Unveiling The Language Of The Land: A Comprehensive Guide To Topographic Map Legends
Unveiling the Language of the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Legends
Related Articles: Unveiling the Language of the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Legends
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Language of the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Legends. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Language of the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Legends
Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, hold a wealth of information about the Earth’s surface. Understanding the language of these maps, known as the map legend, is crucial for deciphering their complexities and extracting valuable insights. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of topographic map legends, delving into their components, functionalities, and significance.
The Essence of the Legend
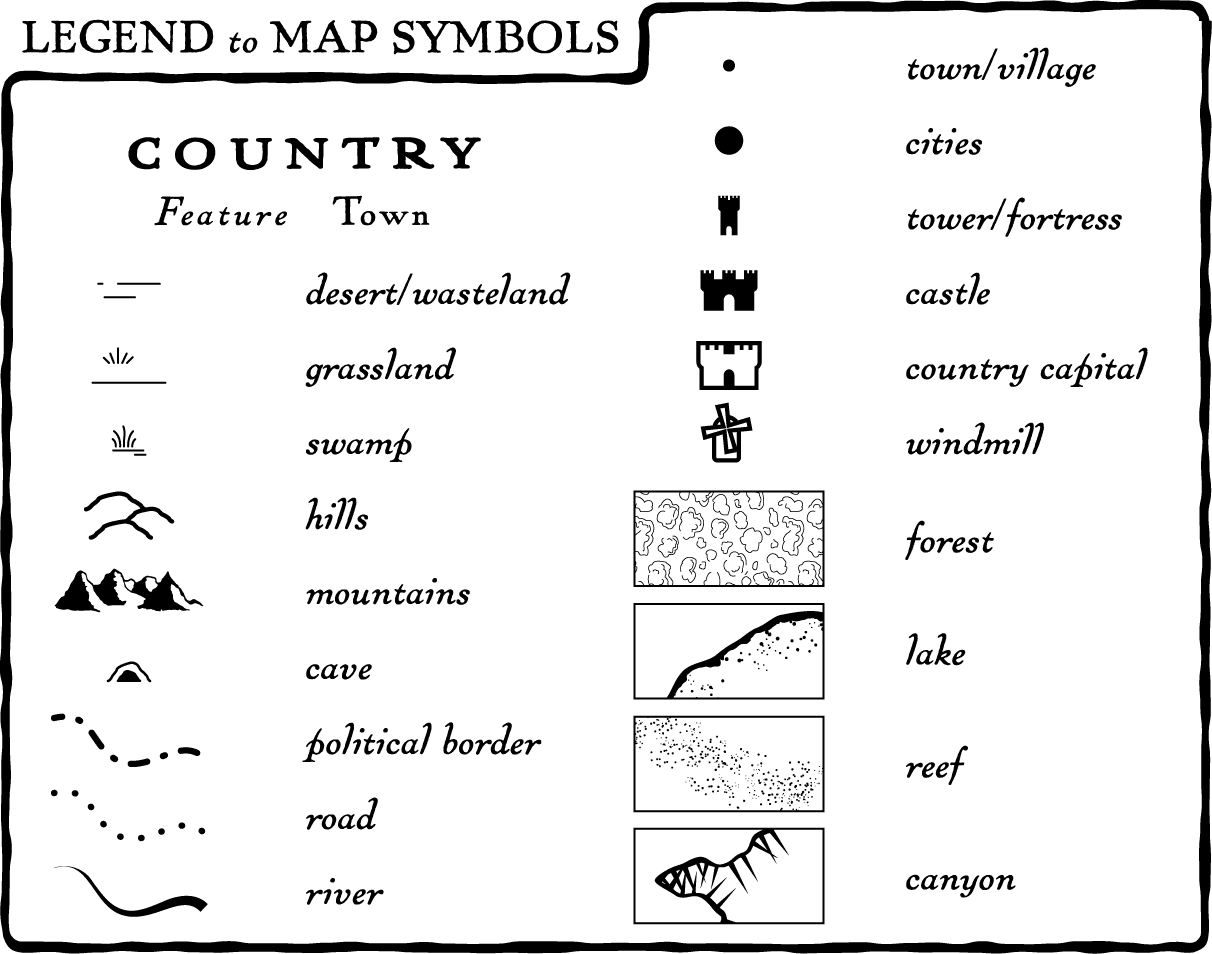
A topographic map legend serves as a key to unlocking the map’s visual language. It acts as a visual glossary, explaining the meaning of the various symbols, lines, and colors employed to represent different features of the terrain. Without a legend, a topographic map would be a bewildering collection of abstract marks, devoid of meaning.
Key Components of a Topographic Map Legend
A typical topographic map legend encompasses several essential components:
- Scale: The scale indicates the ratio between the map’s distances and corresponding distances on the ground. This crucial element allows for accurate measurements and estimations.
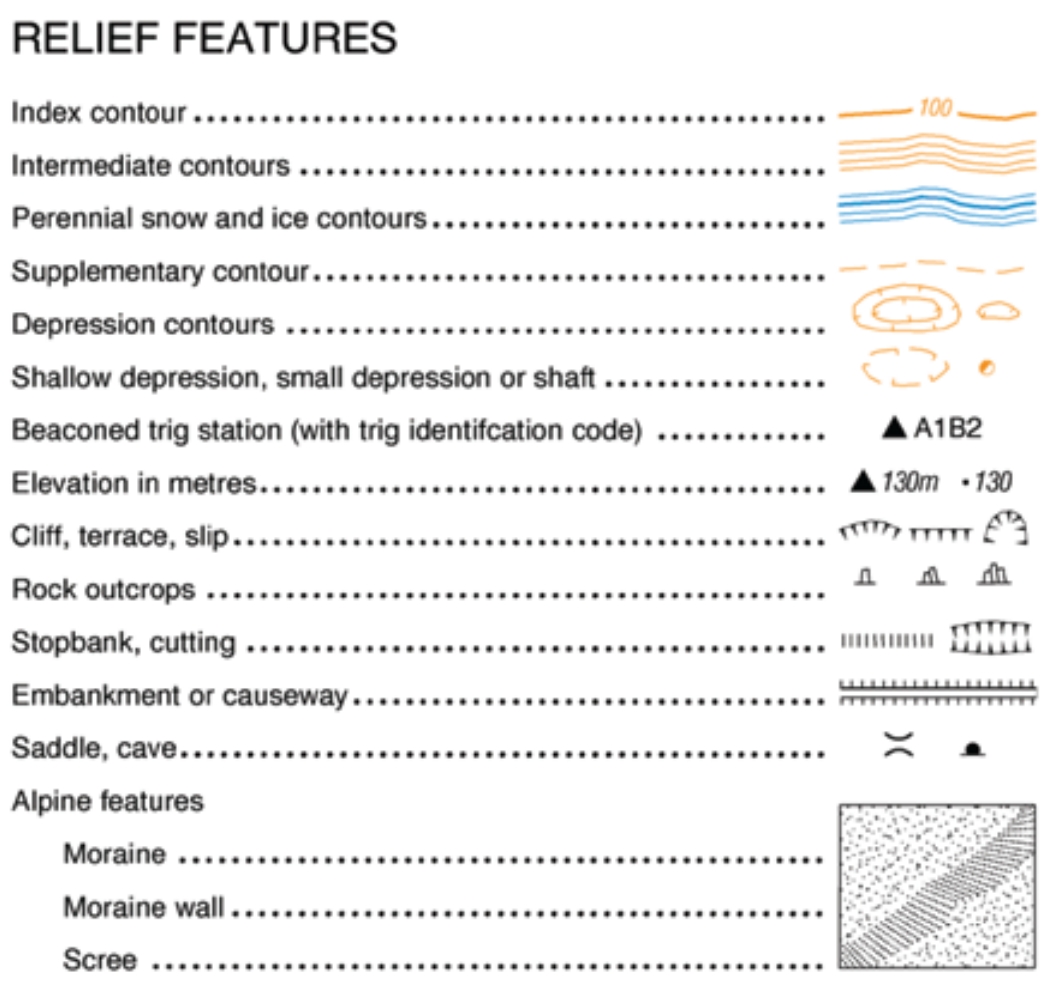
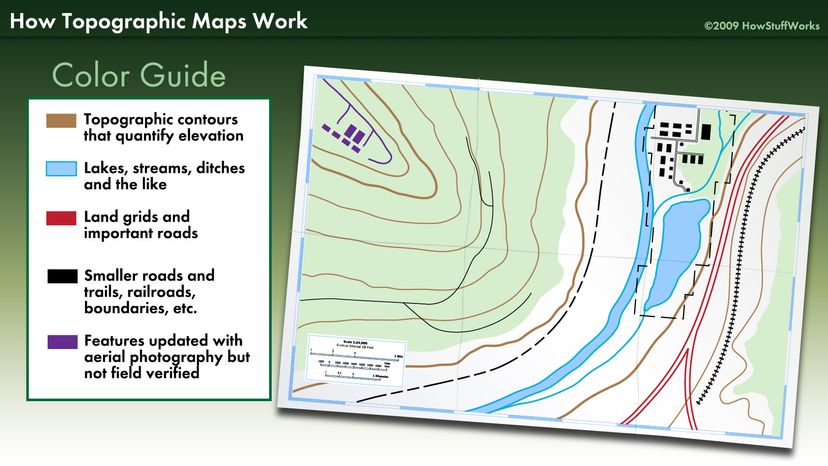
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, revealing the shape and slope of the terrain. The legend clarifies the elevation interval between contour lines, enabling the determination of elevation changes.
- Elevation Symbols: Specific symbols represent different elevations, such as summits, saddles, and depressions. The legend explains the meaning of these symbols, facilitating identification of key topographical features.
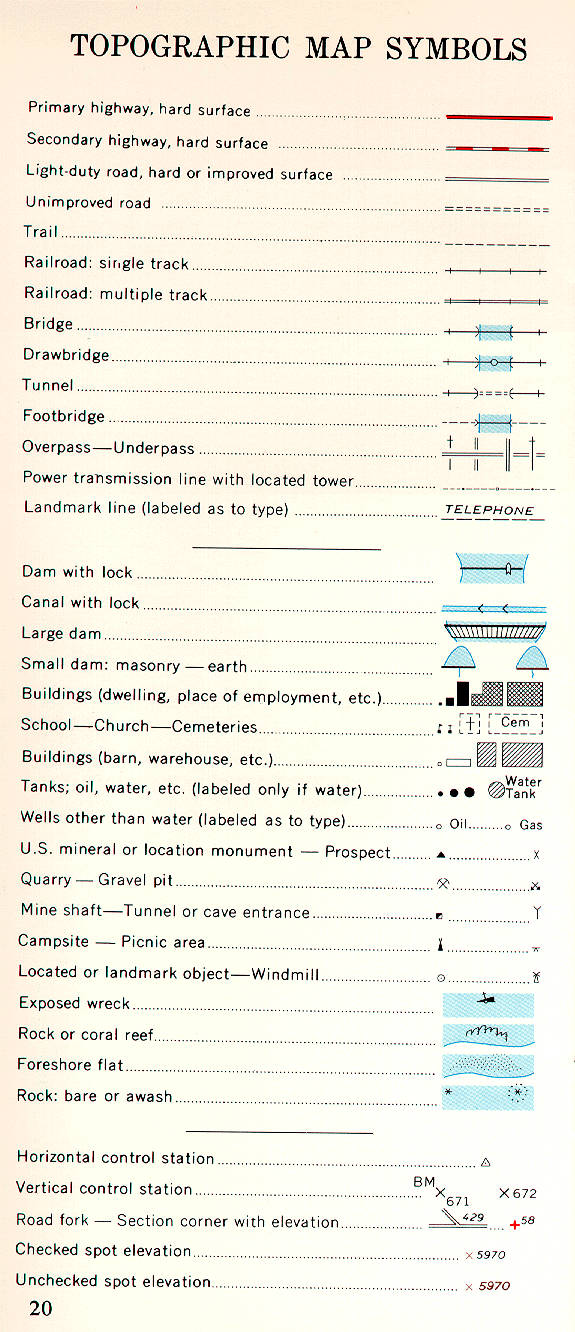
- Water Features: Blue lines and symbols depict rivers, streams, lakes, and other water bodies. The legend clarifies the types of water features represented, including their size and permanence.
- Cultural Features: Symbols representing human-made features such as roads, buildings, and towns are explained in the legend. This information helps in understanding the human impact on the landscape.
- Vegetation: Green symbols and patterns often indicate different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands. The legend explains the meaning of these symbols, providing insights into the natural environment.
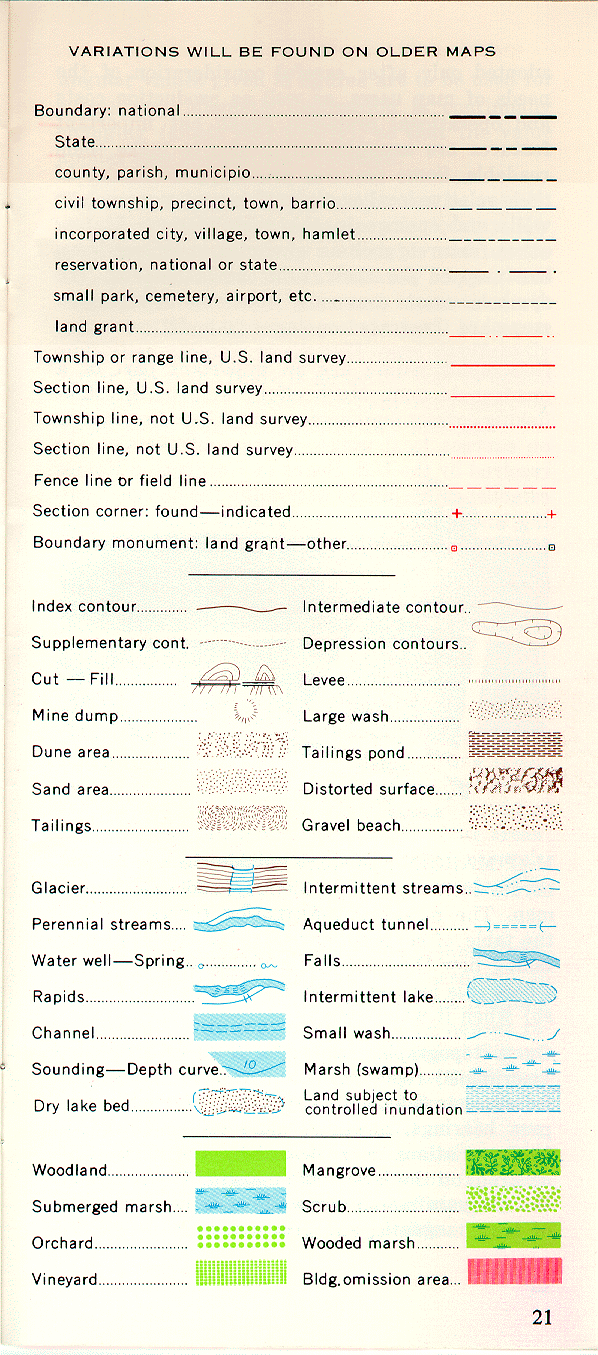
- Other Symbols: The legend may include additional symbols representing specific features like power lines, pipelines, or geological formations.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Legend’s Significance
The topographic map legend goes beyond merely identifying symbols. It plays a crucial role in:
- Navigation: By understanding the terrain’s elevation, slopes, and water features, navigators can plan safe and efficient routes. The legend provides essential information for navigating unfamiliar landscapes.
- Environmental Analysis: The legend enables the identification and study of various environmental features, such as forests, wetlands, and water bodies. This information is vital for understanding ecological processes and making informed decisions about land management.
- Resource Management: Topographic maps, with their detailed depiction of landforms and features, are essential for resource exploration and management. The legend helps in identifying potential sites for mining, agriculture, or infrastructure development.
- Disaster Preparedness: Understanding the terrain’s elevation and slope can aid in predicting potential flood zones, landslides, or other natural hazards. The legend assists in planning for disaster mitigation and response.
- Historical Research: Topographic maps provide valuable insights into past land use, settlement patterns, and infrastructure development. The legend helps in deciphering these historical details.
Frequently Asked Questions About Topographic Map Legends
Q: What are contour lines, and how do they work?
A: Contour lines are lines on a topographic map that connect points of equal elevation. They depict the shape and slope of the terrain. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope. The legend provides the elevation interval between contour lines, allowing for calculations of elevation changes.
Q: How can I determine the elevation of a specific point on the map?
A: To determine the elevation of a specific point, locate the point on the map and identify the contour line passing through it. The legend indicates the elevation of that contour line. If the point lies between two contour lines, estimate the elevation based on the elevation interval.
Q: What are the different types of symbols used on topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps employ a wide variety of symbols, each representing a specific feature. The legend explains the meaning of these symbols. Common symbols include:
- Blue lines: Rivers, streams, and lakes.
- Black lines: Roads, trails, and boundaries.
- Brown lines: Contour lines.
- Green patterns: Forests, grasslands, and wetlands.
- Red symbols: Buildings, towns, and other cultural features.
Tips for Effective Use of Topographic Map Legends
- Study the legend carefully: Before using a topographic map, take time to understand the legend thoroughly.
- Identify key features: Focus on understanding the symbols that represent features relevant to your purpose, such as elevation, water bodies, or cultural features.
- Use the legend in conjunction with the map: Refer to the legend frequently while interpreting the map.
- Practice reading the map: Use practice maps or real-world examples to enhance your map reading skills.
- Seek help when needed: If you encounter difficulties understanding a specific symbol or aspect of the legend, consult with experienced map readers or resources.
Conclusion
The topographic map legend is a vital tool for unlocking the information contained within these maps. By understanding the symbols, lines, and colors used in a legend, users can decipher the complexities of the terrain, navigate landscapes, analyze environmental features, and make informed decisions. Mastering the language of the map legend empowers individuals to extract valuable insights from topographic maps, enriching their understanding of the Earth’s surface and its diverse features.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Language of the Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Legends. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!