons. This information is vital for developing disaster preparedness strategies and mitigating risks.
-
Infrastructure Development: Understanding the topography and land cover helps in planning infrastructure development projects like roads, bridges, and dams. It ensures efficient and sustainable construction and minimizes environmental impact.
-
Environmental Protection: The map provides insights into the distribution of ecosystems and biodiversity. This knowledge is essential for developing conservation strategies and protecting the country’s rich natural heritage.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The map reveals the diverse landscape, highlighting areas of natural beauty and historical significance. This information is valuable for promoting tourism and providing recreational opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the highest peak in the Philippines?
A: The highest peak in the Philippines is Mount Apo, located in the Cordillera Central, with an elevation of 2,954 meters (9,692 feet).
Q: How many volcanoes are there in the Philippines?
A: The Philippines has over 200 volcanoes, with 22 considered active.
Q: What is the largest island in the Philippines?
A: Luzon is the largest island in the Philippines, followed by Mindanao and Visayas.
Q: What is the significance of the Pacific Ring of Fire?
A: The Pacific Ring of Fire is a region of intense seismic and volcanic activity, encompassing the Philippines. It is characterized by frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions due to the convergence of tectonic plates.
Tips for Utilizing the Physical Map of the Philippines:
- Study the legend carefully: Understand the symbols, colors, and icons used to represent different features.
- Use a ruler or scale: Measure distances and estimate areas accurately.
- Compare different maps: Combine information from physical maps with other types like political or thematic maps for a comprehensive understanding.
- Engage in interactive mapping tools: Utilize online platforms that provide interactive maps with detailed information and data layers.
- Connect the map to real-world experiences: Visit places shown on the map to gain a deeper understanding of the country’s geography and its impact on human life.
Conclusion:
The physical map of the Philippines, with its accompanying legend, serves as a valuable tool for understanding the country’s diverse and fascinating landscape. It reveals the intricate interplay of mountains, volcanoes, plains, rivers, and islands, highlighting the profound influence of geography on its history, culture, and development. By carefully studying the map and its legend, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the Philippines’ unique terrain and its importance in shaping the lives of its people.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to the Physical Map of the Philippines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!