Deciphering The Language Of Maps: Understanding The Map Legend
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Map Legend
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Map Legend
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Map Legend. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Map Legend
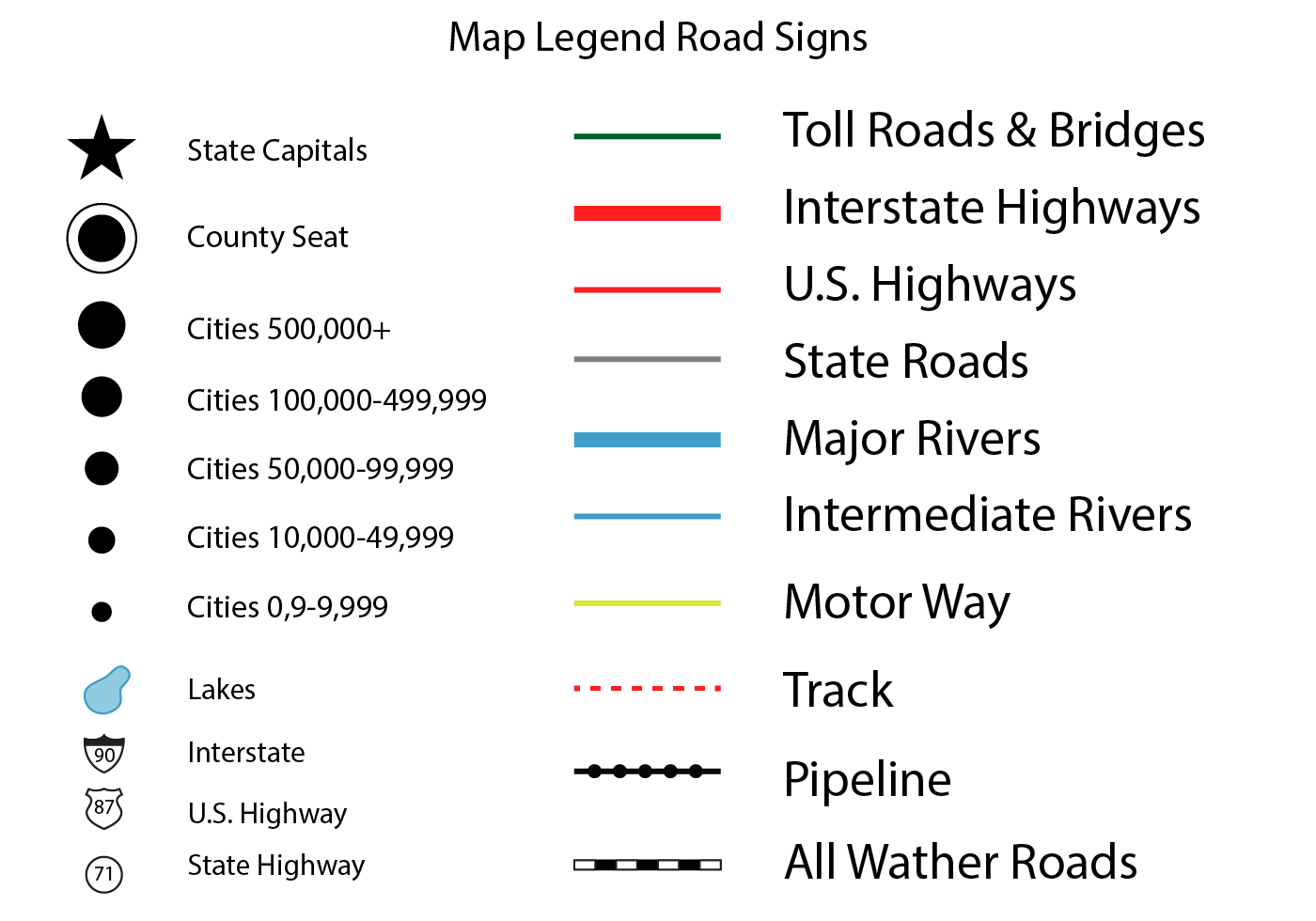
Maps, by their very nature, are visual representations of information. They present complex data in a concise and accessible manner, utilizing symbols, colors, and lines to convey spatial relationships and geographical features. However, without a key to unlock their meaning, these visual cues remain enigmatic. This key, known as the map legend, acts as a translator, bridging the gap between the map’s visual language and the reader’s understanding.
The Essential Role of the Legend
The map legend serves as a vital guide, providing a comprehensive explanation of the symbols, colors, and patterns employed on the map. It acts as a glossary, defining the language of the map and allowing the reader to interpret the information presented. Without a legend, a map becomes a confusing jumble of lines and symbols, devoid of meaning.
Components of a Map Legend
A well-constructed map legend typically consists of the following elements:
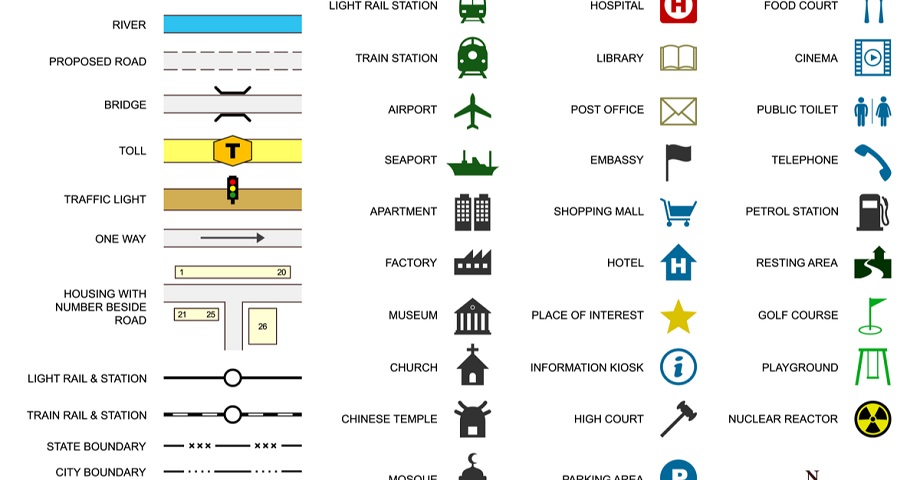
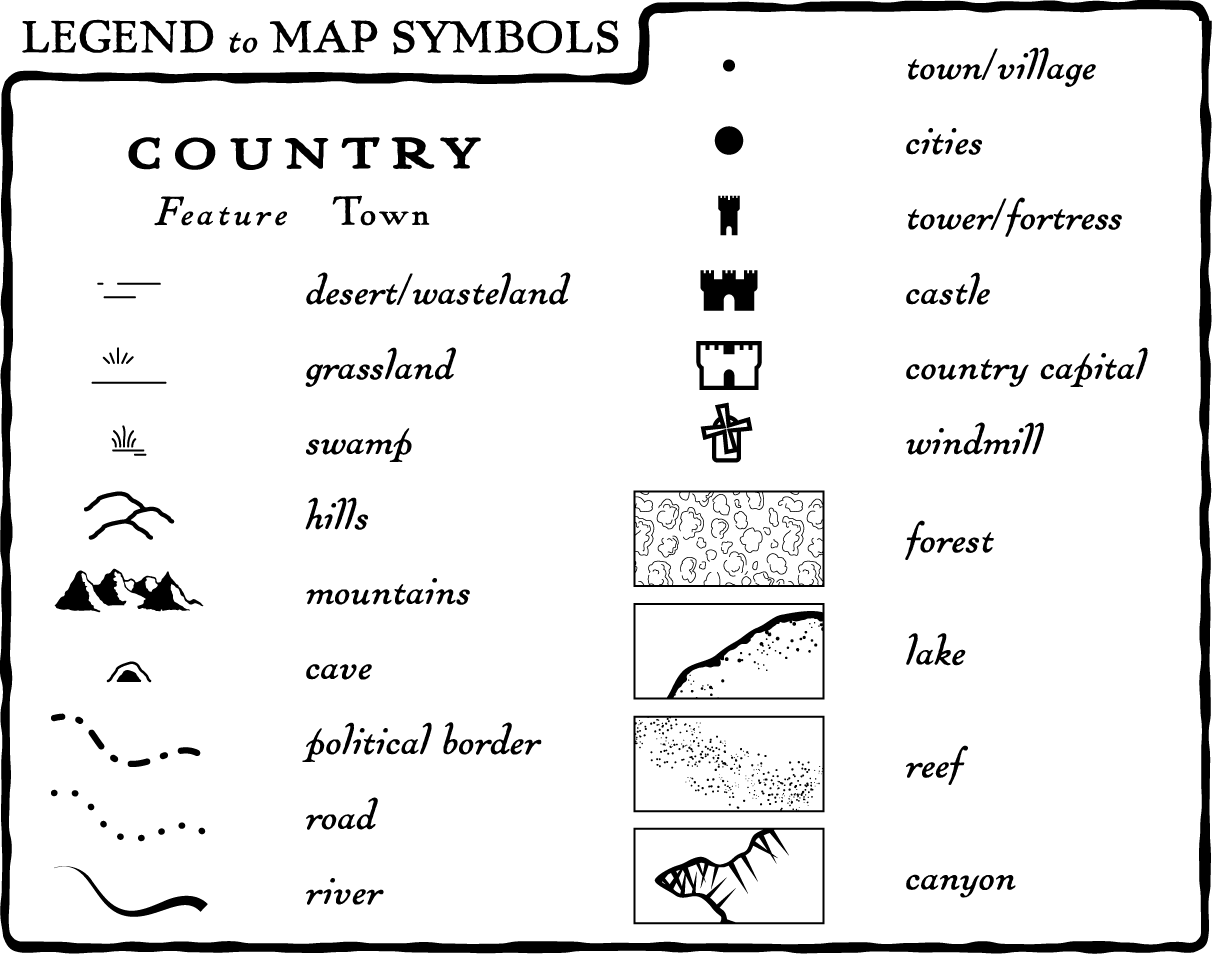
- Symbol Key: This section provides a visual representation of each symbol used on the map, alongside a clear and concise description of what the symbol represents. For instance, a map depicting road types might use different colors or line thicknesses to distinguish between highways, major roads, and local streets. The legend would present each symbol alongside its corresponding road type.
- Color Key: Similar to the symbol key, the color key clarifies the meaning of different colors used on the map. This could include representing various land cover types (e.g., forests, grasslands, water bodies), elevation contours, or population density.
- Scale Bar: This element provides a visual representation of the distance represented by a specific unit on the map. It allows the reader to estimate distances between locations on the map.
- North Arrow: This essential element indicates the direction of true north on the map. It helps orient the reader and understand the relationship between the map and the real world.
- Data Source: This section acknowledges the source of the data used to create the map, providing transparency and allowing the reader to assess the reliability of the information presented.
- Date of Creation: This information indicates when the map was created, providing context for the data and highlighting potential changes that may have occurred since then.
Benefits of a Comprehensive Map Legend
A well-designed map legend offers numerous benefits:
- Clarity and Accessibility: The legend ensures that the map is easily understood by a broad audience, regardless of their prior knowledge or mapping experience.
- Accuracy and Reliability: By providing clear definitions of symbols and colors, the legend enhances the accuracy and reliability of the information presented on the map.
- Enhanced Data Interpretation: The legend empowers the reader to interpret the data presented on the map effectively, drawing meaningful insights and making informed decisions.
- Comparative Analysis: The legend enables the comparison of different elements on the map, highlighting relationships and patterns within the data.
- Effective Communication: A clear and comprehensive legend facilitates effective communication of spatial information, allowing the map to convey its message effectively to its intended audience.
Examples of Map Legends in Action
The importance of map legends is evident across various disciplines:
- Navigation Maps: Road maps rely heavily on legends to distinguish between different road types, traffic conditions, and points of interest.
- Topographical Maps: These maps use legends to represent elevation contours, terrain features, and water bodies, allowing users to navigate challenging terrain.
- Thematic Maps: Maps depicting specific themes, such as population density, economic activity, or environmental conditions, utilize legends to clarify the meaning of different colors, patterns, and symbols.
- Historical Maps: Legends on historical maps can provide valuable context by explaining the symbols used to represent historical events, settlements, or boundaries.
FAQs by a Map Legend
Q: Why is it crucial to understand the legend before interpreting a map?
A: The legend acts as a translator, providing the key to understanding the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map. Without it, the map becomes a meaningless collection of visual elements.
Q: What if the map doesn’t have a legend?
A: The absence of a legend significantly hinders the map’s effectiveness, making it difficult to interpret the information presented. It is crucial to seek out additional information or clarification to understand the map’s meaning.
Q: How can I create a clear and effective map legend?
A: A clear and effective map legend should be:
- Concise and Easily Understandable: Use simple language and avoid technical jargon.
- Visually Appealing: Employ clear fonts, contrasting colors, and appropriate spacing to enhance readability.
- Organized and Logical: Group related elements together and present information in a logical order.
- Comprehensive: Include all necessary elements, such as symbol keys, color keys, scale bars, and north arrows.
Tips by a Map Legend
- Prioritize Clarity: Ensure that the legend is easy to understand for the intended audience.
- Use Consistent Symbols: Employ standardized symbols whenever possible to enhance clarity and familiarity.
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: Design the legend to support the map’s specific objectives and the information it aims to convey.
- Test Readability: Have someone unfamiliar with the map review the legend for clarity and ease of understanding.
Conclusion by a Map Legend
The map legend is an indispensable component of any map, serving as a bridge between the visual language of the map and the reader’s understanding. By providing a clear and comprehensive explanation of the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map, the legend empowers the reader to interpret the information presented accurately, effectively, and meaningfully. Without a legend, a map remains a silent and enigmatic visual, unable to fulfill its purpose of conveying spatial information and facilitating informed decision-making.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding the Map Legend. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
















/https://tf-cmsv2-photocontest-smithsonianmag-prod-approved.s3.amazonaws.com/f54077b1-fff4-4de2-8456-bde95bb173a4.jpg)
































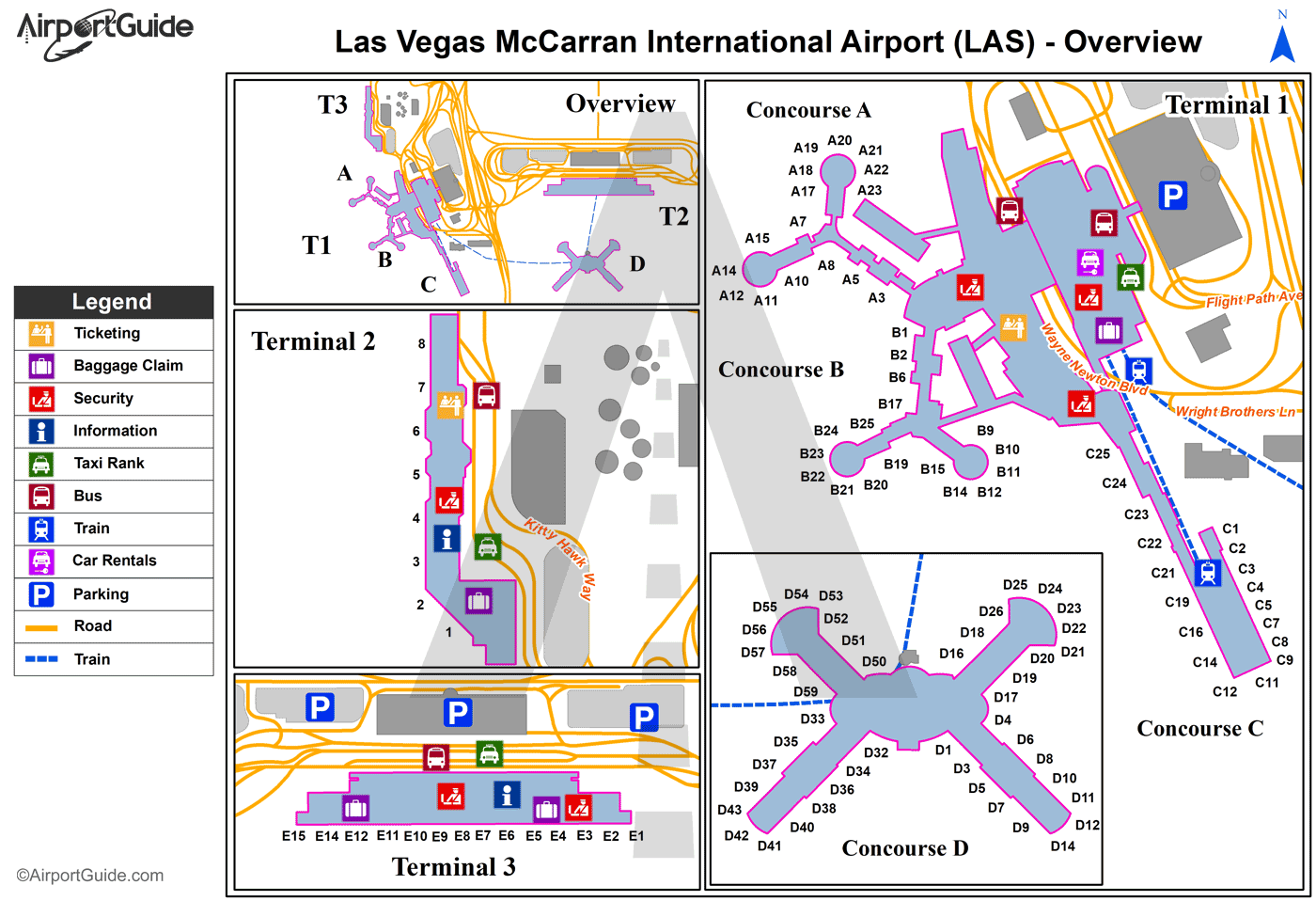
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mccarran-international-airport-guide-4783465_color-e5c6a094d0594cc0880a05805a2a1ba7.jpg)
![McCarran International Airport [LAS] - Terminal Guide [2021]](https://upgradedpoints.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/McCarran-International-Airport-Terminal-Concourse-C.png)

![McCarran International Airport [LAS] - Terminal Guide [2021]](https://upgradedpoints.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/McCarran-International-Airport-Terminal-Concourse-D-647x500.png)