Unveiling Geographic Data with Power BI Filled Maps: A Guide to Legend and Gradient Visualization
Related Articles: Unveiling Geographic Data with Power BI Filled Maps: A Guide to Legend and Gradient Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Geographic Data with Power BI Filled Maps: A Guide to Legend and Gradient Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Geographic Data with Power BI Filled Maps: A Guide to Legend and Gradient Visualization
Power BI, a renowned business intelligence tool, empowers users to transform raw data into insightful visualizations. Among its versatile offerings, filled maps stand out as a powerful means of representing geographic data, enabling users to understand spatial patterns and trends at a glance. This article delves into the intricacies of creating compelling filled maps in Power BI, focusing on the crucial elements of legends and gradients.
Understanding Filled Maps
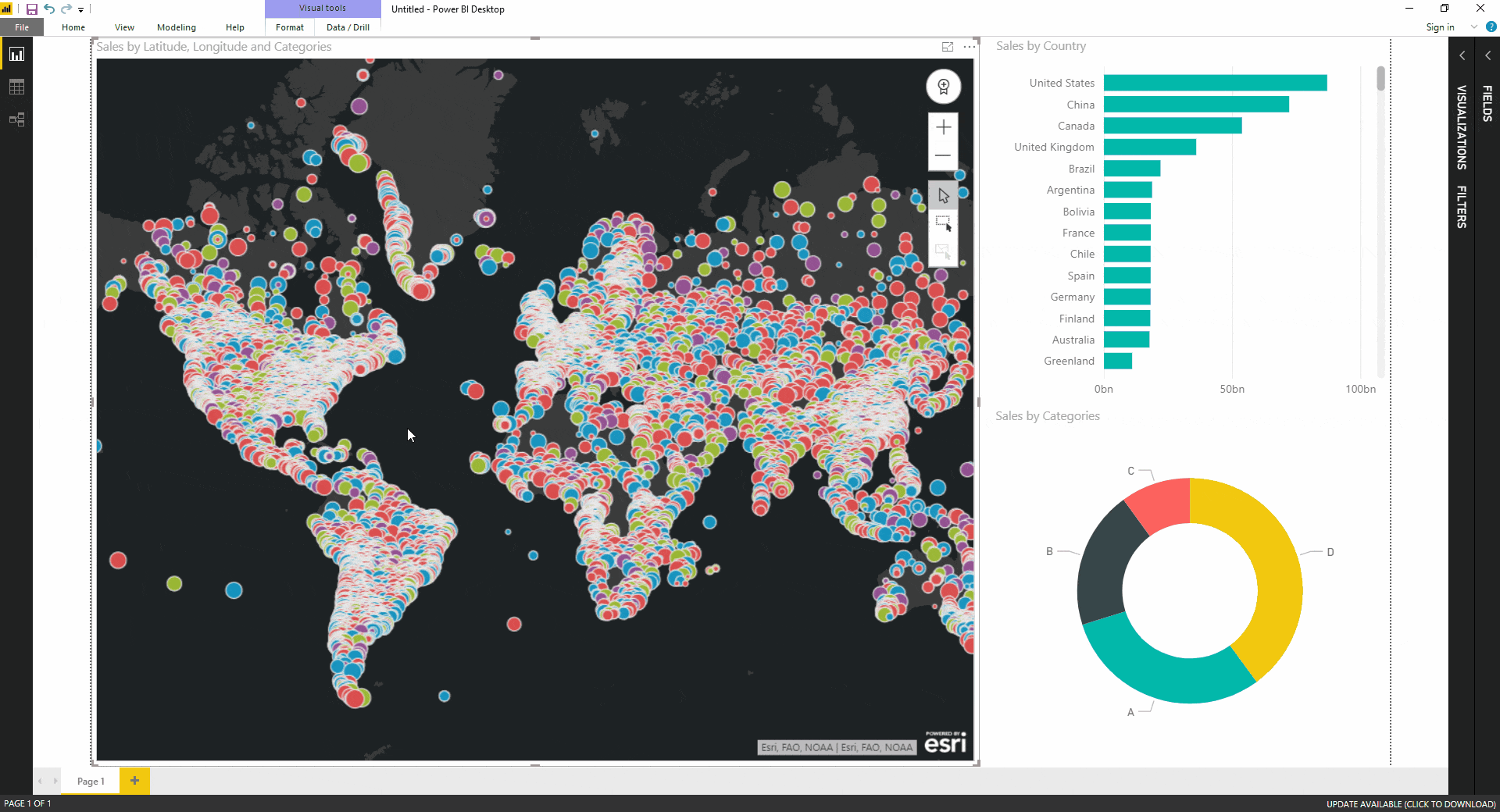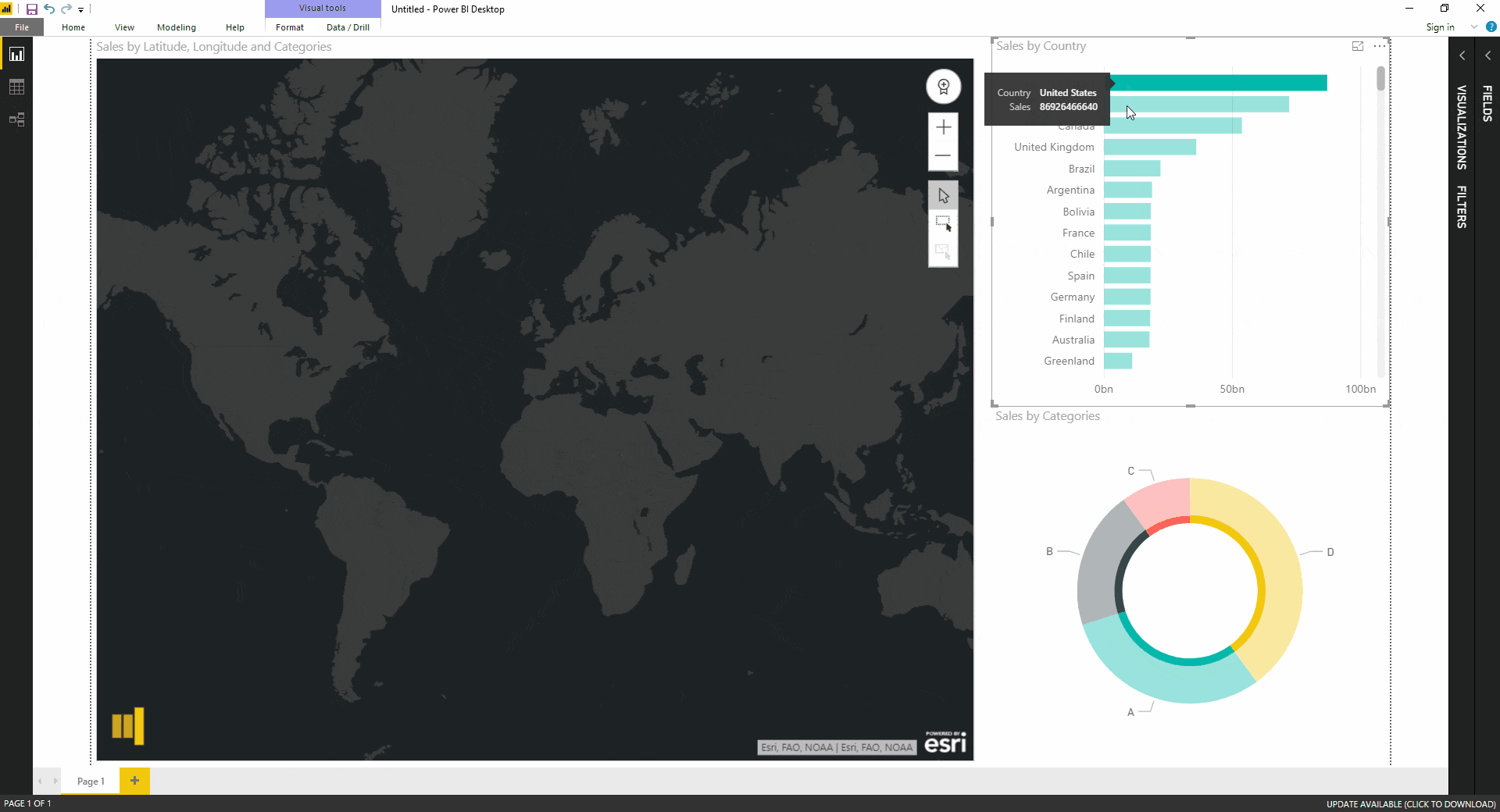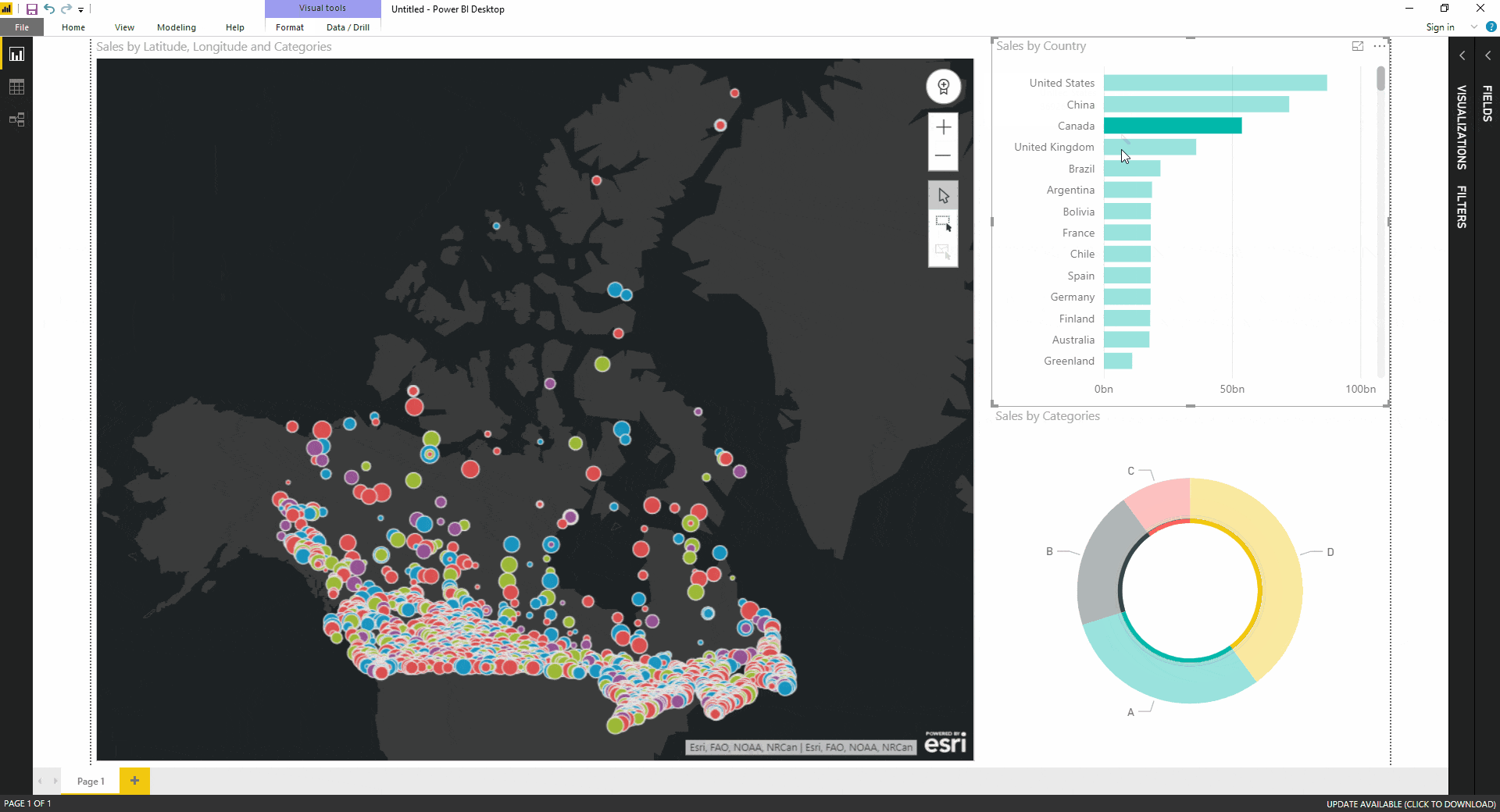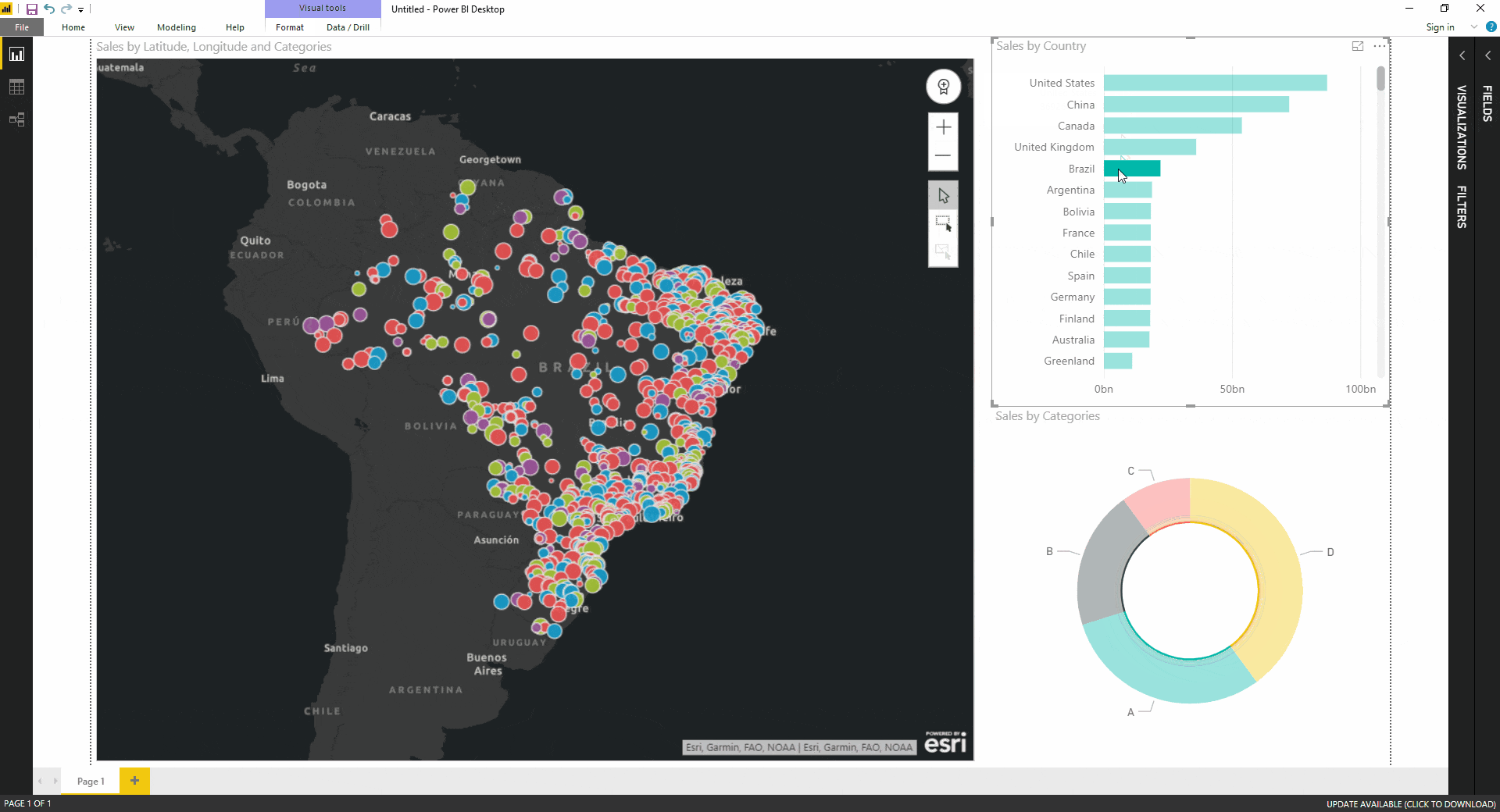
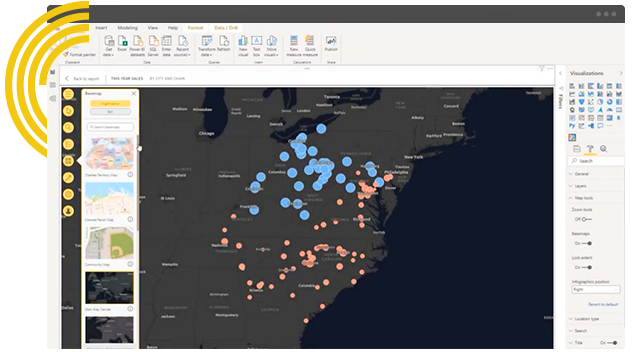
Filled maps, also known as choropleth maps, utilize color gradients to depict data values across geographic regions. Each region is assigned a color based on its corresponding data value, with darker shades typically representing higher values and lighter shades representing lower values. This visual representation allows for immediate identification of areas with high or low data concentrations, facilitating data exploration and analysis.
The Role of Legends
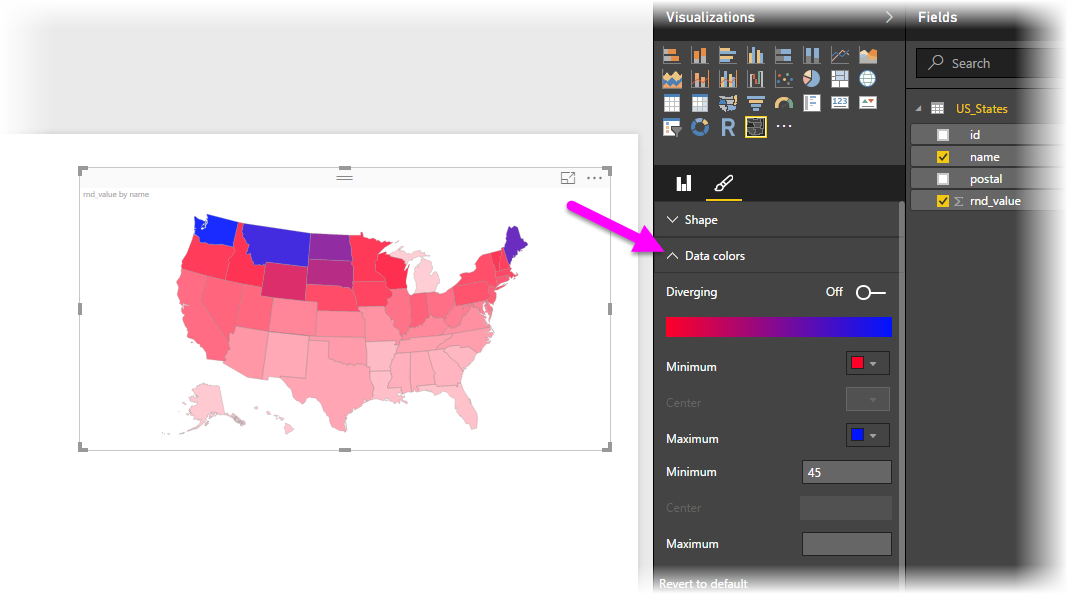
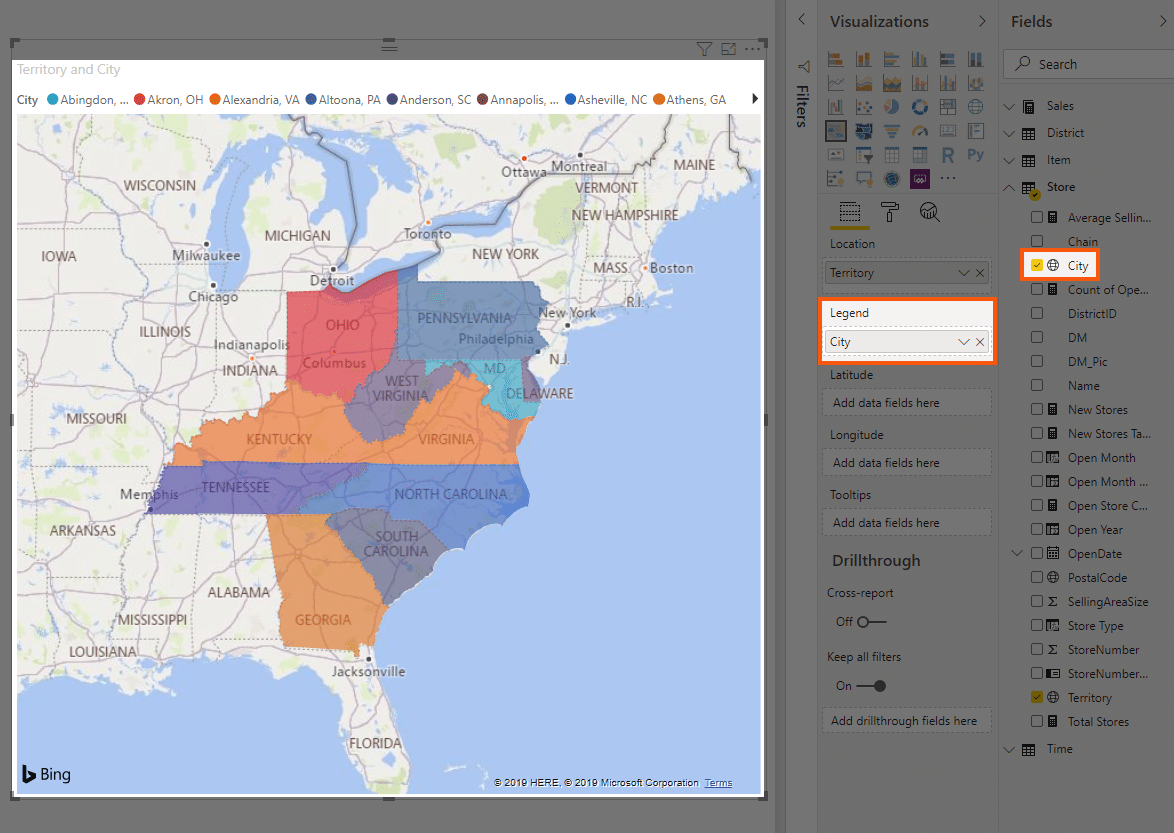
A legend, an integral component of any filled map, serves as a key to understanding the visual representation. It acts as a visual guide, translating the color gradient used on the map into corresponding data values. For instance, a legend might display a range of colors, each associated with a specific data value interval, enabling users to readily interpret the map’s color variations.
Harnessing Gradients for Effective Visual Communication
Gradients play a pivotal role in conveying data patterns effectively. A well-chosen gradient can highlight key trends and disparities, enhancing the map’s overall clarity and impact. Power BI offers a range of gradient options, allowing users to select the most appropriate color scheme for their specific data and audience.
Creating a Filled Map with Legend and Gradient in Power BI
-
Data Preparation: Begin by ensuring your data is properly formatted. Ensure each geographic region has a corresponding data value and that the data is organized in a table format.
-
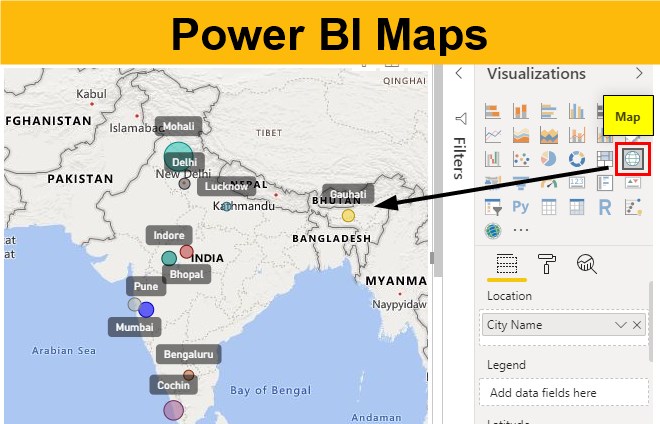
Map Visualization: In Power BI, navigate to the "Visualizations" pane and select the "Filled Map" option. This will create a blank map canvas.
-
Data Linking: Drag the geographic field (e.g., State, Country, City) from your data table to the "Location" field in the "Visualizations" pane. Similarly, drag the data value field (e.g., Sales, Population) to the "Value" field.
-
Gradient Selection: Access the "Format" pane to customize the map’s appearance. Choose a suitable gradient from the "Fill" options. Power BI provides various gradient palettes and allows for custom gradient creation.
-
Legend Configuration: The legend is automatically generated when you create a filled map. Customize its appearance in the "Format" pane. You can adjust its position, size, color, and the display of data value labels.
-
Map Enhancement: Power BI offers additional features to enhance your filled map. You can add tooltips, display data labels directly on the map, and even include map overlays for additional context.
Benefits of Using Filled Maps with Legend and Gradient in Power BI
-
Data Visualization: Filled maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of geographic data, facilitating easy identification of trends and patterns.
-
Trend Identification: The color gradient allows for quick identification of areas with high or low data values, revealing regional variations and potential hotspots.
-
Data Exploration: Filled maps encourage interactive exploration of geographic data, enabling users to zoom in on specific regions and analyze data at different levels of detail.
-
Effective Communication: Filled maps with legends and gradients communicate data insights effectively, making complex information readily understandable for a broader audience.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing visual insights into geographic data, filled maps support informed decision-making, enabling organizations to allocate resources strategically and address regional needs effectively.
FAQs
1. What are some common uses for filled maps with legends and gradients in Power BI?
Filled maps find applications in various fields, including:
- Sales and Marketing: Identifying high-performing regions, targeting marketing campaigns, and understanding customer demographics.
- Finance: Analyzing financial performance across different geographic locations, identifying investment opportunities, and assessing risk.
- Healthcare: Mapping disease prevalence, identifying healthcare access disparities, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Environmental Science: Visualizing pollution levels, monitoring deforestation, and assessing climate change impacts.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing population density, poverty rates, and social indicators to understand social inequalities and inform policy decisions.
2. What types of data are suitable for visualization with filled maps?
Filled maps are particularly effective for visualizing data that can be mapped onto geographic regions, such as:
- Quantitative Data: Data that can be measured numerically, such as sales figures, population density, crime rates, and pollution levels.
- Categorical Data: Data that can be categorized into groups, such as income levels, age groups, and political affiliations.
3. How can I choose the best gradient for my filled map?
Selecting an appropriate gradient depends on the data being visualized and the intended message. Consider the following factors:
- Data Range: Choose a gradient that effectively spans the entire data range, ensuring clear differentiation between high and low values.
- Color Contrast: Select colors that provide sufficient contrast, enabling easy identification of different data values.
- Color Meaning: Consider the connotations of different colors and choose a palette that aligns with the data being visualized and the desired message.
- Accessibility: Ensure the gradient is accessible to users with color blindness or other visual impairments.
4. How can I improve the clarity and readability of my filled map?
To enhance clarity and readability, consider the following tips:
- Appropriate Scale: Select a map scale that balances detail with readability.
- Clear Labels: Use clear and concise labels for geographic regions and data values.
- Minimalist Design: Avoid cluttering the map with unnecessary elements.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporate tooltips and data labels to provide additional information upon user interaction.
5. Are there any limitations to using filled maps with legends and gradients in Power BI?
While filled maps offer powerful data visualization capabilities, they do have limitations:
- Data Granularity: Filled maps may not be suitable for visualizing data at a very fine level of granularity, as it can lead to overplotting and reduced clarity.
- Data Distribution: Filled maps can be misleading if data is not evenly distributed across geographic regions.
- Visual Perception: The interpretation of color gradients can be subjective and influenced by cultural factors.
Tips
- Experiment with Different Gradients: Explore various gradient palettes and custom gradients to find the most effective visual representation for your data.
- Consider Data Context: Use additional map layers or annotations to provide context and enhance understanding of the data.
- Test for Accessibility: Ensure your filled map is accessible to users with visual impairments.
- Seek Feedback: Share your filled map with colleagues or stakeholders to gather feedback and refine its design.
Conclusion
Power BI filled maps with legends and gradients offer a powerful and versatile approach to visualizing geographic data. By leveraging the inherent visual appeal of color gradients and the clarity provided by legends, users can effectively communicate data insights, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. By carefully selecting the appropriate gradient, configuring the legend, and optimizing the map’s design, users can create compelling visualizations that effectively convey geographic data patterns and trends.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Geographic Data with Power BI Filled Maps: A Guide to Legend and Gradient Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!